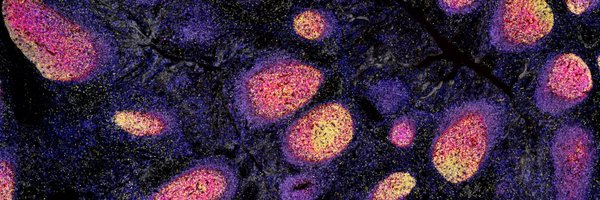
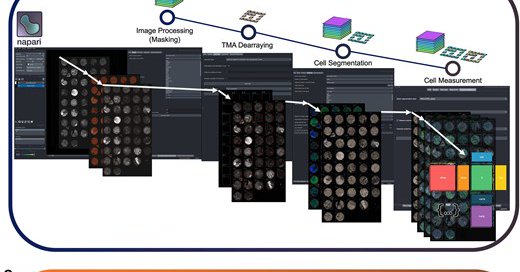
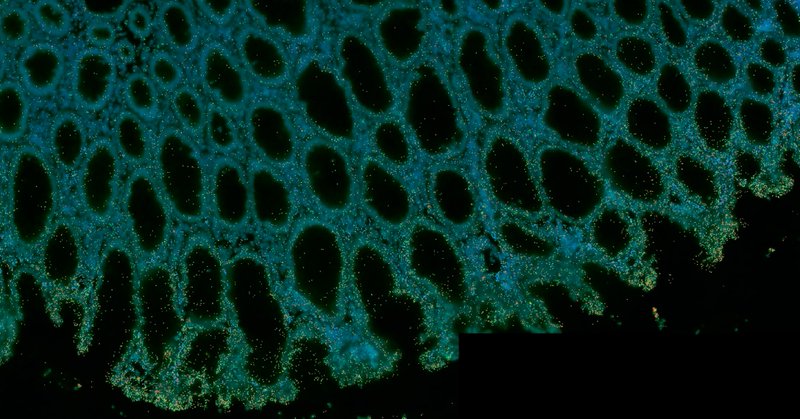
Queensland Spatial Biology Centre
@Qld_SBC
Followers
91
Following
277
Media
48
Statuses
288
A ground-breaking research hub that is reshaping the future of healthcare through cutting-edge spatial biology techniques.
Brisbane, Queensland
Joined October 2023
RT @WesleyResearch: New technical analysis methods paper for spatial proteomics data by the @Qld_SBC! . PRISM: a Python package for interac….
academic.oup.com
Abstract. Tissue microarrays (TMAs) enable researchers to analyse hundreds of tissue samples simultaneously by embedding multiple samples into single array
0
4
0
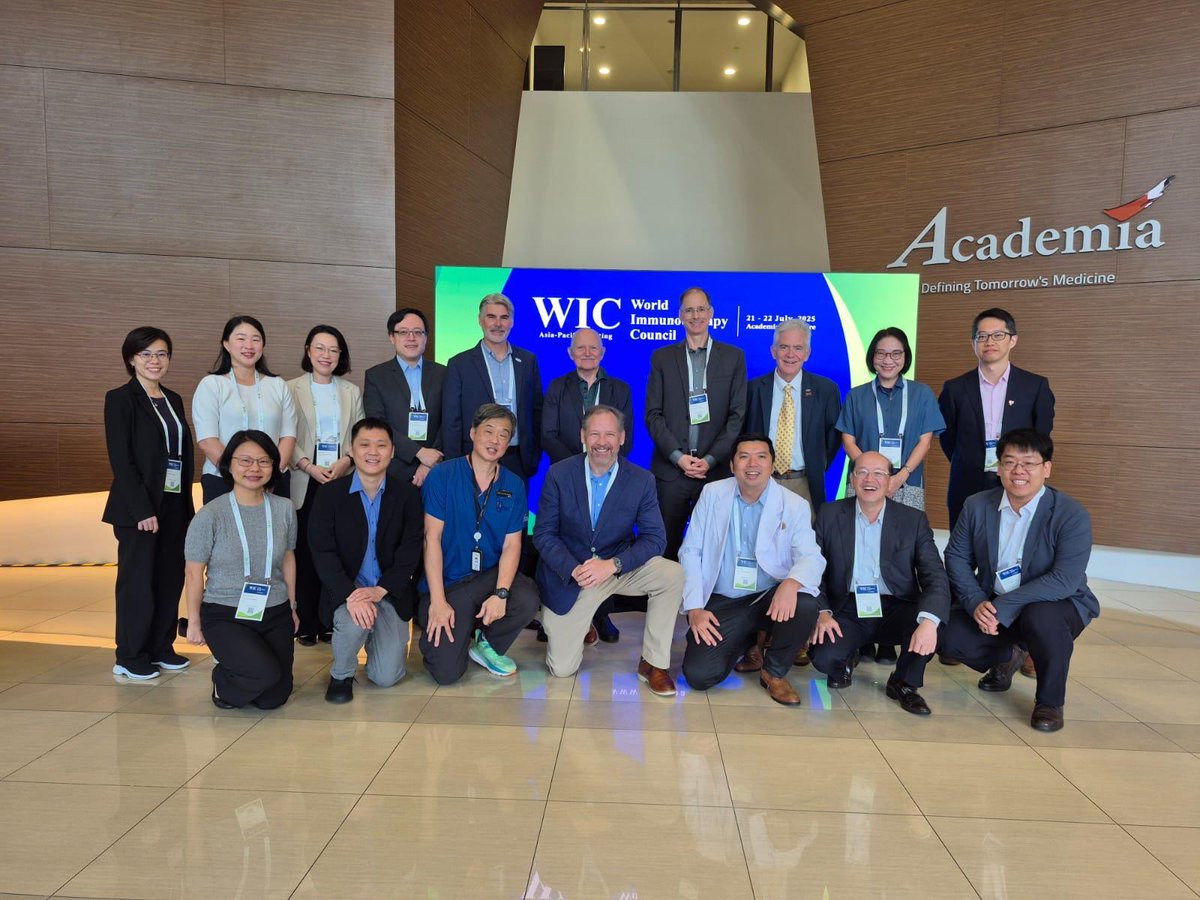
🛫 @aruthak presented at the World Immunotherapy Council (WIC) Asia-Pacific (APAC) Conference, in Singapore this week. A/Prof Kulasinghe shared his leading research on #multiomics and its role in precision medicine, particularly focusing on mechanisms of #resistance in #cancer.
0
2
4
RT @WesleyResearch: In a world-first discovery from the @Qld_SBC , doctors can now check hundreds of markers in a single biopsy to show whi….
0
3
0
RT @WesleyResearch: Did you catch the @Qld_SBC on @Channel9?. @aruthak shared an exciting world-first discovery! His team has profiled hu….
0
4
0
🙏 Finally, massive thanks to Passe and Williams Foundation, @PARFoundation, @WesleyResearch, @AGRF_genomics Sequencing facilities, collaborating clinicians, and patients who donated samples. [11/12]
1
0
4
🎉Led by the incredible team including @chinwee10, @NBerrell45653, @megldono, James Monkman, @CCRG_Research’s John Fraser, @aruthak, and more!.Collaboration between @QLD_SBC, #FrazerInstUQ, @WEHI_research, and @brukerspatial. [10/12]
1
0
5
🤝 This study demonstrates one of the first multi-model workflows between GeoMx IPA and WTA assays and highlights the utility of the high plex IPA assay to identify prognostic biomarkers in mucosal HNSCC. Now look to apply this to #Immunotherapy Clinical Cohorts! [9/12]
1
0
4
🧬 However, we also identified markers associated with T-regs and T cell dysfunction, CTLA-4 and FOXP3, in the tumour regions of patients who had worse clinical outcomes. Highlighting the importance of a large proteomic panel to functionally characterise the TME. [7/12]
1
0
4
🔍 We found lymphocyte markers within the tumour regions for both good and poor response to therapy. Firstly, we identified CD3e as well as high intra-tumoral CXCR5 expression (linked to positive infiltration of lymphocytes) in patients with improved outcomes. [6/12]
1
0
4
👀 Next, we wanted to find markers might be associated with clinical response that were unique to protein expression and not found when we look at RNA alone. [5/12]
1
0
4
💡 Looking at the protein/RNA expression we found structural species highly correlated whereas functional genes related to metabolic and chemokine functions were uncorrelated. Highlighting critical differences between utilising assay types to study biological functions. [4/12]
1
0
4
✨We profiled 84 mucosal HNSCC patient tissue samples using next-generation ultra-high plex spatial protein profiling (580-proteins, Immuno-Oncology Proteome Atlas) and spatial transcriptome mapping (18,000 mRNA, Whole Transcriptome Atlas) from @brukerspatial [3/12]
1
1
6
🚀Using the @brukerspatial GeoMx we compared their latest Immuno-Oncology Proteome Atlas (IPA) with their whole transcriptome atlas to find differences between the ‘omes’. The IPA includes 580 antibodies from @Abcam and covers the major hallmarks of cancer. [2/12]
1
0
4
🚨Excited to share our latest paper from the #ClinicaloMxLab #QSBC where we spatially resolved >580 proteins in head and neck cancer! This is the largest spatial proteomic panel currently commercially available for fresh frozen and FFPE samples 💪.[1/12]
2
6
6
RT @WesleyResearch: Members of WRI had the pleasure of attending the Art of Medicine exhibition at @gabbaart. An inspiring initiative explo….
0
2
0
RT @WesleyResearch: In a feature in @NatureBiotech, @aruthak from the @Qld_SBC , discusses the future of spatial biology and the transform….
nature.com
Nature Biotechnology - As the next generation of spatial transcriptomics tools hits the market, researchers are uncovering previously unknown interactions that could transform clinical research.
0
5
0