Mikhail Genkin
@MGENK
Followers
89
Following
48
Media
11
Statuses
39
Computational Neuroscientist at Cold Spring Harbor Lab
Joined July 2012
Exited to share our study where we find that encoding principles of cognitive variables are similar to those of sensory variables.
biorxiv.org
The brain represents sensory variables in the coordinated activity of neural populations, in which tuning curves of single neurons define the geometry of the population code. Whether the same coding...
Cognitive processes are elusive: each decision takes a unique path observed only in spikes of heterogeneous neurons. In a new preprint, we trace decisions spike-by-spike to uncover the dynamics and geometry of the neural population code for choice. https://t.co/piIAbYTzCZ
0
3
26
“Like a group of skiers descending a mountain, each [neuron] prefers a slightly different path, but all are shaped by the same slope,” says @Princeton’s @EngelTatiana on her lab’s new @Nature study of how the brain makes decisions. 📰: https://t.co/INO7lzuFav
0
6
16
Out today in @Nature: we show that individual neurons have diverse tuning to a decision variable computed by the entire population, revealing a unifying geometric principle for the encoding of sensory and dynamic cognitive variables. https://t.co/sqNl4v8CgR
7
93
387
A unifying perspective on neural manifolds and circuits for cognition — a Perspective by Christopher Langdon, Mikhail Genkin & Tatiana A. Engel @chrismlangdon @MGENK @EngelTatiana
https://t.co/bpoWdL1xxY
0
3
8
What approach can explain the link between the brain and behavior? Shall we focus on neural circuits or manifolds? With @chrismlangdon & @MGENK, we provide a unifying perspective on manifolds and circuits, just out in @NatRevNeurosci: https://t.co/sM4xKUEZ6o.
#tweeprint 👇
2
120
333
ChatGPT is sometimes amazing, and sometimes hilariously wrong. Here, it confidently explains to me why an abacus is faster than a GPU. 😃
194
700
5K
In decision-making tasks excitatory and inhibitory neurons show selectively for an upcoming choice. @EngelTatiana, @anne_churchland, and I explore the effects of inhibitory choice selectivity in decision making circuits using mean-field and RNN models.
biorxiv.org
During perceptual decision-making, the firing rates of cortical neurons reflect upcoming choices. Recent work showed that excitatory and inhibitory neurons are equally selective for choice. However,...
2
17
60
Excited to share our bioRxiv preprint with @EngelTatiana. Cortical neurons show mixed selectivity for multiple task variables. We develop a latent circuit model for inferring interpretable circuit mechanisms from heterogeneous neural responses. https://t.co/KivuC5bOnq
biorxiv.org
Higher cortical areas carry a wide range of sensory, cognitive, and motor signals supporting complex goal-directed behavior. These signals are mixed in heterogeneous responses of single neurons tuned...
1
11
38
What advantages can neuro-inspired ANN architectures have for motor control / robotics? We translate C. elegans locomotion circuits into an ANN model controlling a simulated Swimmer agent. https://t.co/QxeQrMcXJE
https://t.co/Emi1IUvYyd w/ @TonyZador, @EngelTatiana
2
35
115
Out today in @NatureComms the work led by @YanliangShi. We show that cortical state dynamics and selective attention define the spatial pattern of noise correlations. Many thanks to @SteinmetzNeuro, Tirin Moore, and @boahen_k for the great collaboration. https://t.co/Syqjknl9QF
0
14
96
Excited to see this work with @MGENK and @owenkhughes out in @NatureComms today. The paper is open access: https://t.co/rkcEDMfmaB The code + tutorials are available on GitHub:
github.com
The framework for inferring Langevin dynamics from spike data - GitHub - engellab/neuralflow: The framework for inferring Langevin dynamics from spike data
New work with @MGENK and @owenkhughes: Learning non-stationary Langevin dynamics from stochastic observations of latent trajectories. Inference of non-stationary latent dynamics from spikes, applied to models of decision-related neural activity. https://t.co/o4gvMM6ait
1
10
20
Our study on learning Langevin dynamics from noisy observations of non-stationary systems is published in Nat Commun. Our method infers the dynamics underlying decision-making from spiking activity. Paper: https://t.co/DBGsoxWZX0. Python package: https://t.co/jGVbRfzpwB
0
2
29
Tomorrow, Sep. 24, 11am - 2 pm at @CogCompNeuro, @EngelTatiana will talk about flexible computational framework for modeling neural population dynamics during decision-making, and I will give a tutorial on our python package neuralflow: https://t.co/9meBFisiTG.
github.com
The framework for inferring Langevin dynamics from spike data - GitHub - engellab/neuralflow: The framework for inferring Langevin dynamics from spike data
0
2
11
Join us tomorrow Sep 24 11am-2pm ET for the virtual @CogCompNeuro Keynote & Tutorial. I will talk about flexible models of neural population dynamics and decision making, and @MGENK will give a tutorial on our software package https://t.co/29v63GnuWZ.
https://t.co/rKlsdBWKeB
1
5
29
After the rough year of separation and isolation, everyone was looking forward to traveling to see our families. All Russians working in the US on a visa cannot do it. If they leave the US, they won’t be able to come back. Our parents cannot come either. No visas = more isolation
Students who started their studies in the US have to interrupt or abandon the pursuit of their degree. This restriction is perhaps the most disruptive to the lives of ppl with selected ethnicity ever since the Muslim travel ban by the Trump administration.
0
2
7
Today I will be talking about the flexible identification of decision-making dynamics from heterogeneous neural responses. Check out my talk at 2:20 pm. @CosyneMeeting.
0
1
5
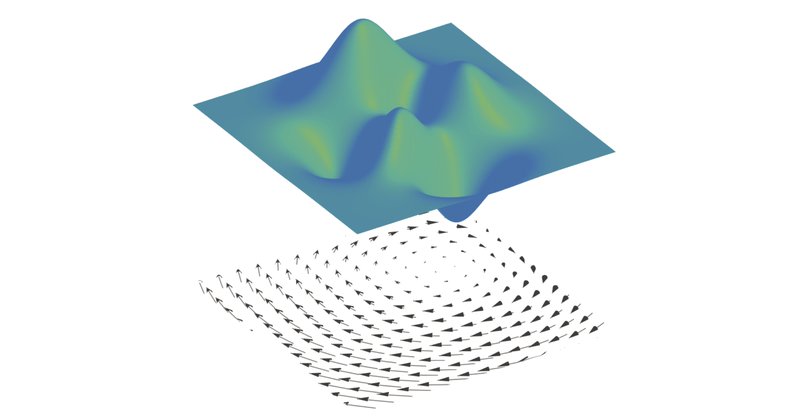
We test our framework using two models of decision-related neural activity, with stepping and ramping dynamics. Our framework accurately infers the force potential for Langevin dynamics, noise magnitude, and the initial state distribution from realistic amounts of spike data.
0
0
0
We present a framework for learning non-stationary Langevin dynamics from stochastic observations. Our framework accounts for the non-equilibrium initial and final states of the system and for the possibility that the system's dynamics can control the duration of observations.
1
0
0
Non-stationary dynamics play a key role in systems that perform computations, e.g., transient neural dynamics underlie decision-making in the brain. Inferring a Langevin equation for such systems is challenging when data contains observation noise, such as neural spiking.
1
0
2
Excited to share our arXiv preprint with @owenkhughes and @EngelTatiana. We develop a framework for inferring non-stationary Langevin dynamics from stochastic observations and test it on spike data generated from decision-making models. Link: https://t.co/N7yaZCM2Gs
1
3
15