Cory Simpson, MD, PhD, FAAD (he/him)
@CorySimpsonMD
Followers
2K
Following
9K
Media
114
Statuses
1K
Physician-scientist @UWMedicine @DermatologyUW focused on advanced microscopy, keratinocyte biology, teledermatology, and genetic/autoimmune blistering disease.
Seattle, WA
Joined January 2019
New paper from @SimpsonLabUW @DermatologyUW is online @JCI_insight🍾We found ERK hyperactivation disrupts cell-cell adhesion in epidermis, linked this pathway to both drug-induced & spontaneous Grover disease & identified MEK inhibition as a novel therapy: https://t.co/Ko48RnTxNp
1
6
21
Excited to be representing @SimpsonLabUW in sunny 😎 San Diego 🌴 for #ASCB2024 #CellBio2024 @ASCBiology
0
0
17
Starting the migration to the other place, using handle @SimpsonLabUW …hoping to find the old #sciencetwitter and #dermtwitter crowds.
0
1
4
Proud of med student Rafael Homer whose summer research project @SimpsonLabUW @DermatologyUW won 2nd place in the @uwsomwwami Wyoming site poster competition! Rafael also won a travel award to attend the Western Medical Research Conference & was chosen for an oral presentation🤩
1
2
13
Exciting week @SimpsonLabUW @DermatologyUW celebrating🍾our newest paper @JCI_insight (see separate🧵). which uncovered a mechanism that drives the pathology #Grover disease and was reversed using MEK inhibitors. Special thanks to Arti for making an amazing Indian lunch buffet!
New paper from @SimpsonLabUW @DermatologyUW is online @JCI_insight🍾We found ERK hyperactivation disrupts cell-cell adhesion in epidermis, linked this pathway to both drug-induced & spontaneous Grover disease & identified MEK inhibition as a novel therapy: https://t.co/Ko48RnTxNp
1
1
21
Hope this will finally move the needle for severe drug reactions like SJS & TEN, nightmare consults in #dermatology. No Rx has great evidence to halt skin/mucosal sloughing that can be fatal. JAKi remains to be rigorously tested in patients/RCT but could change standard of care.
0
1
6
Nature research paper: Spatial proteomics identifies JAKi as treatment for a lethal skin disease
nature.com
Nature - Cell-type-resolved spatial proteomics of the skin from patients with toxic epidermal necrolysis reveals that it is driven by JAK/STAT signaling, leading to successful treatment of this...
2
17
85
This program has been an outstanding opportunity for networking with peers, receiving grant feedback, learning how to navigate the new PI path, and getting sage career advice from leading physician-scientists. 10/10 highly recommend @the_asci. Consider applying
Early-Faculty Physician-Scientists! Nominations are open for the ASCI Young Physician-Scientist Awards. Award Benefits include access to @JointMeeting, networking and career development opportunities. Deadline: Oct. 23 More info: https://t.co/yz0SAfJR7u
0
0
1
Proud of all co-authors & grateful to our collaborators @umichmedicine & @PennSbdrc including @drdremchu. Thanks to @NIH_NIAMS & @FIRST_Skin for lab support and @LEOFondet for funding my effort to find shared mechanisms & treatment strategies for rare skin #blistering diseases.
1
0
3
Finally, we reasoned the same mechanism could drive spontaneous Grover disease (ie, not drug-induced). Accordingly, we found ERK hyper-activation in Grover disease lesions and propose MEK inhibitors may be therapeutic for this idiopathic disorder lacking any FDA-approved therapy.
1
0
0
In fact, we found multiple different MEK inhibitors restored cell-cell adhesion despite B-RAF blockade. This was consistent with subsequent clinical trial data in which patients treated w/DUAL inhibitors of both B-RAF and MEK no longer got Grover disease as a side effect.
1
0
0
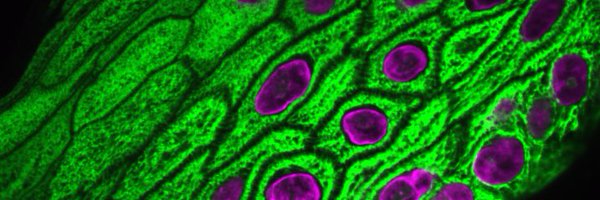
In keratinocytes, we showed ERK hyperactivation was sufficient to disrupt desmosomes & reduce cohesion, explaining why the epidermis falls apart in Grover disease. Importantly, blocking ERK activation w/an FDA-approved MEK inhibitor (trametinib) rescued keratinocyte cohesion.
1
0
0
We validated these findings in skin biopsies from patients who were treated w/vemurafenib and developed drug-induced Grover disease. These biopsies showed hyper-activation of ERK within lesional epidermis, which correlated with the disruption of cell-cell junctions (desmosomes).
1
0
0
We used a kinase reporter to show that the B-RAF inhibitors used in the clinical trials (dabrafenib/Dab or vemurafenib/Vem) induced paradoxical ACTIVATION of ERK in live human epidermal keratinocytes.
1
0
0
The story starts w/an unexpected side effect of B-RAF inhibitors seen in clinical trials for cancer. Some patients developed a skin blistering disorder called Grover disease, in which keratinocytes lose their connections to one another, leading to splitting of the epidermis.
1
0
0
Early-Faculty Physician-Scientists! Nominations are open for the ASCI Young Physician-Scientist Awards. Award Benefits include access to @JointMeeting, networking and career development opportunities. Deadline: Oct. 23 More info: https://t.co/yz0SAfJR7u
0
12
20
Great lunch @SimpsonLabUW @DermatologyUW for lots of celebrating including Arti’s birthday 🥳 More good news to share soon now that I’m out from under the cloud of this R01 submission 😮💨📝 ✅🤞
0
1
18
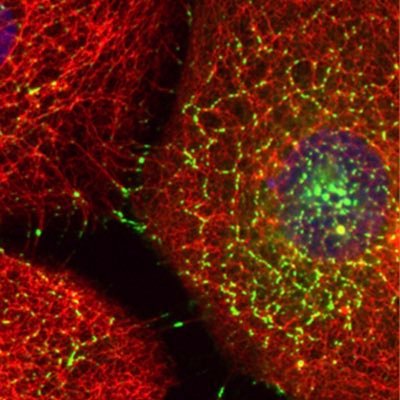
I'm excited to announce that I am on the job market for tenure-track Assistant Professor positions in cell biology, with a focus on the integrated roles of keratin filaments and organelle biology! Please feel free to reach out, share/RT🔁!
2
25
110
Very proud of Akshata for representing @SimpsonLabUW @DermatologyUW at the @UWISCRM Fall Symposium. She did a great job at her 1st poster session explaining her work developing quantitative methods to assess our model of #HaileyHailey disease, a rare #skin #blistering disorder.
0
2
18
Last day of Early Bird Registration! Can't wait to engage in transformative dialogue with skin scientist and clinicians!
0
7
12