Nature Reviews Drug Discovery
@NatRevDrugDisc
Followers
43K
Following
1K
Media
2K
Statuses
4K
Editorial team of Nature Reviews Drug Discovery.
London
Joined April 2009
How multispecific molecules are transforming pharmacotherapy https://t.co/f1AV7ohs7T
https://t.co/FZ6GzkDyFJ This article in the December issue discusses how drugs designed to engage two or more entities are overcoming development barriers such as toxicity and redundancy
1
37
131
Advances in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus https://t.co/ulqoVHF07x
https://t.co/rxrnJTRwOq This Review in the December issue covers specific immune targets and emerging efforts to restore immune homeostasis such as CAR T cell therapies to remove pathogenic B cells
1
71
209
For readers interested in GLP-1-based therapies for metabolic diseases and beyond, here's a recent review https://t.co/yk9bDSLdvq
https://t.co/X714Dj2BNb
1
36
160
Top product forecasts for 2026 https://t.co/GZKMy2NFJe The top ten cohort is projected to generate sales of US$198 billion in 2026, driven by the GLP-1-based products for metabolic diseases. Find out more in this new article by Paul Verdin @evaluatepharma
1
3
21
For readers interested in genome editing therapeutics, this Review in the December issue discusses progress in the application of CRISPR-based genome editing to treat inherited blood disorders such as sickle cell disease https://t.co/17vKngvi46
https://t.co/dt2ldNjVAR
3
39
127
Vertex #CRISPR therapy hits early goal in children with blood disorders https://t.co/y4eqVZvfSR
@ByJonGardner #ASH25 $VRTX
biopharmadive.com
Casgevy, now a "national priority" drug, helped kids with sickle cell and beta thalassemia, results which may help toward a label expansion and stronger commercial uptake.
0
3
9
Epigenetic editing: from concept to clinic https://t.co/dy0bt4Ui4O
https://t.co/O7Ps5IKXjk Epigenetic editing aims to reprogramme gene expression by rewriting epigenetic signatures, without editing of the genome. Find out about progress in the field in this new Review
2
82
265
For readers interested in drugs targeting TNF superfamily members such as APRIL and their receptors, here's a comprehensive review https://t.co/6NpGq39kct
https://t.co/T9RirqrjR2
0
14
62
First-in-class APRIL inhibitor secures approval for rare kidney disease https://t.co/NT7FNKPXzc The FDA has granted accelerated approval to Otsuka’s sibeprenlimab for primary immunoglobulin A nephropathy
0
7
33
The milestone of 100 approved kinase inhibitors is both a major win and an important reality check. It shows how far drug design has come and how powerfully these medicines have changed cancer treatment. It also signals that the easier targets are mostly taken. The next
The FDA has recently approved the 100th small-molecule kinase inhibitor, a quarter of a century on from the landmark approval of imatinib. Read about progress and the key trends in the field in this article in the December issue https://t.co/VjvGosMwXN
0
2
8
For readers interested in drug repurposing, this article overviews computational approaches to drug repurposing and evaluates available in silico resources https://t.co/D3oygNnglg
https://t.co/ZGfAgFlr27
0
15
36
Stimulating medicines repurposing in the EU: a pilot project https://t.co/AZ6OdTv2vs This new article discusses a project testing a framework to support not-for-profit organizations and academia to generate the evidence needed for a regulatory submission of a repurposed drug
2
7
21
The FDA has recently approved the 100th small-molecule kinase inhibitor, a quarter of a century on from the landmark approval of imatinib. Read about progress and the key trends in the field in this article in the December issue https://t.co/VjvGosMwXN
2
14
32
Our December issue is live! Read about how multispecific molecules are transforming pharmacotherapy, CRISPR-based genome editing for blood disorders, advances in the treatment of lupus, progress with small-molecule kinase inhibitors and more here https://t.co/MsTSYMWOPE
2
5
22
Chemical modifications can improve the stability, efficiency and specificity of RNA therapeutics, while reducing their immunogenicity - find out more in this review https://t.co/sEugYpvX26
https://t.co/F8UxINqUMS
1
41
165
How new experimental design and computational tools are opening drug-discovery paths for intrinsically disordered proteins!
Intrinsically disordered proteins are dysregulated in disease, but have been considered 'undruggable'. This Review in the October issue discusses experimental and computational approaches to conquer this barrier in drug discovery https://t.co/CtK66DUq4y
https://t.co/uCOjGSckx8
0
2
10
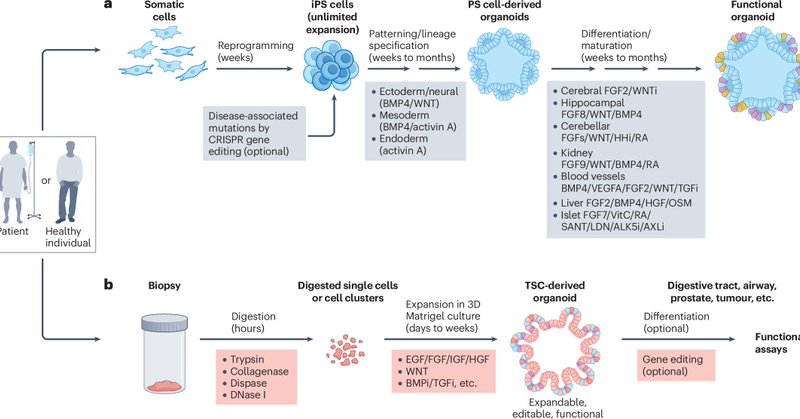
Organoids, 3D stem-cell structures, mimic human tissues better than 2D models, enabling superior study of diseases, drug effects, and patient-specific responses. PMID:41225057, Nat Rev Drug Discov 2025, @NatRevDrugDisc
https://t.co/OmT73U35Wc
#AI #Pharma #BioMed #RNA #ASHG #ESHG
nature.com
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery - Human organoids provide physiologically relevant, 3D models for studying disease mechanisms, drug efficacy and toxicity. This Review examines organoid generation...
0
4
8
For readers interested in drug development for malaria, here's a review covering strategies to combat drug resistance in malaria, HIV and tuberculosis https://t.co/fVzBMoGN8S
https://t.co/CdT0JFaNEm
1
7
33
Novel antimalarial passes key phase III test https://t.co/emfhsnN5pA Novartis’s ganaplacide plus lumefantrine (GanLum) is as effective as standard-of-care artemether plus lumefantrine (Coartem) for acute, uncomplicated malaria due to P. falciparum
1
3
21
Epigenetic editing: from concept to clinic https://t.co/dy0bt4Ui4O
https://t.co/O7Ps5IKXjk Epigenetic editing aims to reprogramme gene expression by rewriting epigenetic signatures, without editing of the genome. Find out about progress in the field in this new Review
2
82
265