Julia Zeitlinger (@[email protected])
@JuliaZeitlinger
Followers
2K
Following
7K
Media
4
Statuses
491
Investigator at the Stowers Institute for Medical Research, interested in regulatory genomics in development and evolution.
Joined October 2019
Applications are OPEN for our #CompBio Scholars Program! Work alongside scientists at the forefront of discovery. ⬇️
🚨 If you’re an early-career computational biologist or #bioinformatician ready to grow in a collaborative, world-class #research institute — now is the time to apply to our #CompBio Scholars program. Learn more + apply
0
2
1
Nice to see this out. I completely changed my research direction 7 years ago. I am so grateful for all the people who made this possible!
How do you teach #AI to read #DNA? 🧬 Investigator @JuliaZeitlinger is featured by @ASBMB for her pioneering work using AI to decode the genome’s hidden grammar. 📖 Read more:
0
0
14
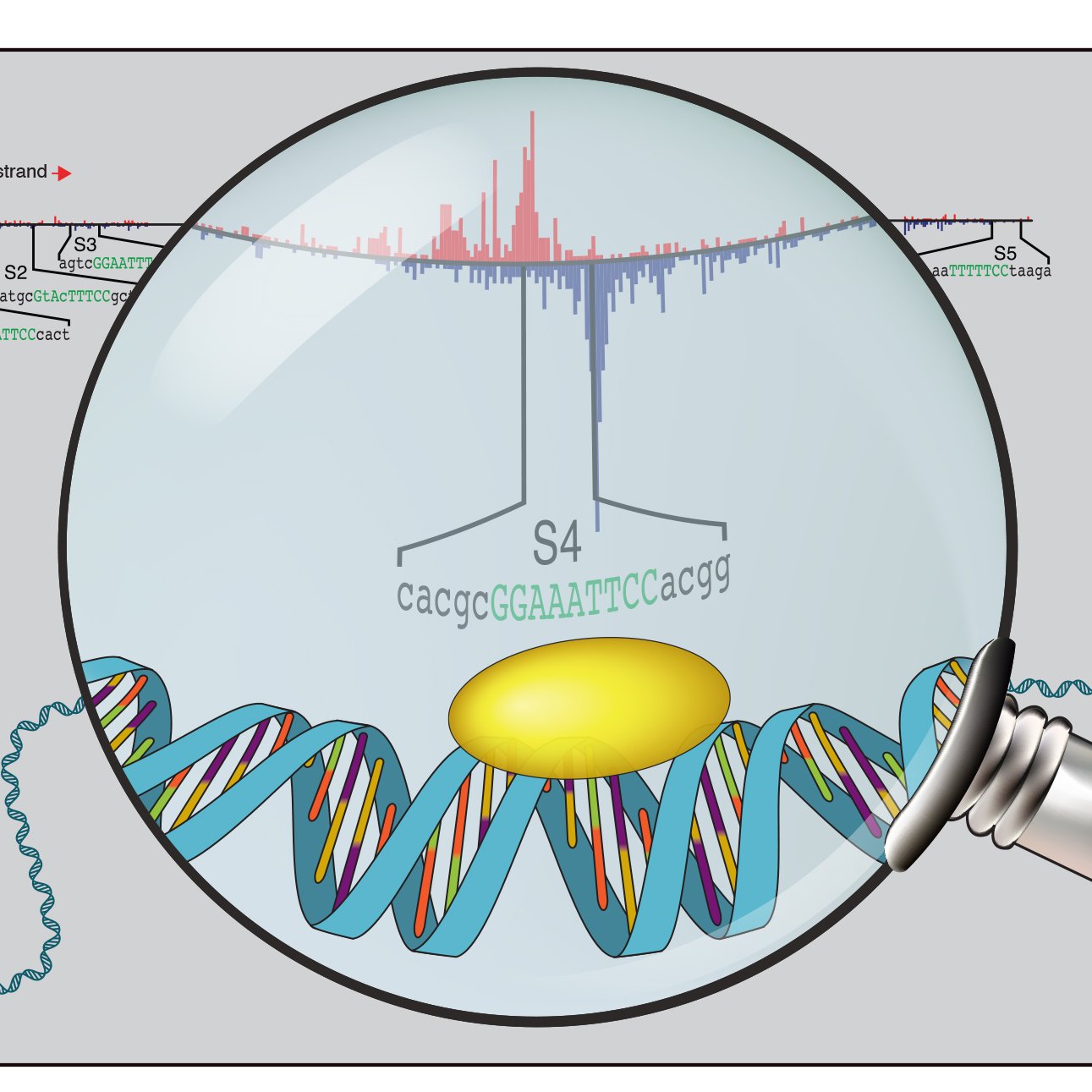
Which mutations rewire function of regulatory DNA? Excited to share SEAM: Systematic Explanation of Attribtuion-based Mechanisms. SEAM is an explainable AI method that dissects cis-regulatory mechanisms learned by seq2fun genomic deep learning models. Led by @EESetiz 1/N 🧵👇
2
29
138
Using #AI & collaboration with @anshulkundaje & @Avsecz, her team developed BPNet to predict TF interactions. https://t.co/2QUtvj6dV4
@ASBMB @ScienceStowers
asbmb.org
Using fruit flies and artificial intelligence, Julia Zeitlinger’s lab is decoding genome patterns — revealing how transcription factors and nucleosomes control gene expression, pushing biology toward...
0
4
6
Really enjoyed reading the new Giorgetti lab preprint that makes the case that not all E-P interactions are created equal - it is the subset of long-lived extrusion-mediated E-P interactions that are most transcriptionally important: https://t.co/PRHX4JU9xC
0
4
23
We are excited to share GPN-Star, a cost-effective, biologically grounded genomic language modeling framework that achieves state-of-the-art performance across a wide range of variant effect prediction tasks relevant to human genetics. https://t.co/FTm3byYp67 (1/n)
17
161
517
This October, join scientists at the intersection of machine learning, structural #biology, & bioinformatics to explore this question & more at #SRCKC25. Hear from a previous Stowers Research Conferences attendee⬇️ Register: https://t.co/d5yEruPypf
0
2
6
In the genomics community, we have focused pretty heavily on achieving state-of-the-art predictive performance. While undoubtedly important, how we *use* these models after training is potentially even more important. tangermeme v1.0.0 is out now. Hope you find it useful!
3
23
97
I'm glad that I had a chance to contribute to this wide-ranging article discussing the myriad ways ML is being used in genomics:
nature.com
Nature - Scientists are seeking to decipher the role of non-coding DNA in the human genome, helped by a suite of artificial-intelligence tools.
0
10
49
Join @LenPennacchio, @ZhipingWeng, @xielablife, me and all speakers in beautiful Suzhou, China for this year's CSH Asia Systems Biology of Gene Regulation & Genome Editing meeting, Oct 20-24. Let's bring the international communities together! Abstract deadline Sept 5! More infos
2
16
46
It is with great sadness that we announce the passing of William “Bill” Neaves, the founding President & CEO of the Institute. A visionary leader and passionate advocate for scientific discovery, he will be deeply missed. Read more about his legacy:
stowers.org
1943 – 2025
0
1
3
Looking forward to my first talk in a distillery!
0
3
17
Please RT. I really look forward to this meeting!
If you're interested in development and gene regulation, you do not want to miss this meeting organized by @JuliaZeitlinger @saukaspengler and myself in April 2026!
0
4
10
Our work on "Evaluating the representational power of pre-trained DNA language models for regulatory genomics" led by @AmberZqt with help from @NiraliSomia & @stevenyuyy is finally published in Genome Biology! Check it out! https://t.co/AFBC9Qu4x3
genomebiology.biomedcentral.com
Background The emergence of genomic language models (gLMs) offers an unsupervised approach to learning a wide diversity of cis-regulatory patterns in the non-coding genome without requiring labels of...
Do current genomic language models (pre-trained on whole genomes) learn a foundational understanding of biology in the non-coding region of human genomes? A new evaluation led by @AmberZqt suggests not yet! 1/N paper:
1
42
124
There is still time until July 18 to submit an abstract to CSH Asia conference “Nuclear Architecture and Function”. Check out the fantastic lineup of speakers! https://t.co/6lD2d7Jo3D
0
1
7
The Cold Spring Harbor Asia (CSHA) meeting - Nuclear Architecture and Function is coming up soon! (Sept 1-5, 2025). Abstract submission deadline extended to July 18. Fantastic speakers & beautiful city (Suzhou) with Royal Garden. Check out here:
0
7
24
Pretty pleased with what I’ve seen inside this model (aka sequence rules learned), some of their predictions better recapitulate our CRISPR experiments in mouse than our own, smaller models. Excited to see the release!
Happy to introduce AlphaGenome, @GoogleDeepMind's new AI model for genomics. AlphaGenome offers a comprehensive view of the human non-coding genome by predicting the impact of DNA variations. It will deepen our understanding of disease biology and open new avenues of research.
0
5
25
Excited to launch our AlphaGenome API https://t.co/gL6Je8t2xf along with the preprint https://t.co/ZeLzhR7VBl describing and evaluating our latest DNA sequence model powering the API. Looking forward to seeing how scientists use it! @GoogleDeepMind
5
17
79
This a really exciting leap forward for genomic sequence to activity gene regulation models. It is a genuine improvement over pretty much all SOTA models spanning a wide range of regulatory, transcriptional and post-transcriptional processes. 1/
Happy to introduce AlphaGenome, @GoogleDeepMind's new AI model for genomics. AlphaGenome offers a comprehensive view of the human non-coding genome by predicting the impact of DNA variations. It will deepen our understanding of disease biology and open new avenues of research.
2
49
267