Alexis Tabah
@AlexisT
Followers
286
Following
373
Media
0
Statuses
53
ICU doctor and researcher - @eurobact2. welcomeICU and others
Australia
Joined June 2007
RT @CRE_RESPOND: 🌟REMINDER Join A/Prof Patrick Harris and UQCCR Infectious Diseases team🌟 . 📢 Early Diagnostics Seminar .⏲️12 midday AEST….
0
7
0
RT @CRE_RESPOND: Looking forward to @criticcaredoc our European Collaboration Co-Lead, presenting in-person at our forum, Friday 19 July. P….
0
4
0
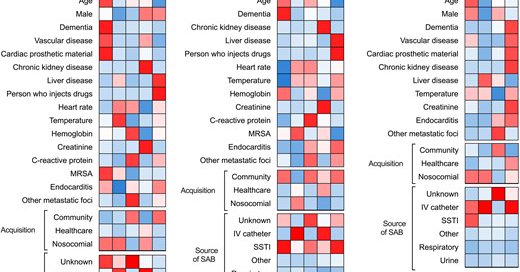
RT @davidantibiotic: This is such a great paper! We all know that patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia are such a heterogeneous g….
academic.oup.com
We studied 1430 patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia in 3 separate cohorts and used latent class analysis to identify 5 distinct and reproducible
0
32
0
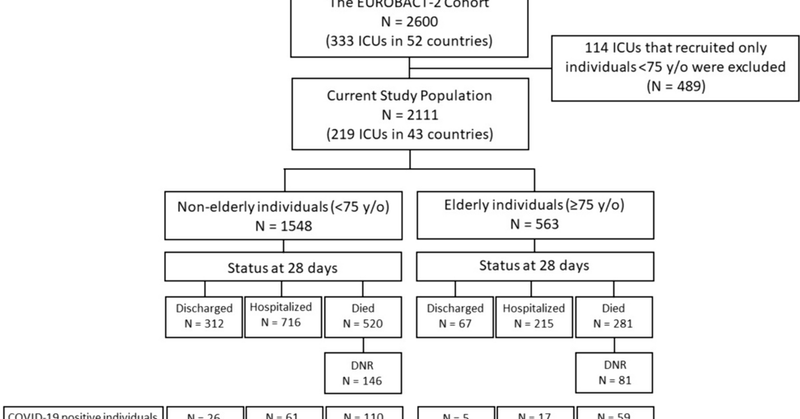
Presentation, management, and outcomes of older compared to younger adults with hospital-acquired bloodstream infections in the intensive care unit - an excellent analysis of the @eurobact2 database . by Ili Margalit, Dafna Yahav Tomer Hofman & team.
link.springer.com
Infection - Older adults admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) usually have fair baseline functional capacity, yet their age and frailty may compromise their management. We compared the...
0
2
3
RT @jasonroberts_pk: BLING-3 results in 10hrs… Does continuous infusion of beta-lactam antimicrobials decrease day 90 mortality in sepsis.….
criticalcarereviews.com
The most up-to-date critical care website in the world
0
23
0
RT @CIDJournal: Rapid diagnostic tests and antimicrobial stewardship programs for the management of bloodstream infection: what is their re….
0
18
0
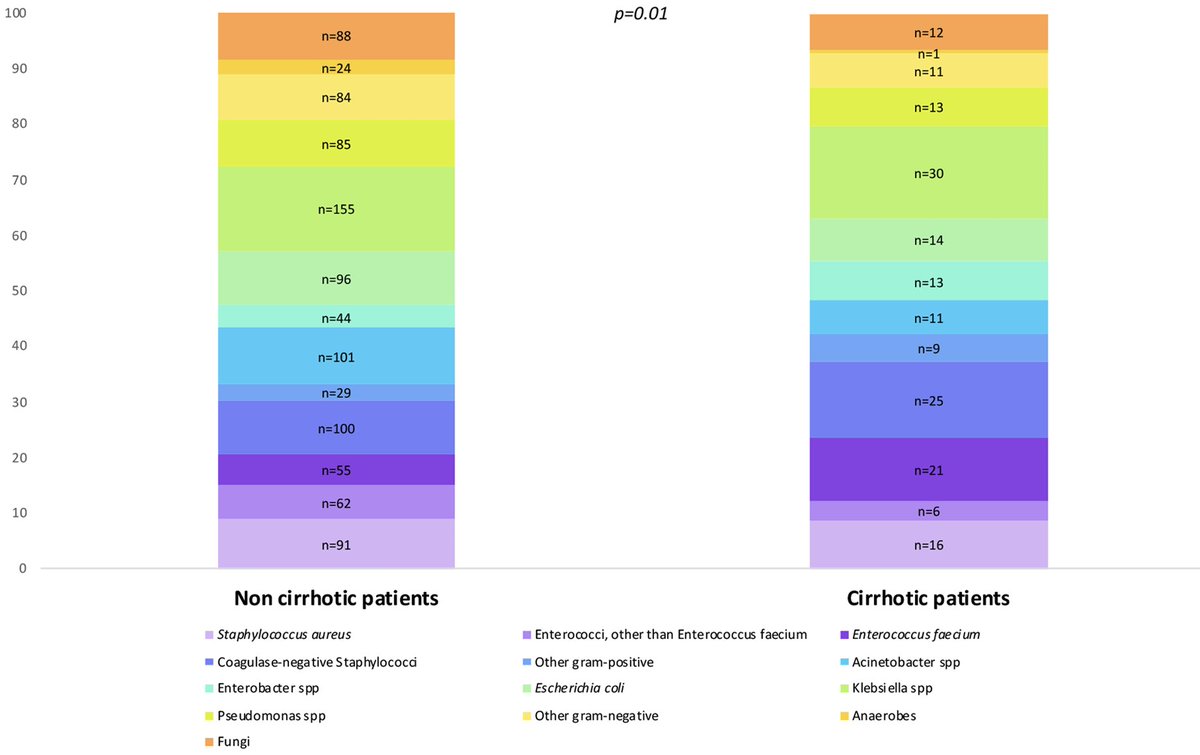
A @eurobactII study by Hannah Wozniak - thank you to everyone involved @ICUREsearch_eu @JF_Timsit @ESICM @ESCMID @MarcLeone8 @andymoz78 et al.
Hospital-acquired bloodstream infection in cirrhotic patients . Causative bacteria: Klebsiella spp (16.5%), CNS (13.7%), and E. faecium (11.5%) .E. faecium was more common in cirrhotic patients than non-cirrhotic patients after confounder adjustment. 🔓
0
2
7
RT @YukiKotani5: Hospital-acquired bloodstream infection in cirrhotic patients . Causative bacteria: Klebsiella spp (16.5%), CNS (13.7%),….
0
6
0
RT @maheshramanan: Thanks @UNSWMedicine @georgeinstitute . It was a big team effort. Original idea from my mentor Prof Venkatesh. Also I….
0
2
0
RT @PeterCDoll: meanwhile in the southern GBR. mass coral bleaching (& recent mortality) at all reefs & sites surveyed this weekend, affec….
0
36
0
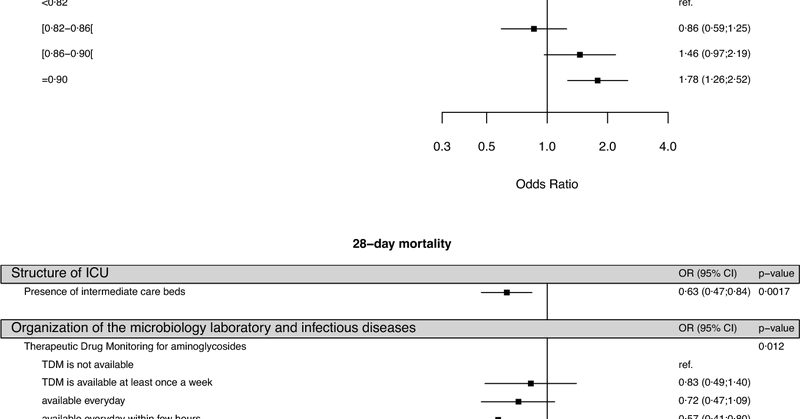
RT @andymoz78: Latest paper from @AlexisT Nicole Buetti and @EuroBact2 team. Factors associated with early adequate antimicrobial therapy….
link.springer.com
Intensive Care Medicine - The primary objective of this study was to evaluate the associations between centre/country-based factors and two important process and outcome indicators in patients with...
0
7
0
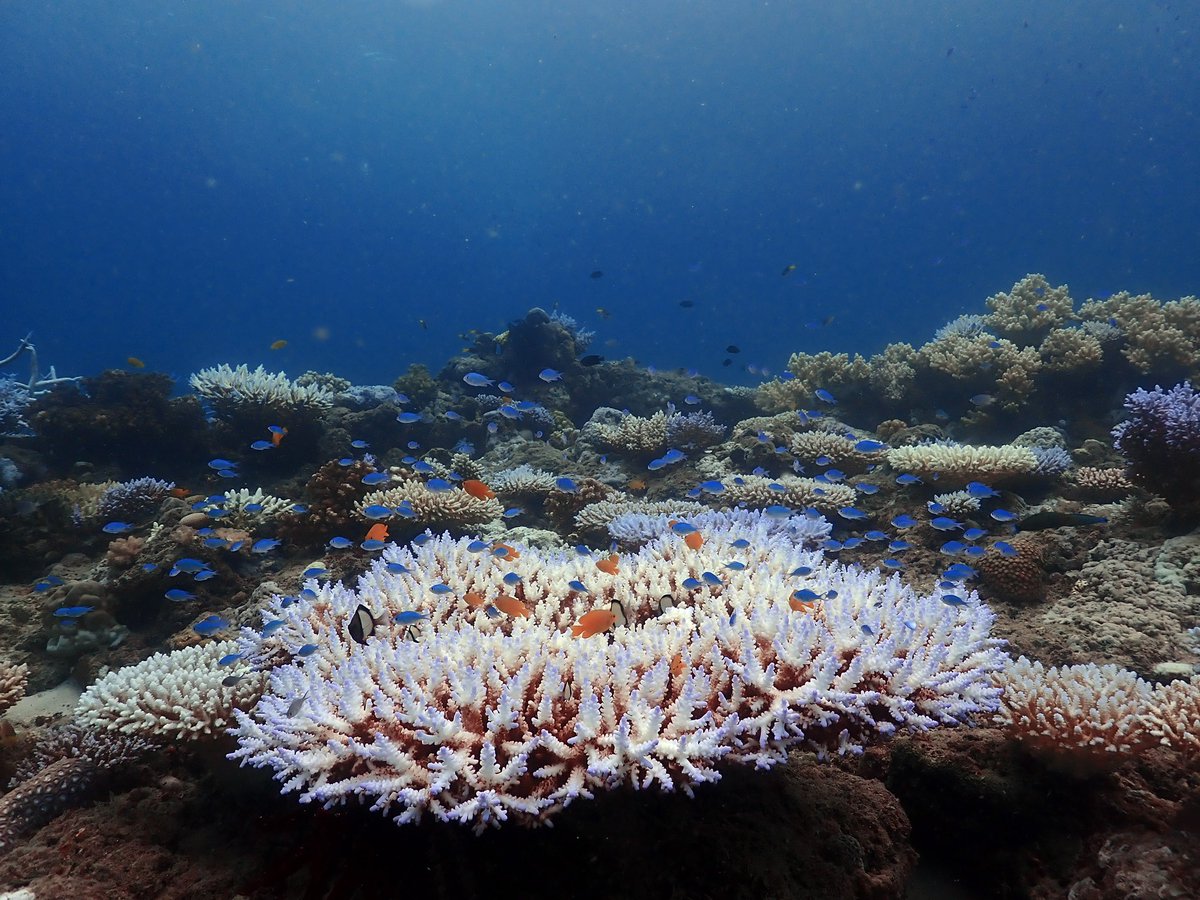
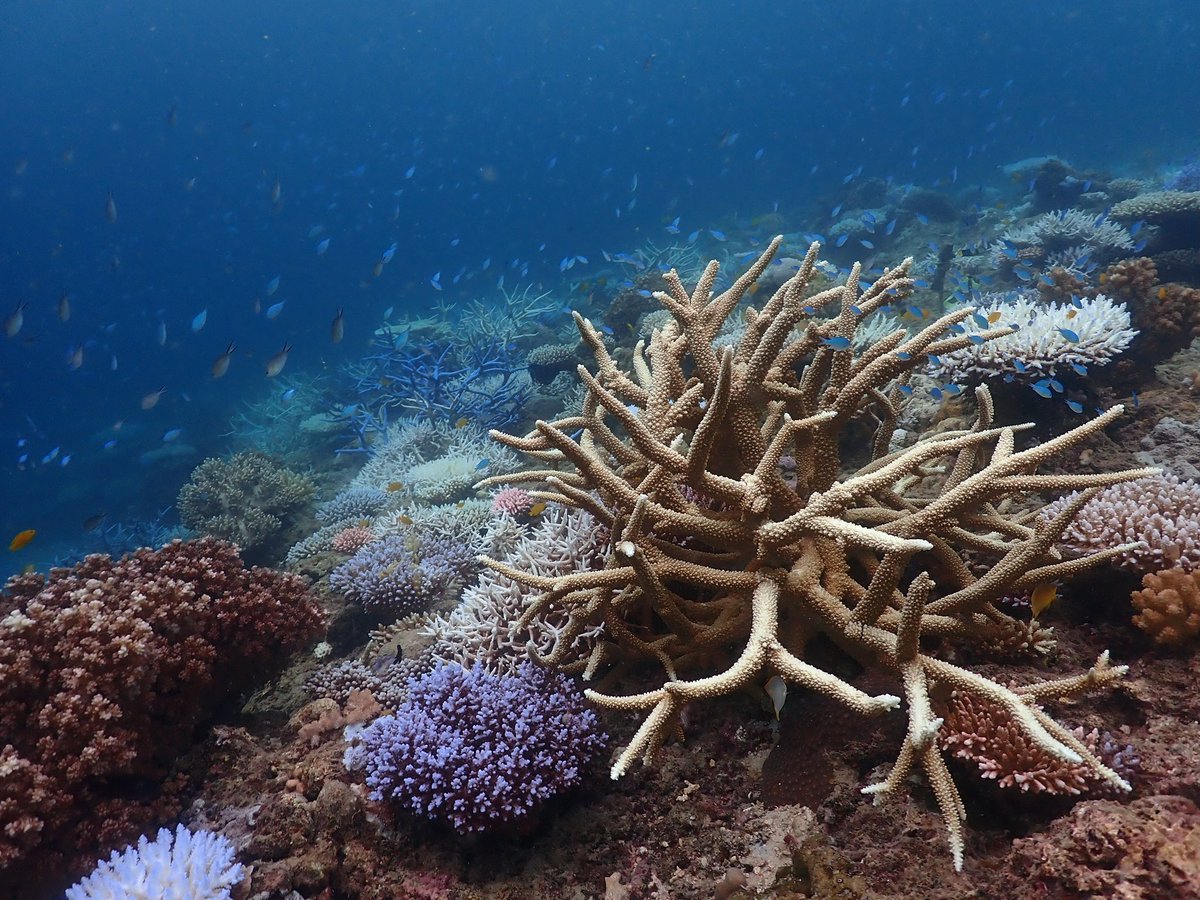
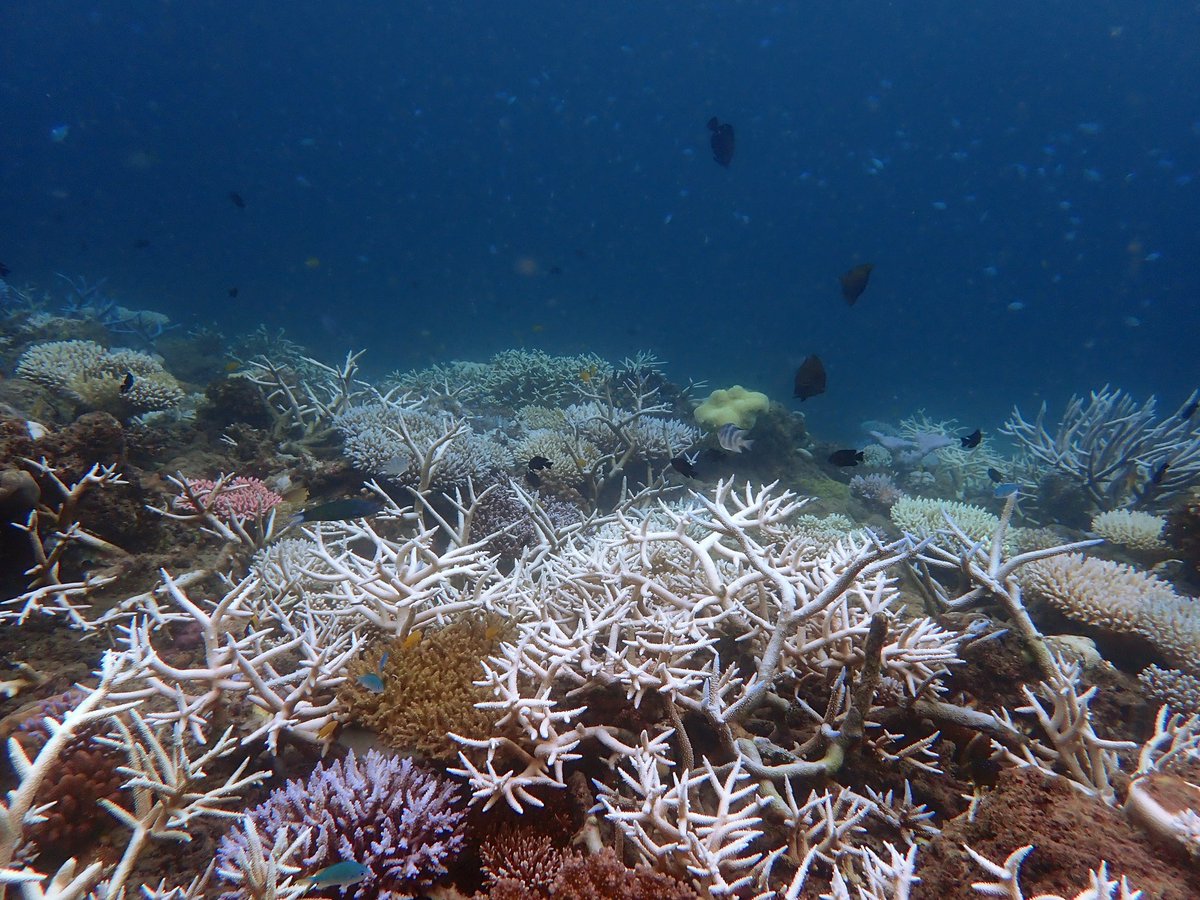
Extremely sad data coming from the great barrier reef in Australia. don't look up, don't look down . .
More underwater images of the mass bleaching unfolding in the northern GBR. Water temperatures appear to be dropping after prolonged heating of >5 DHW, but the coral bleaching at this reef is severe (>80% colonies), with exceptionally high rates of mortality in juvenile corals.
0
0
0
An excellent study on the @EuroBact2 database led by Niccolo Buetti - this was made possible by the 600+ investigators at 201 ICUs included in this paper - thank you very much for your contribution.
The role of centre and country factors on process and outcome indicators in critically ill patients with hospital-acquired bloodstream infections @yourICM @EuroBact2 @AlexisT @JF_Timsit @akovamurat @andymoz78 @criticcaredoc .
0
2
8
RT @AbdullahTarikA1: The role of centre and country factors on process and outcome indicators in critically ill patients with hospital-acqu….
link.springer.com
Intensive Care Medicine - The primary objective of this study was to evaluate the associations between centre/country-based factors and two important process and outcome indicators in patients with...
0
1
0
RT @CRE_RESPOND: You're invited to an exciting 3-day workshop on Antimicrobial Optimisation: Population pharmacokinetic modeling and dosing….
0
7
0