Laurence Howe
@laurencejmshowe
Followers
132
Following
112
Media
3
Statuses
39
Statistical genetics, epidemiology, views own.
Bristol, UK
Joined December 2019
Primary caveat is heterogeneity between in-vitro gene perturbations and heterozygous pLoF variants in-vivo but this is likely something that can be measured / harmonised with additional data in future.
1
0
0
Gene pLoF burden tests of disease are often underpowered because of the low frequency of pLoF variants. LoF-IV combines data across all genes highlighted in the perturbation screen so can have higher power (as in MR).
1
0
0
LoF-IV is an adaptation of Mendelian randomization with cellular 'exposures'. If higher abundance of a cell-type reduces disease risk and CRISPR-Cas9 perturbation of a gene increases cell-type abundance, then LoF of that gene should reduce disease risk in humans.
1
0
0
In-vitro assays are an important component of drug development but assessing assay-phenotype relevance is challenging. Here propose an instrumental variable framework LoF-IV using gene perturbation screen data (CRISPR-Cas9) and pLoF data from population biobanks.
Genetic instrumental variable framework for assessing relevance of in-vitro cellular phenotypes to organism-level phenotypes https://t.co/Db8kOc4Jts
#biorxiv_genetic
1
2
3
Whole genome sequencing of half-a-million UK biobank participants https://t.co/nWdSw42ShY
medrxiv.org
Whole-genome sequencing (WGS) provides a comprehensive view of the genome, enabling detection of coding and non-coding genetic variation, and surveying complex regions which are difficult to genoty...
2
23
73
Hot GWAS of self-reported alcohol flushing in ~15k East Asians. The proportion of the ALDH2 variant, rs671, was 45.5% in flushers vs 8.7% in non-flushers. https://t.co/UNjsRta3Ob
3
9
49
🚨 PUBLISHED TODAY @NatureGenet 📰 Within-sibship genome-wide association analyses decrease bias in estimates of direct genetic effects 🧑🏾🤝🧑🏼 Laurence J. Howe, Ben Brumpton, @explodecomputer , Neil M. Davies, and colleagues 👇🏼 https://t.co/UZBdpYakrx
nature.com
Nature Genetics - Within-sibship genome-wide association analyses using data from 178,076 siblings illustrate differences between population-based and within-sibship GWAS estimates for phenotypes...
0
42
119
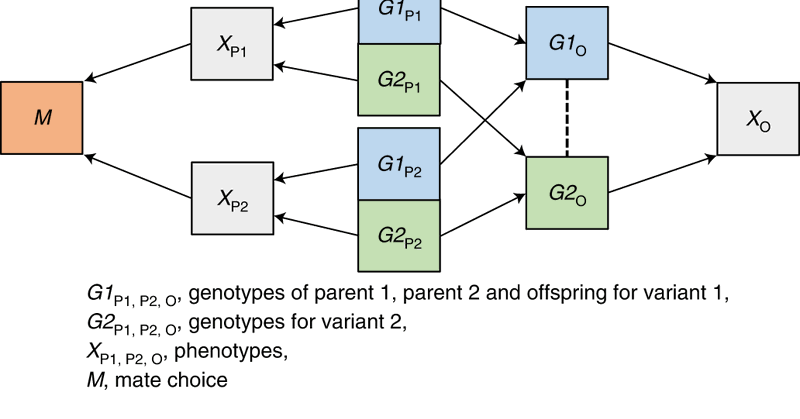
Within-sibship analyses are common in epidemiological studies. But is there a role for within-spouse pair comparisons? @laurencejmshowe Thomas Battram @bristimtom Fernando Hartwig @explodecomputer @nm_davies examine this here
journals.plos.org
Author summary There is growing evidence that genome-wide association studies capture associations relating to environmental factors, such as indirect effects from parental genotypes. Within-family...
0
5
16
How do spouses' sleep patterns interact? Using data on up to 175k spouse-pairs in UK Biobank and 23andMe, we investigated correlations between a number of self-reported and accelerometer-assessed sleep traits
Correlations in sleeping patterns and circadian preference between spouses https://t.co/USTHzKzRLk
#medRxiv
1
12
45
12. Feedback welcome and please do get in touch if interested in within-family projects. Early-stage consortium website: https://t.co/PLZGx8gJSL
3
1
5
12. This project was a massive collaborative effort. Thanks to many great co-authors and cohorts, including: @nm_davies @explodecomputer @bmbrumpton @michelnivard @carolinehaywar7 @mendel_random @evans1_d @bristimtom
1
1
4
11. However, conventional population GWAS designs remain the gold standard for “gene discovery” and prediction and are likely to be more useful in terms of power until more family data is available.
1
1
1
10. To adress the shortage of family data, we advocate that future population biobanks aim to ascertain more families. This will also allow estimation of indirect genetic effects, evaluation of assortative mating etc
1
1
5
9. These results illustrate the importance of within-family data for genetic epidemiology analyses of many social and behavioural phenotypes. In contrast, not many differences for more clinical phenotypes.
1
2
7
8. Following on from previous studies using UKB data, larger samples of siblings provided within-family evidence for polygenic adaptation on taller height. https://t.co/yeJf2sK1fM
1
1
2
7. We also observed differences when using within-sibship/population estimates in down-stream analyses (LDSC h2/ rg/ MR) such as lower h2 estimates and genetic correlations disappearing.
1
1
4
6. We found that within-sibship genetic association estimates were smaller for height, education, smoking, cognitive ability, depressive symptoms and age at first birth.
1
3
4
5. To enable comparisons, we generated within-sibship and “standard population model” GWAS estimates using the same individuals.
1
1
4
4. We conducted a within-sibship GWAS of ~160,000 individuals, including 17 cohorts and 25 phenotypes, to investigate which phenotypes are affected by these additional sources of association.
1
1
5