Angli Xue
@anglixue
Followers
242
Following
806
Media
12
Statuses
307
NHMRC Investigator Fellow/Postdoc at Garvan Institute with @drjosephpowell | PhD with @jyang1981 | #SingleCellOmics #StatisticalGenetics #ComplexTraits
Sydney, NSW, Australia
Joined May 2013
New preprint alert: https://t.co/RugxCYzlSH. Excited to share our analysis on the impact of genetic variants on single-cell chromatin accessibility in blood, using scATAC-seq and WGS from over 1,000 donors and 3.5M nuclei as part of TenK10K phase 1 🧬 🧵👇 (1/n)
medrxiv.org
Understanding how genetic variation influences gene regulation at the single-cell level is crucial for elucidating the mechanisms underlying complex diseases. However, limited large-scale single-cell...
2
34
86
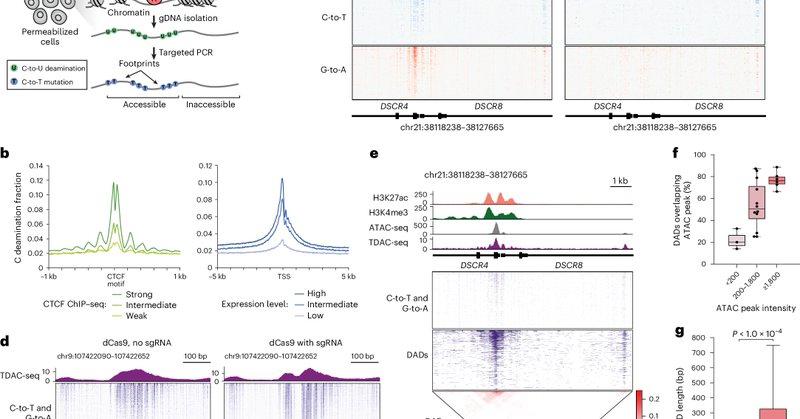
TDAC-seq is a method for targeted chromatin accessibility profiling that uses cytidine deaminases and long-read sequencing to resolve the effects of CRISPR edits on single chromatin fibers. @brian_b_liau @heejin_roh @sshen8 @YanHu41082612
https://t.co/KxVbE6iPnx
nature.com
Nature Methods - This paper presents TDAC-seq, a targeted chromatin-accessibility-profiling method using cytidine deaminases and long-read sequencing, to resolve the effects of CRISPR edits on...
1
5
21
This TenK10K study offers the most comprehensive single-cell chromatin accessibility QTL (caQTL) resource to date 👉3.5M PBMCs from 1,042 donors 👉243,273 caQTLs for 28 immune cell types 👉60% of them cell-specific 👉10-30% more colocalized signals for disease traits than eQTLs
1
20
81
1. 🚨New preprint: https://t.co/LFazdldaPY. We explored causal effects of gene expression in immune cell types on complex traits and diseases by combining single-cell expression quantitative trait loci (sc-eQTL) mapping in 5M+ cells from 1,925 donors in TenK10K study and GWAS. 🧵
medrxiv.org
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have been instrumental in uncovering the genetic basis of complex traits. When integrated with expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) mapping, they can...
2
28
90
There are a lot of more interesting findings in this study. For more detail check out the preprint at https://t.co/r89zLFx8xg, and feel free to DM me or drop me an email at a.xue[AT] https://t.co/DjCUe7B3qO if any questions. (15/n)
medrxiv.org
Understanding how genetic variation influences gene regulation at the single-cell level is crucial for elucidating the mechanisms underlying complex diseases. However, limited large-scale single-cell...
0
0
0
You are more than welcome to explore other TenK10K studies for different topics and biological questions: https://t.co/gOHlg4ubU0 led by @AnnaSECuomo
https://t.co/JTFCPPHr8P led by @htanudisastro
https://t.co/1Hy0JtST36 led by @AH_AlbertHenry & @senabouth (14/n)
1
1
2
and a special shout out to the core contributors to the TenK10K cohort, Rachael McCloy, @chin_venessa, @katiedelange, @gemtreee, @AlexWHewitt, @dgmacarthur, @drjosephpowell (13/n)
1
0
0
A big thanks to all co-authors, especially my supervisor @drjosephpowell, & TenK10K team @jianan114476, Oscar Dong, @HaoLHuang, @PeterAllen225, Ellie Spenceley, Eszter Sagi-Zsigmond, Blake Bowen, @AnnaSECuomo @AH_AlbertHenry, @htanudisastro, @zhenqiao_zz and many others! (12/n)
1
0
1
.. using paired multiome data without QTL information. This improvement further enhanced gene regulatory network inference, leading to the identification of 128 additional transcription factor (TF)–target gene pairs (a 22% increase), some of which show druggable potential. (11/n)
1
0
0
scATAC-seq and caQTL signals also boost the gene regulatory network inference, especially when using unpaired multiome data. We inferred peak-to-gene relationships from unpaired multiome data by incorporating caQTL and eQTL, achieving up to 80% higher accuracy compared to (10/n)
1
0
0
The genetic impact on chromatin accessibility not only shows cell type-specific patterns but also varies across cell states. We further detected 3,080 caQTLs whose allelic effects showed significant interaction with epi-genetic age. (9/n)
1
0
0
Integrating caQTLs with GWAS+eQTL improves fine-mapping of causal variants. We identified 671 credible sets for inflammatory bowel disease, 428 of which are single-variant sets, and replicated a causal variant for ETS2 in monocytes recently reported in Stankey et al. 2024. (8/n)
1
0
0
Next we ask why do GWAS hits often miss eQTLs? We integrated 60 GWAS from disease and blood traits with eQTLs and caQTLs and found caQTL integration yields 9.8–30% more colocalizations than eQTLs alone, particularly at distal elements or loci with multiple causal variants. (7/n)
1
0
0
We highlight an interesting example where a chromatin peak chr10:45592479-45592785 shows a negative effect on the gene expression level of MARCH8 in NK cells but a positive effect in Conventional Dendritic Cell 2 (cDC2). (6/n)
1
0
0
Integrating caQTL results with eQTLs from scRNA-seq of 1,925 donors and 5.4M cells revealed over 70,000 colocalized signals, including 25,280 candidate cis-regulatory elements (cCREs) further supported by causal inference using Mendelian randomization (MR). (5/n)
1
0
0
More than half of caQTLs show cell type–specific patterns. For example, the chromatin peak chr13:24670806–24672096 contains caQTLs in CD4 TCM and CD14 monocytes, and their top variants (13:24671328:T:C in CD4 TCM and 13:24570579:C:A in CD14 Mono) are independent (LD ≈ 0). (4/n)
1
0
1
We curated one of the largest population-level (n = 1,042) scATAC-seq data from peripheral blood with WGS data, which enabled us to characterize 440,996 chromatin peaks across 28 immune cell types and mapped 243,273 caQTLs. (3/n)
1
0
2
Chromatin accessibility QTLs (caQTLs) capture the direct impact of non-coding variants on elements like enhancer and promoter, yet existing maps lack scale and diversity. We presents a significant cell type–resolved caQTL resource and demonstrates its translational utility. (2/n)
1
0
1
Excited to share that scPRS is now out @NatureBiotech! We developed a new single-cell-resolved #PRS using deep learning. https://t.co/6aX1QLzyDq
nature.com
Nature Biotechnology - A graph neural network framework enables individualized genetic risk prediction at the single-cell level.
6
37
160