Joshua Godwin
@godwinjs71
Followers
131
Following
586
Media
0
Statuses
35
PhD student at @AuburnU in MASL (@drmikeroberts). Research interest include: skeletal muscle biology, ribosomes, ECM, and hypertrophic mechanisms.
Auburn, AL
Joined March 2018
Thrilled to see our topical review “Mitigating skeletal muscle wasting in unloading and augmenting subsequent recovery” published in @JPhysiol. Big thanks to @MarcasBamman for coordinating this project! https://t.co/V7Od2MC0v2
physoc.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Abstract figure legend Summary of what is known during unloading (based on current literature) regarding changes in muscle protein synthesis (MPS) rates, muscle protein breakdown (MPB) rates and...
0
15
43
Effects of training status on atrophy-hypertrophy outcomes with leg immobilization & recovery resistance training. Awesome pre-print led by @maxmichel_ and help from @godwinjs71 @DanielPlotkin_ and others with collab from @MattStockPhD & @MarcasBamman
biorxiv.org
We sought to examine how resistance training (RT) status in young healthy individuals, either well-trained (T, n=10 (8 males)) or untrained (UT, n=11 (8 males)), affected muscle size and molecular...
6
19
62
Relative rDNA copy number is not associated with resistance training-induced skeletal muscle hypertrophy and does not affect myotube anabolism in vitro | @godwinjs71 @maxmichel_ @DrMikeRoberts | #myotwitter
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Ribosomal DNA (rDNA) copies exist across multiple chromosomes, and interindividual variation in copy number is speculated to influence the hypertrophic response to resistance training. Thus, we...
0
5
15
Congrats Joao Bergamasco @mairascarpelli @TalissonChaves_ and MuscuLab Team. Another fantastic collab with @DrMikeRoberts Lab - @godwinjs71 @phc_mesquita @maxmichel_
journals.lww.com
(AR-DNA) induced by resistance training (RT) and hypertrophy outcomes in women and men. This study aimed to investigate the acute and chronic effects of RT on skeletal muscle total AR, cAR, and nAR...
3
9
25
Stellar 2-year effort by @godwinjs71 with help from @maxmichel_ @cleiton_libardi @ChrisFryPhD @IVechetti @jjmcca2_john and several others. Integrative look into Vimentin as a mechanosensitive gene during skeletal muscle hypertrophy.
biorxiv.org
Our laboratory has performed various experiments examining the proteomic alterations that occur with mechanical overload (MOV)-induced skeletal muscle hypertrophy. In the current study we first...
0
11
34
Proud of this one by @DanielPlotkin_ and the lab. Going to keep down this rabbit hole. Interested in thoughts here. Myosin heavy chain fragmentation as a potential marker of protein degradation in response to resistance training and disuse atrophy
biorxiv.org
We sought to examine how resistance exercise (RE), cycling exercise, and disuse atrophy affect myosin heavy chain (MyHC) protein fragmentation in humans. In the first study (1boutRE), younger adult...
0
17
52
Nice to see that our FIM-ID method was highlighted in an eLife Digest "Getting the measure of muscles" https://t.co/WtoJB5ezwV.
elifesciences.org
Resistance training and other forms of exercise may promote muscle growth by stimulating the body to make more myofibrils.
1
9
55
Fantastic work led by @godwinjs71 with collab from Gustavo and Andy showing rDNA copy number is not associated with resistance training-induced skeletal muscle hypertrophy in a larger human cohort and does not affect myotube anabolism.
biorxiv.org
Ribosomal DNA (rDNA) copies are organized in tandem repeats across multiple chromosomes, and inter-individual variation in rDNA copy number has been speculated to be a modifier of the hypertrophic...
1
8
38
PRE-PRINT RT, denervated fiber, senescent cell dissertation project in middle-aged folks by X-less Brad Ruple with Mason, Mads, @godwinjs71 @NicholasJKontos @maxmichel_ @ZiegenfussTim @seer_bio @AusRob_PhD @LBruceGladden and @AbigailMackey1.
biorxiv.org
Denervated myofibers and senescent cells are hallmarks of skeletal muscle aging. However, sparse research has examined how resistance training affects these outcomes. We investigated the effects of...
0
10
45
A Novel Imaging Method (FIM-ID) Reveals that Myofibrillogenesis Plays a Major Role in the Mechanically Induced Growth of Skeletal Muscle
biorxiv.org
An increase in mechanical loading, such as that which occurs during resistance exercise, induces radial growth of muscle fibers (i.e., an increase in cross-sectional area). Muscle fibers are largely...
1
27
96
Great muscle marker follow-up in an attempt to explain why HIIT after 7 wks of RT leads to the loss of muscle hypertrophy (@phc_mesquita dissertation). 1st au @maxmichel_, and great team help from @godwinjs71, @DanielPlotkin, @cleiton_libardi and more.
physoc.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
We recently reported that vastus lateralis (VL) cross-sectional area (CSA) increases after 7 weeks of resistance training (RT, 2 days/week), with declines occurring following 7 weeks of subsequent...
5
11
42
@phc_mesquita J Phys pub from his dissertation out after excellent reviews. Great collab with Dr. Kavazis's lab and help from @godwinjs71 @casey_sexton1 @ShelbyOsburn8 @cleiton_libardi @LBruceGladden and others.
physoc.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Abstract figure legend We investigated the effects of resistance training (RT) on performance and molecular adaptations to a subsequent block of endurance training (ET). We hypothesized that RT-ind...
1
16
30
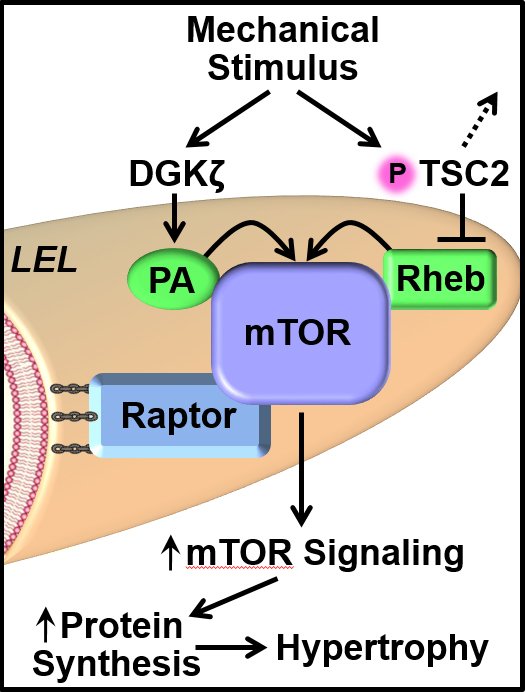
Mechanisms of mechanical overload-induced skeletal muscle hypertrophy: current understanding and future directions | Physiological Reviews https://t.co/EPr0nXas9M THE definitive review on muscle hypertrophy. Proud to be part of the team led by
journals.physiology.org
Mechanisms underlying mechanical overload-induced skeletal muscle hypertrophy have been extensively researched since the landmark report by Morpurgo (1897) of “work-induced hypertrophy” in dogs that...
7
79
264
Out just now! @AJPCellPhys Skeletal muscle memory @dcturner93 and I try to provide the most comprehensive review of the advances in skeletal muscle memory research to date! https://t.co/B8egGxdlcw
0
31
127
Training near vs. further away from failure (per Zourdos' work) leads to interesting neural adaptations. https://t.co/LHI2B6H8R4
@MattStockPhD collab; (team: Brad Ruple, @DanielPlotkin_, @masmith__, @godwinjs71, @Casey_Sexton1, @NickKontos12, @cleiton_libardi and others).
physoc.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Limited data exist examining how resistance training to failure affects applied outcomes and single motor unit characteristics in previously trained individuals. Here, we show that training near...
1
19
61
Myofiber hypertrophy adaptations following 6-weeks of low load resistance training with blood flow restriction in untrained males and females From @TannerReece7 @godwinjs71 @XphysNerd @JeremyRpearson @DrMikeRoberts @KU_NeuroMechLab
https://t.co/j0uGL23DbE
1
4
17
PREPRINT by @phc_mesquita from the Kavazis lab examining if a block of resistance training alters subsequent endurance training adaptations in muscle. Help from @godwinjs71 @Casey_Sexton1 @ShelbyOsburn8 @cleiton_libardi @LBruceGladden and others.
biorxiv.org
We investigated the effects of performing a period of resistance training (RT) on the performance and molecular adaptations to a subsequent period of endurance training (ET). Twenty-five young adults...
3
15
39
Great talks today @seacsm by @DrMikeRoberts, @godwinjs71, and Brad Ruple. Always a great time hearing about cutting edge skeletal muscle research. Awesome job representing the MASL gentlemen!
0
2
9
Fantastic ECM response to resistance training story by @godwinjs71 and the lab. More data coming in this arena soon.
journals.physiology.org
We determined if skeletal muscle extracellular matrix (ECM) content and remodeling markers adapted with resistance training or were associated with hypertrophic outcomes. Thirty-eight untrained males...
1
11
32
Extracellular matrix content and remodeling markers do not differ in college-aged men classified as higher- and lower-responders to resistance training @DrMikeRoberts 👏🏻👏🏻👏🏻
journals.physiology.org
We determined if skeletal muscle extracellular matrix (ECM) content and remodeling markers adapted with resistance training or were associated with hypertrophic outcomes. Thirty-eight untrained males...
0
4
21