The Colonna Lab
@TheColonnaLab
Followers
4K
Following
66
Media
15
Statuses
91
We study innate immunity with a focus on ILCs, macrophages, and DCs. The account is led by trainees. @wusm_pathology @WUSTLmed
St. Louis, MO
Joined April 2021
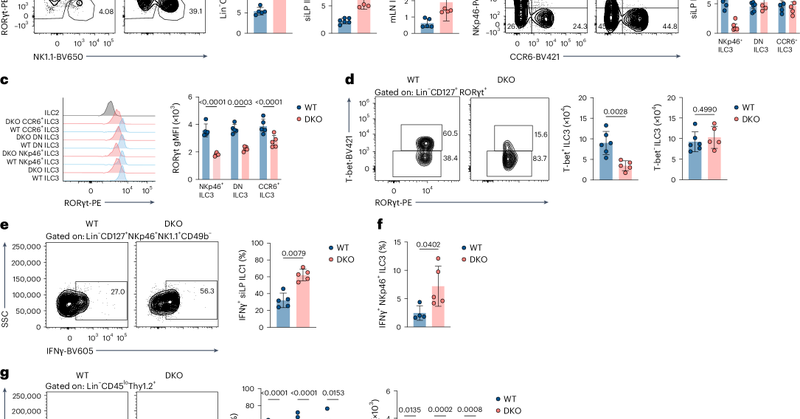
Our new study led by Bishan Bhattarai shows that circadian proteins REV-ERBα/β protect gut health by maintaining ILC3 homeostasis. Without them, ILC3s turn into IFNγ+ ILC1s, fueling inflammation. Chick it out! https://t.co/f3HaHEODzz
nature.com
Nature Immunology - Colonna and colleagues show that the clock genes encoding REV-ERBα and REV-ERBβ maintain ILC3 functions in the gut by controlling the expression of RORγt.
0
23
91
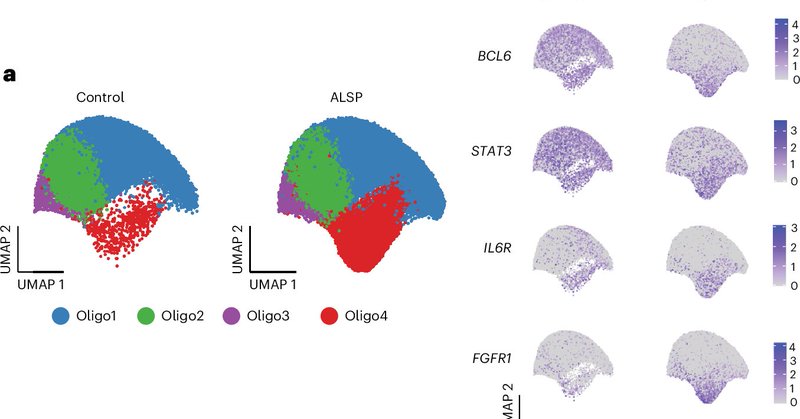
Check out Research Briefing for our recent paper in Nature Immunology @DuSiling
https://t.co/UjsyIt79Vi
nature.com
Nature Immunology - We show that mutations in the CSF1R gene, which cause the rare neurodegenerative disease ALSP, lead to the loss and abnormal activation of microglia. This triggers glial stress...
1
7
48
🧵1/ Excited to share my first publication from the @ColonnaLab in @NatImmunol! We investigated how mutations in the human CSF1R gene disrupt microglia and impair white matter integrity in a rare but devastating neurodegeneration called ALSP. https://t.co/39kxODSumy
nature.com
Nature Immunology - Adult-onset leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids and pigmented glia is a neurodegenerative disorder caused by pathogenic CSF1R mutations. Here the authors find that...
7
21
113
Our new study by @DuSiling reveals how CSF1R mutations in adult-onset leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids and pigmented glia (ALSP) disrupt glial homeostasis. Key roles for oligodendrocytes, astrocytes & STAT3 signaling. https://t.co/k2PsmXO9mX
1
34
117
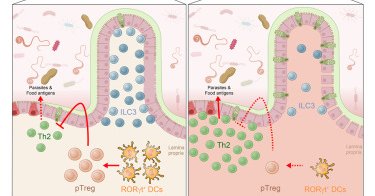
Congrats to @KedmiRanit’s group! RORγt⁺ APCs prime food-specific pTregs and induce oral tolerance. Infection or food poisoning temporarily bypasses this, allowing CD8αβ T cell responses to mimicked food antigens without breaking long-term oral tolerance.
nature.com
Nature - Immune tolerance to dietary antigens is mediated by a circuit of dedicated antigen-presenting cells and T cells, ensuring protective effector responses without compromising the...
2
3
22
Find the referenced papers below: Brown: https://t.co/emADApLMLM Mucida: https://t.co/CIcqHoP0Xx Littman: https://t.co/F4yBTXweBJ Gardner: https://t.co/R5amWicVLb Schraml: https://t.co/HgE9kK3lHL Colonna:
cell.com
Deleting a regulatory element in the Rorc gene depletes RORγt+ dendritic cells from the intestine in mice, leading to a reduction of regulatory T cells and impaired oral tolerance to antigens. This...
1
4
13
As RORγt⁺ APC gain attention for their tolerogenic roles, Schraml’s group also highlights their inflammatory potential. Key questions remain: How are RORγt⁺ APC specified? Are eTAC and RORγt⁺ DC distinct or the same? What dictates tolerance vs. inflammation? Fast-moving field!
1
2
6
Big shoutout to Brown’s group: IRF8-dependent TC are essential for inducing food-specific pTregs & establishing oral tolerance! In line with recent work from Mucida’s, Littman’s, Gardner’s, and our group highlighting the role of RORγt⁺ APC in this process. https://t.co/emADApLMLM
science.org
In the intestine, peripherally induced regulatory T (pTreg) cells play an essential role in suppressing inflammatory responses to food proteins. However, the identity of the antigen-presenting cells...
1
9
26
Congratulations to physicist Carl Bender of @washuartsci and immunologist Marco Colonna @washumedicine, who have been elected to the @americanacad for their pioneering work in quantum theory and immune pathways in Alzheimer’s.
source.washu.edu
Two Washington University in St. Louis faculty are among nearly 250 newly elected members of the American Academy of Arts & Sciences, one of the nation’s most prestigious honorary societies. They are...
1
6
29
Excited to share that our work by @PatFernRod and @TongWu99 is published in Cell: RORγt+ DCs are required to induce oral tolerance. Their absence reduces pTregs and impairs oral tolerance to dietary antigens. Read more:
0
18
69
Loss of ATG7 in microglia impairs UPR, triggers ferroptosis, and weakens amyloid pathology control https://t.co/ktqB6ozwp6, in this work we linked autophagy with UPR and ferroptosis in the microglial response to AD @CaiZhangying @TheColonnaLab 🥳🍻🆗
rupress.org
Microglia contain Aβ plaques in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). In an AD mouse model, microglial Atg7 deletion impaired plaque coverage, increasing Aβ diffusion
0
9
20
Cai et al. @TheColonnaLab @washumedicine show that, in an #Alzheimers mouse model, microglial Atg7 deletion impairs plaque coverage, increasing Aβ diffusion & neurotoxicity, linked to reduced UPR, increased oxidative stress, & #ferroptosis of #microglia
https://t.co/C8v5WYp6Wu
0
4
10
Excited to share that our work is featured on the cover of the latest issue of Cell Host & Microbe! Check it out! @TheColonnaLab @VinoloM @pewtrusts
#Microbiology #Immunology #CellHostMicrobe
0
10
26
Our new paper in Cell Host & Microbe: Low-fiber diets worsen C. difficile infection by increasing epithelial MHC-II and expanding pathogenic CD4+ IELs. Fiber-derived acetate and FFAR2 boost ILC3 IL-22, suppressing colonic MHC-II and aiding recovery. https://t.co/YRBA7anvOa
0
7
30
Our work by Fachi et al. @zefachi is out in PNAS! We show how NKp46+ ILC3s boost early gut defense against C. difficile infection by producing GM-CSF to support neutrophils. A potential path to new CDI treatments! https://t.co/eGErtKTImU
0
10
41
Farewell party for David, a student from Ulrike Schleicher lab, who was a visiting student in our lab! Good luck David
0
1
18
🧵 Excited to share my first preprint from my PhD @kipnislab and @TheColonnaLab: "Brain-Engrafted Monocyte-derived Macrophages from Blood and Skull-Bone Marrow Exhibit Distinct Identities from Microglia." 🧠🦴 https://t.co/czMqzFmKXz
biorxiv.org
Microglia are thought to originate exclusively from primitive macrophage progenitors in the yolk sac (YS) and to persist throughout life without much contribution from definitive hematopoiesis. Here,...
7
34
135
Check out our newest resource led by @jaeger_natalia and @UlezkoAlina describing the NK-ILC1 gradient in human tissues: https://t.co/cM8P9tDKym. The IEL contains true mature (PRDM1+) and immature (PRDM1-) EOMES-ILC1, while other tissues harbor ILC1-like NKs expressing ZNF683.
2
11
36
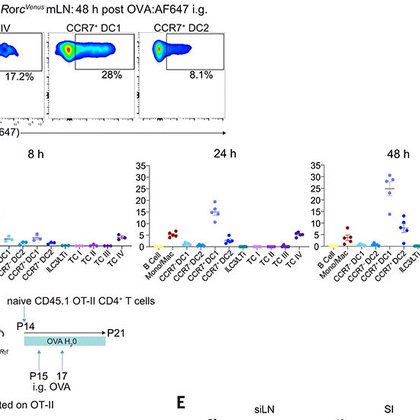
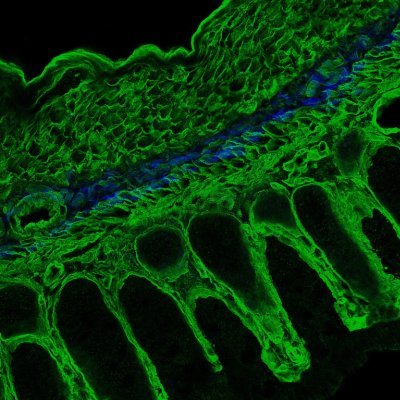
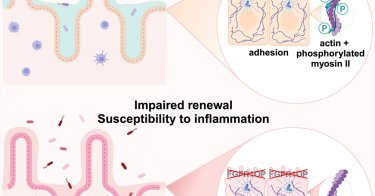
Collaboration with @TheColonnaLab & others, in press at @Dev_Cell: The FGFR1OP gene, implicated in #Crohns, contributes to intestinal barrier function by modulating the actin cytoskeleton in crypt cells. (1/2)
cell.com
Trsan et al. show that deletion of the centrosomal protein FGFR1OP in mouse intestinal cells disrupts crypt architecture, impairs regeneration, and causes inflammation. FGFR1OP is crucial for...
2
12
37
Our new paper led by @TihanaTrsan, collaboration with @TheXavierLab, investigating the link between FGFR1OP and Crohn’s disease. Deletion of FGFR1OP, a centrosomal protein, in mouse gut cells disrupts crypt architecture, causing inflammation and fatality
cell.com
Trsan et al. show that deletion of the centrosomal protein FGFR1OP in mouse intestinal cells disrupts crypt architecture, impairs regeneration, and causes inflammation. FGFR1OP is crucial for...
2
12
62