Michael Williamson
@m_r_williamson
Followers
206
Following
976
Media
23
Statuses
114
Postdoc in the Deneen lab @bcmhouston @CAGTHouston. PhD from UT Austin. Interested in glial biology, neural repair, learning and memory. 🇨🇦
Houston, TX
Joined March 2018
Excited to share our new work out in @Nature !. Learning-Associated Astrocyte Ensembles Regulate Memory Recall.
nature.com
Nature - A study in mice shows that learning induces c-Fos expression in a subset of astrocytes in the hippocampus, and that ensembles of these learning-associated astrocytes are involved in the...
7
41
216
We have a new review out in TINS! . A functional perspective on astrocyte heterogeneity.
cell.com
Astrocytes are glial cells of the central nervous system (CNS) that perform an array of diverse functions that are essential for brain activity. Studies on the functional diversity of astrocytes...
0
0
2
RT @Dev_journal: In this 'Development at a Glance', @m_r_williamson, Sanjana Murali and Benjamin Deneen @BCMFromtheLabs @CAGTHouston give a….
0
2
0
RT @rust_ruslan: Our review is now out in @Brain1878! We discuss how the blood-brain barrier can both help and hinder brain function and dr….
0
25
0
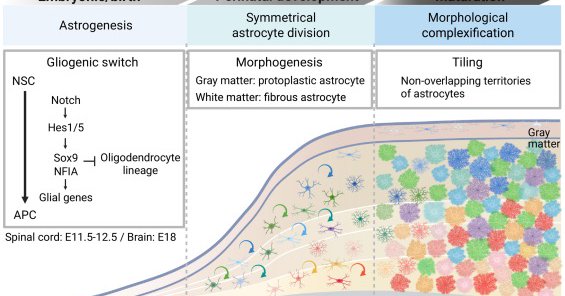
Sharing our new short review on development and diversity of astrocytes!.
journals.biologists.com
Summary: This Development at a Glance article provides an overview of astrocyte ontogeny and morphogenesis, highlighting mechanisms that regulate the development of astrocytes, the most abundant...
0
3
10
RT @Akaron0884: Very excited to share part of my postdoctoral work from the @RyanLabTCD, out now in @Nature. Here, my brilliant co-author @….
nature.com
Nature - Cold-sensitive engrams contribute to learned thermoregulation in mice that are returned to an environment in which they previously experienced a cold challenge, through a network formed...
0
21
0
RT @BCMFromtheLabs: Baylor College of Medicine @bcmhouston wins 2025 #STATMadness for 2 consecutive years! Congratulations to the B. Deneen….
0
1
0
RT @llinas_marta: We keep celebrating! Our latest publication in @NatureNeuro is finally out! Using our new tool AstroLight we demonstrate….
0
46
0
RT @debo_Astrocyte: I get a lot of questions on the #NIH #K99 #postdoc to faculty transition award. Decided to pen my thoughts and experie….
0
67
0
RT @JasonSynaptic: In this episode of TWiN we discuss provocative data showing that astrocytes may be more intimately involved in memory th….
nature.com
Nature - A study in mice shows that learning induces c-Fos expression in a subset of astrocytes in the hippocampus, and that ensembles of these learning-associated astrocytes are involved in the...
0
5
0
RT @BCMFromtheLabs: B Deneen, @m_r_williamson, W. Kwon et al changed the way we understand memory. Learn more, here: .
blogs.bcm.edu
In this study, researchers at Baylor College of Medicine changed the way we understand memory.
0
1
0
RT @m_r_williamson: Excited to share our new work out in @Nature !. Learning-Associated Astrocyte Ensembles Regulate Memory Recall. https:/….
nature.com
Nature - A study in mice shows that learning induces c-Fos expression in a subset of astrocytes in the hippocampus, and that ensembles of these learning-associated astrocytes are involved in the...
0
41
0
@amy_gleichman We think these experiments (and many more in the paper) suggest that memory engrams are comprised of cooperating ensembles of astrocytes and neurons. These findings open the door to many exciting new directions!
2
2
5
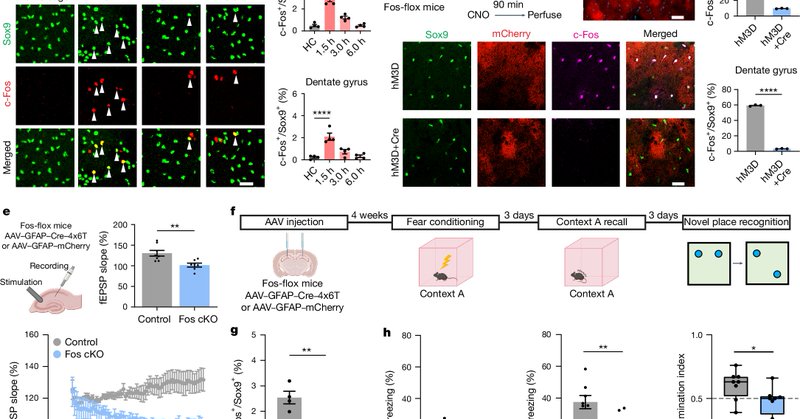
@amy_gleichman Second, we found that expression of the transcription factor NFIA was increased in learning-associated astrocytes and was responsible for many of the transcriptional changes in astrocytes after fear learning. NFIA deletion from learning-associated astrocytes impaired memory.
1
0
5
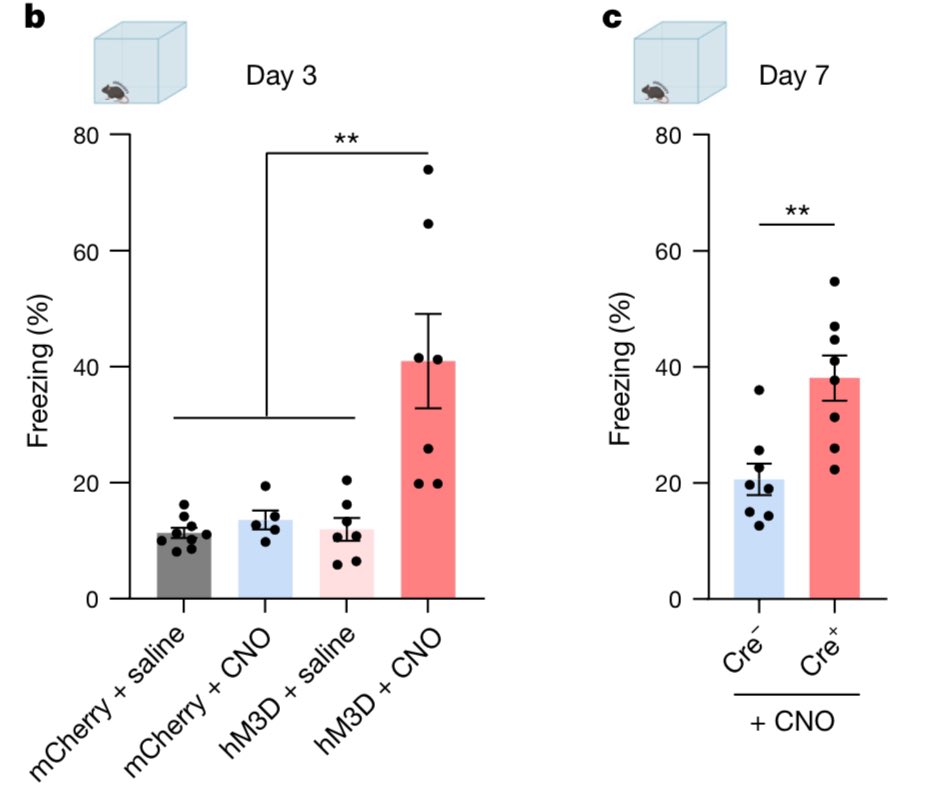
@amy_gleichman We did two key experiments to really test the possibility that astrocyte ensembles might be a part of the memory engram. First, we artificially activated fear-tagged astrocyte ensembles in a novel context and found that this elicited freezing, which is indicative of fear recall.
1
0
2
@amy_gleichman When we chemogenetically activated learning-associated astrocytes, the frequency of synaptic potentials was specifically increased in engram neurons, leaving non-engram neurons unaffected. The specificity of this effect was a big surprise!
1
0
1
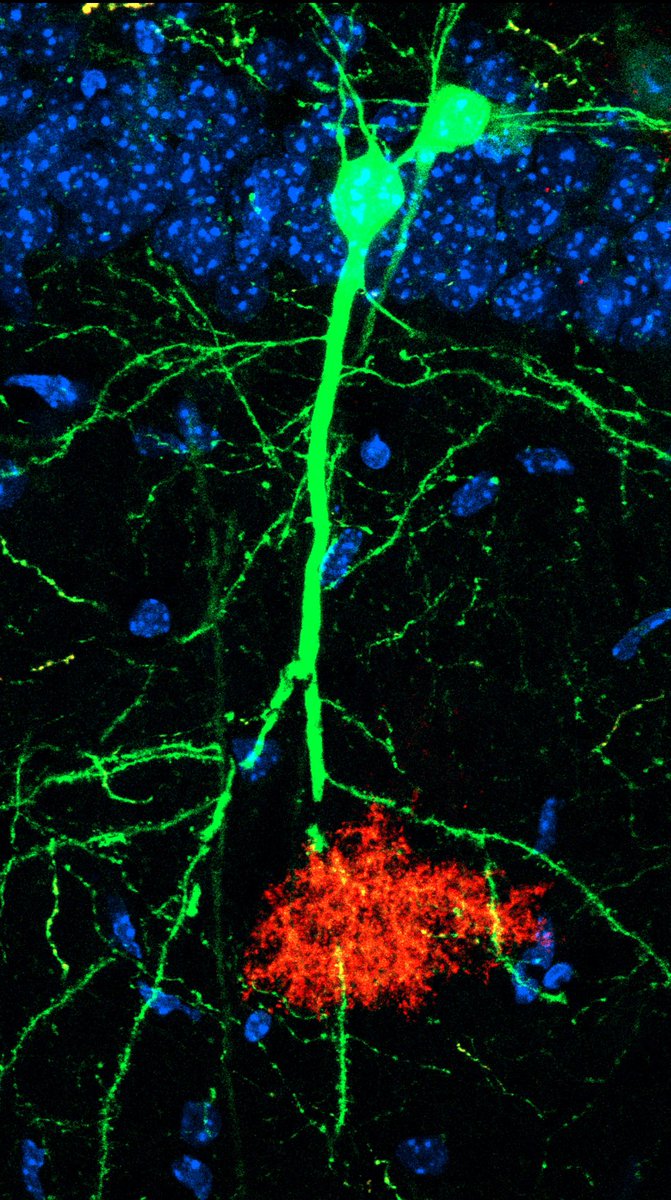
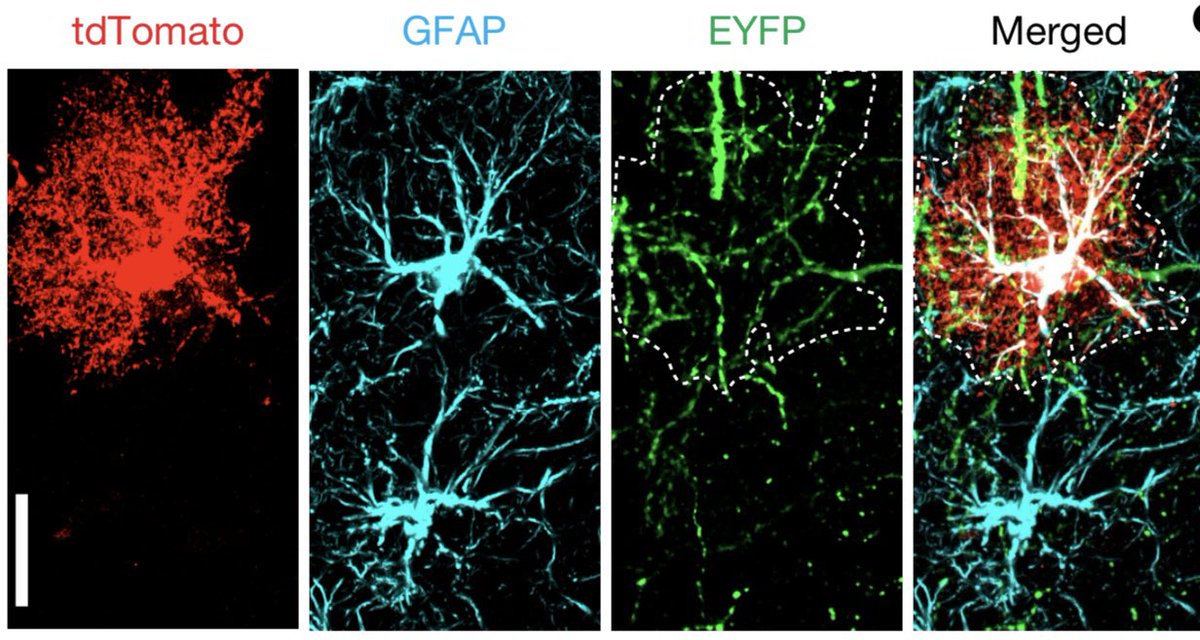
@amy_gleichman We wanted to define the interactions between engram neurons and learning-activated astrocytes that were tagged during fear learning. We found that learning-associated astrocytes were closely affiliated with the dendrites and synapses of engram neurons.
1
0
3
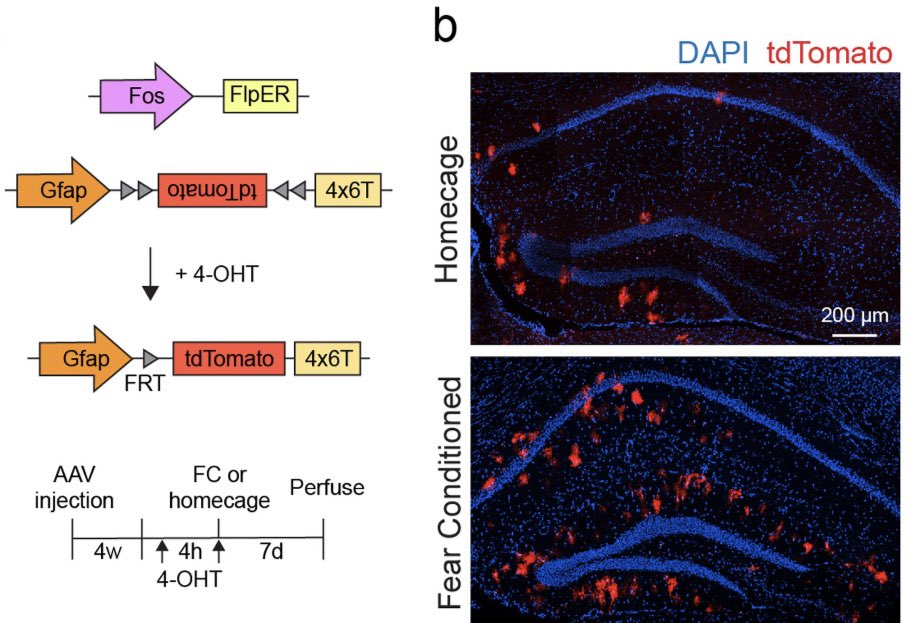
@amy_gleichman We found that astrocytes that were initially activated by fear learning reliably re-expressed c-Fos upon subsequent exposure to the same conditioning context, which indicates that the same astrocyte ensemble is activated both during learning and recall.
1
0
3
@amy_gleichman To study learning-associated astrocyte ensembles in more detail, we developed new viral tools that allowed us to tag and manipulate astrocytes that were activated by a learning event.
1
0
3