MRC Laboratory of Medical Sciences (LMS)
@MRC_LMS
Followers
6K
Following
5K
Media
1K
Statuses
7K
TeamScience: #Aging #SexDifferences #Environment #Genes #Metabolism #CellFate; Translation: #Multimorbidity; Training: #Transdisciplinary & #ClinicianScientist
London
Joined February 2009
As of March 2025, we will no longer be actively posting on X. We’ll continue to monitor our account so we can respond to DMs and urgent communications.
1
0
3
You can stay up to date with the LMS via our other channels: Bluesky https://t.co/XGJE1w8CyK Instagram https://t.co/7FAeqhz8s8 LinkedIn https://t.co/XvrxSTitFP Facebook https://t.co/EyEUnir9PY Threads
0
0
1
Great to bump into my old chum Matthew Freeman of the @Dunn_School in that powerhouse of medical science, the @MRC_LMS!
0
1
5
🎄Our Festive Jumper Day is here! 🧑🎄 Today we're wearing festive knits to support @SBFamiliesProj, helping local families in Hammersmith & Fulham. LMS partners with local organisations to support our Hammersmith & Fulham community
0
0
4
Thank you so much for reading our little sum up of this review paper! And congrats for getting to the end! 🧵: 12/12
0
0
1
While there is much to be excited over, the authors state that there are a range of challenges to this field. This is mainly the variation within senescent cells which make them hard to monitor and also target. 🧵: 11/12
1
0
2
Very excitingly a number of these therapies are currently in clinical trials! Senomorphics are in phase II trials for diseases ranging from Alzheimer’s disease to Covid-19, while senomorphics are in phase II trials to treat ageing. 🧵: 10/12
1
0
1
It may also be possible to treat age-related disease by reverting senescence. However, this method may be quite risky, as entering senescence is a strategy for avoiding cancer, so there is a chance of causing cancer. 🧵: 9/12
1
0
1
Senomorphic treatments work by neutralising the harm of senescent cells rather than destroying them 🏳️ This means that senescent cells that may be necessary will not be killed, while still relieving symptoms. However, the treatment would need to be taken often. 🧵: 8/12
1
0
1
Interestingly, these senolytic drugs can be used to treat cancer, in a method called a one-two punch 🥊 By inducing senescence in tumour cells, the senolytics can then be used to clear the cancer! 🧵: 7/12
1
0
1
What makes this method even better is these results were achievable using intermittent senolytic treatment, and they had minimal side effects. However, these results were found in mice and not humans. 🧵: 6/12
1
0
1
Senolytics are compounds that cause senescent cells to die. This is the most researched method and there’s a lot of evidence demonstrating its efficacy. Proof of concept studies have shown that senolytics cannot only treat but also prevent age-related disease in mice. 🧵: 5/12
1
0
1
The methods developed for targeting senescence can broadly be categorised as senolytics, senomorphic and reverting or delaying senescence. 🧵: 4/12
1
0
1
Senescent cells, also referred to as zombie cells 🧟♂️, have exited the cell cycle. As we age, we accumulate senescent cells, leading to age-related disease. This review looks at how researchers are targeting senescent cells to treat these diseases. 🧵: 3/12
1
0
1
Senescence is an area of focus for LMS research so to celebrate we’re sharing this top-level overview of the paper. The article was written by Dr Domnhall McHugh and Dr Imanol Durán, who work with Professor Jesús Gil – a world leader in senescence research. 🧵: 2/12
1
0
1
A new review entitled “Senescence as a therapeutic target in cancer and age-related diseases” from the Senescence group has been published in @NatRevDrugDisc! 🥳 🧵: 1/12 https://t.co/OdkgiY5vtD
1
1
4
Amazing work from @DrDeclanORegan and @KathrynMcGurk!! 🫀
Research | The inner heart surface has a meshwork of muscles called trabeculae. McGurk et al. report the genetic regulation of heart trabeculae across common and rare variants, revealing pathways implicated in heart development and cell fate. 👉 https://t.co/OJ2U3arGCI
0
0
7
The heart condition dilated cardiomyopathy can be caused by the cumulative influence of hundreds or thousands of genes and not just by a single “aberrant” genetic variant, finds a new study co-led by Dr @tomlumbers @UCL_IHI with @imperialcollege @MRC_LMS
ucl.ac.uk
A potentially life-changing heart condition, dilated cardiomyopathy, can be caused by the cumulative influence of hundreds or thousands of genes and not just by a single “aberrant” genetic variant,
0
3
9
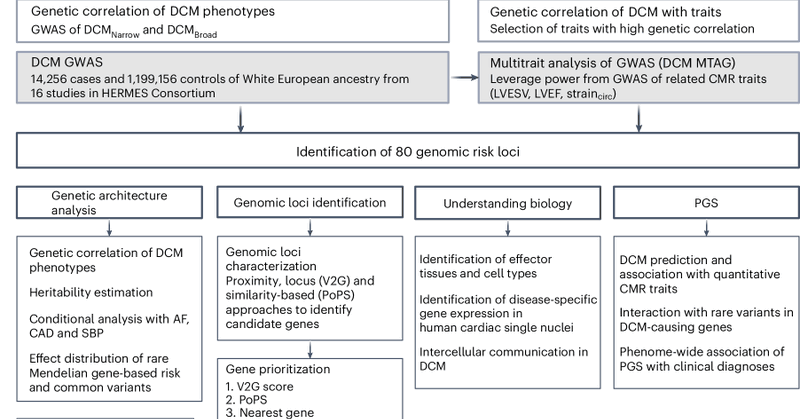
🧬 Out today - our DCM GWAS in @NatureGenet 📍 https://t.co/UYO9jNR9Co All made possible with friends and collaborators from @HERMESgenetics @AH_AlbertHenry @tomlumbers @drjamesware @MRC_LMS @BHFCoREImperial @ImperialNHLI See 🧵 for the cool science
nature.com
Nature Genetics - Genome-wide association analyses comprising 14,256 cases and 1,199,156 controls and incorporating correlated cardiac magnetic resonance imaging traits provide insights into the...
Delighted to share our dilated cardiomyopathy GWAS from HERMES Consortium as a preprint. A massive team effort involving >1.2m participants from 16 studies, and 100+ colleagues. @AlbertHenry @TomLumbers @JamesWare
https://t.co/bAbQRPcivs 🧵below 1/5
4
14
58
Amazing to see our research getting picked up!
UK study shows that dilated #cardiomyopathy can be caused by the cumulative influence of hundreds or thousands of genes, not just by a single faulty gene 🧬 https://t.co/xtkRLIT8S1
#DCM
0
1
4