Reza Maroofian
@RMaroofian
Followers
511
Following
855
Media
1
Statuses
141
Geneticist at UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology @UCLIoN. Interested in Rare Diseases, Neurogenetics & Genomic Medicine.
London, England
Joined October 2022
From our recent work on BORCS5 to BORCS8—and now BLOC1S1 as the latest culprit in the BORC/BLOC-1 pathway—"BORCopathies" are emerging. Biallelic BLOC1S1 variants impair lysosome transport & autophagy in neurons, causing a severe brain disorder with hypomyelination & epilepsy.
BLOC1S1 variants cause lysosomal and autophagic defects resulting in a hypomyelinating leukodystrophy with epileptic encephalopathy #RareDisease #Genetics #morbidgene
0
1
9
RT @IonSynapse: New Job Alert! 🔔Join our neurogenetics team @UCLIoN as a Research Technician - a fantastic opportunity to gain hands-on exp….
jobs.ac.uk
0
2
0
Biallelic PDE1B variants cause a novel early-onset movement disorder with hypotonia, dystonia/ataxia, developmental delay & intellectual disability—paralleling PDE10A deficiency & underscoring cAMP/cGMP signaling in basal ganglia. Read the full study here:
movementdisorders.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Background Breakdown of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) in basal ganglia cells through hydrolysis of diesteric bonds, primarily by PDE10A and PDE1B,...
0
1
10
12 yrs ago, we identified a homozygous AIRIM variant in a large NDD family—more families followed, but the gene’s function remained unknown. Over the decade, AFG2A & AFG2B were linked to similar phenotypes. Now we know they all form a complex with CINP, key to ribosome biogenesis.
Excited to announce our paper describing how allelic variants in ribosome biogenesis factors cause neurodevelopmental disorders. Congratulations to co-first authors Chunyang Ni and Yudong Wei, our collaborator @leo_jwu and all the other authors.
0
6
28
Our new study characterises ELFN1 deficiency as a novel autosomal recessive neurodevelopmental disorder marked by epilepsy, GDD/ID, & movement disorders. Biallelic ELFN1 variants disrupt synaptic protein trafficking—validated through functional assays and mouse/zebrafish models.
Neurogenetics alert! Biallelic loss of function variants in ELFN1 cause a neurodevelopmental disorder with DD/ID, seizures and movement disorder. @rhysdore
0
2
14
We define the recessive ELOVL1-related disorder, part of an emerging group of neurocutaneous syndromes caused by biallelic ELOVL1/4 variants. Monoallelic ELOVL1/4/5 variants lead to spastic paraplegia & ataxia. These genes encode enzymes that elongate very-long-chain fatty acids.
An important study by Wong et al. on neuro-ichthyosis linked .to biallelic ELOVL1 variants. In this hypomyelinating leukodystrophy, commonly observed abnormal movements included spasticity, head tremor, and myoclonus.
0
1
18
RT @FraMagrinelli: 🚨 We’re hiring a highly motivated Postdoc! .Join us at @UCLIoN to study the neurobiology of PSMF1, a new gene linked to….
ucl.ac.uk
UCL is consistently ranked as one of the top ten universities in the world (QS World University Rankings 2010-2022) and is No.2 in the UK for research power (Research Excellence Framework 2021).
0
10
0
RT @Brain1878: The dystonin gene encodes three major isoforms: DST-a, -b, and -e. Jacob et al. report that variants exclusively affecting D….
0
2
0
RT @IonSynapse: Join our team at @UCLIoN as a Senior Research Technician and Analyst for Next Generation Sequencing 🧬.Play a key role in ad….
ucl.ac.uk
UCL is consistently ranked as one of the top ten universities in the world (QS World University Rankings 2010-2022) and is No.2 in the UK for research power (Research Excellence Framework 2021).
0
4
0
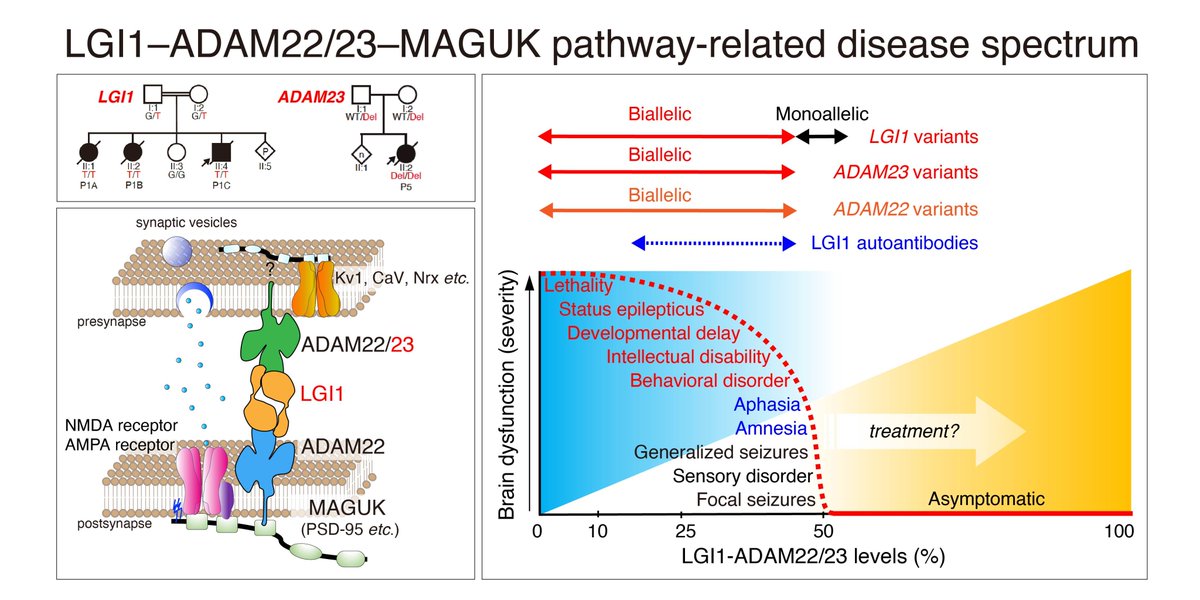
We define the critical role of the LGI1–ADAM22/23 pathway in developmental & epileptic encephalopathy (DEE)—essential for regulating synaptic transmission and brain excitability. Previously linked ADAM22 to DEE, now we report biallelic LGI1 & ADAM23 variants causing lethal DEE.
Hirano et al. define a novel neurological disease spectrum involving the LGI1–ADAM22/23 pathway, identifying ultra-rare biallelic LGI1 variants in developmental and epileptic encephalopathy, and a biallelic ADAM23 variant in lethal neonatal epilepsy.
0
1
10
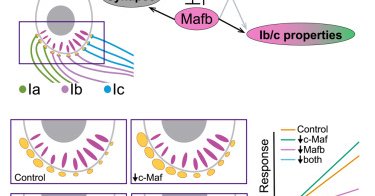
RT @CellReports: Combinatorial transcriptional regulation establishes subtype-appropriate synaptic properties in auditory neurons https://t….
cell.com
Bastille and colleagues demonstrate that two closely related transcription factors, c-Maf and Mafb, have both redundant and independent effects on the diversification and functional differentiation...
0
2
0
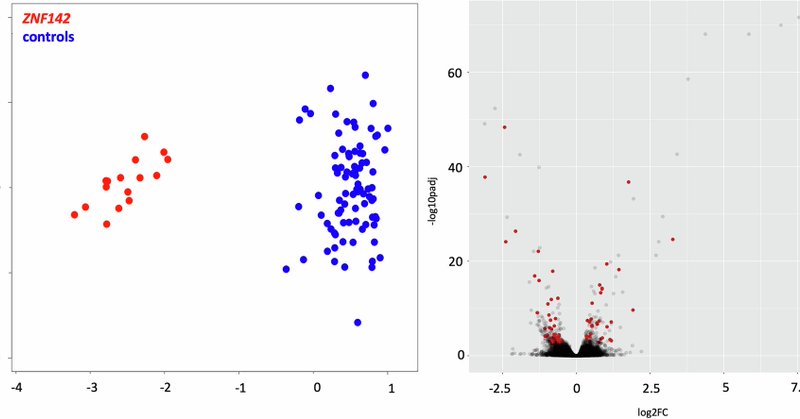
RT @BibliotecaHUVH: Biallelic loss-of-function variants in ZNF142 are associated with a robust DNA methylation signature affecting a limite….
nature.com
European Journal of Human Genetics - Biallelic loss-of-function variants in ZNF142 are associated with a robust DNA methylation signature affecting a limited number of genomic loci
0
1
0
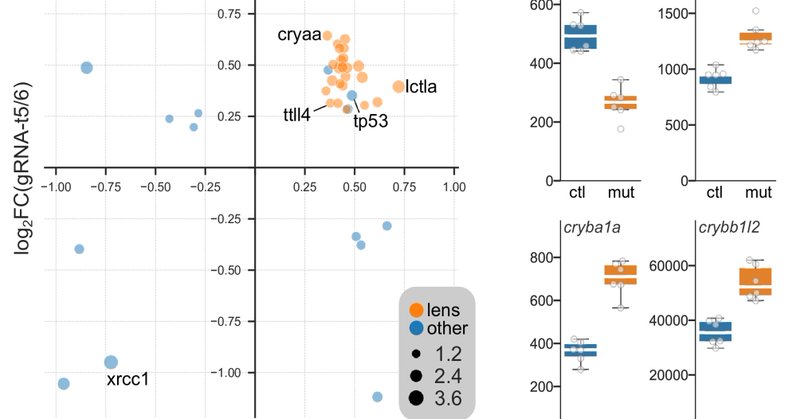
Loss of XRCC1 disrupts cerebellar development in zebrafish due to toxic PARP1 accumulation. Strikingly, parp1 knockdown rescues the XRCC1 phenotype, supporting PARP1 inhibition as a potential therapy in recessive XRCC1-related neurodegenerative disorders.
nature.com
Scientific Reports - Parp1 deletion rescues cerebellar hypotrophy in xrcc1 mutant zebrafish
0
1
19
RT @GS_Lab_Bham: Proud to present our work identifying a role for DIAPH1 and gamma-actin in regulating DSB repair and how defects in this p….
nature.com
Nature Communications - DNA double strand break repair pathways ensure genome stability and prevent disease. Here the authors show that the actin nucleating factor DIAPH1 and γ-actin promote...
0
4
0
We previously reported a novel recessive paediatric neurodegenerative disorder linked to BORCS8. Our latest study identifies BORCS5 as a new NDD gene, showing a broader neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative spectrum with clear genotype–phenotype correlation. Read the preprint:.
Pathogenic variants in BORCS5 Cause a Spectrum of Neurodevelopmental and Neurodegenerative Disorders with Lysosomal Dysfunction #medRxiv.
0
1
17
RT @AJHGNews: 📣New from @RDExeter & co!.📄Bi-allelic UGGT1 variants cause a congenital disorder of glycosylation.
cell.com
Bi-allelic UGGT1 variants cause a distinct congenital disorder of glycosylation (UGGT1-CDG) with variable severity, characterized by neurodevelopmental impairment, seizures, dysmorphic features, and...
0
4
0
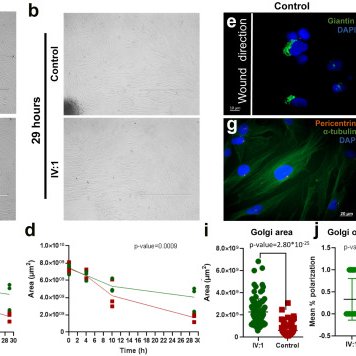
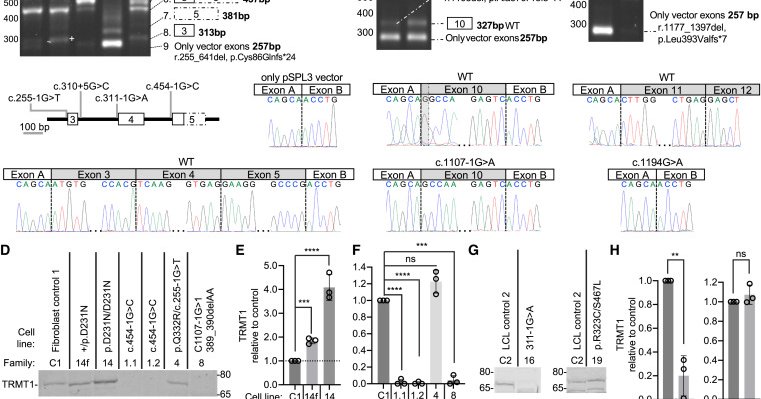
Our lab characterises the autosomal recessive TRMT1-related neurodevelopmental disorder through a large cohort, patient cells, and zebrafish—linking defective tRNA methylation to intellectual disability and expanding the emerging group of "tRNAopathies".
cell.com
We identify bi-allelic variants in TRMT1, encoding a tRNA-modification enzyme, that cause intellectual disability and developmental delay. Functional studies in human cells and zebrafish provide...
0
3
24
RT @UCLIoN: For #RareDiseaseDay2025, @IonSynapse is celebrating the invaluable contributions of our international collaborators, whose dedi….
0
11
0
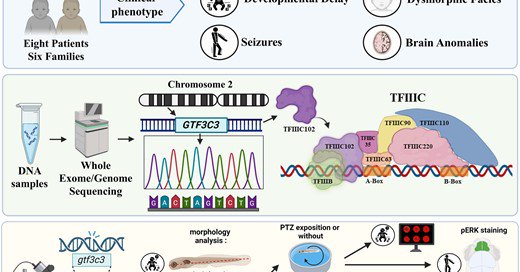
As part of 2 parallel studies, we delineated a new subtype of neurodevelopmental disorder linked to biallelic GTF3C3 variants. One study models the disorder using zebrafish, while the other utilizes fly. Check both papers below: &
academic.oup.com
Abdel-Hamid et al. identified biallelic GTF3C3 variants in four individuals with neurodevelopmental disorders, including developmental delay/intellectual d
1
3
16