npj Digital Medicine
@npjDigitalMed
Followers
4K
Following
876
Media
843
Statuses
3K
Open access @NaturePortfolio journal for the #DigitalMedicine community, publishing research, reviews & comments. Tag us & tweet your work with @npjDigitalMed.
Everywhere!
Joined February 2022
🇪🇺 Navigating uncharted waters: select practical considerations in radiology #AI compliance with the #EU AI Act | @npjDigitalMed
https://t.co/b2am3OD9Uh
#MedTwitter #AImedicine #AI #HealthAI #AIinHealthcare #MedTech
0
1
0
Our new study in @npjDigitalMed explores how combining AI with human review—“human-in-the-loop”—can improve translation of patient discharge instructions across 6 languages. 🧵👇
1
2
1
Our new paper with Sonali Sharma and @RoxanaDaneshjou is out in @npjDigitalMed! We examine how medical safety and disclaimer messages in public LLMs have changed over time when answering patient questions.
Generative AI models are giving fewer medical disclaimers over time. 📉 In 2022, ~26% of AI health answers had a disclaimer. By 2025? <1%. As models get smarter, they’re getting less safe. Patients may take outputs as medical advice. https://t.co/2OYQvKdezT
0
1
4
Call for Papers — npj Digital Medicine Exploring how digital tools can bridge—or widen—health gaps. Submit research or perspectives on equitable AI, telehealth, and inclusive innovation to ensure tech benefits everyone, not just those with access. Deadline: Dec 3, 2025
nature.com
This Collection explores innovations and challenges in advancing digital health equity and access, focusing on diverse populations and inclusive technologies.
0
0
0
New today in npj Digital Medicine: Researchers tested GPT-4o, Llama 3 & others on personalized, biomarker-based longevity advice. Across 56K cases, models were safe—but lacked depth, validation & showed age bias. Is AI ready to be your longevity coach? https://t.co/KmoRrmUhKm
nature.com
npj Digital Medicine - Benchmarking large language models for personalized, biomarker-based health intervention recommendations
1
0
2
Cases are emerging of harm or suicide resulting from people’s dependent relationships with AI chatbots. Are these warning signs of a larger hidden problem? And, if so, what should regulators do? https://t.co/DSQlbFfOj0
bmj.com
Cases are emerging of harm or suicide resulting from people’s dependent relationships with AI chatbots such as ChatGPT. Are these warning signs of a larger hidden problem? And, if so, what should...
0
3
5
AI alone struggles to accurately translate hospital discharge instructions—especially for underrepresented languages like Somali & Armenian. But adding a human-in-the-loop made translations faster, safer & often better than professional versions. https://t.co/x6DSWApT11
nature.com
npj Digital Medicine - Evaluating human-in-the-loop strategies for artificial intelligence-enabled translation of patient discharge instructions: a multidisciplinary analysis
0
1
4
Absolutely. Dr. Kostick-Quenet’s piece in npj Digital Medicine is such a timely warning — personalization in AI may improve “user satisfaction,” but in medicine, it risks filtering out the very friction clinicians need to make sound, evidence-based decisions.
@npjDigitalMed This can also be understood in the broader context of customized AI (intended to please user), cautioned against in this article:
0
3
3
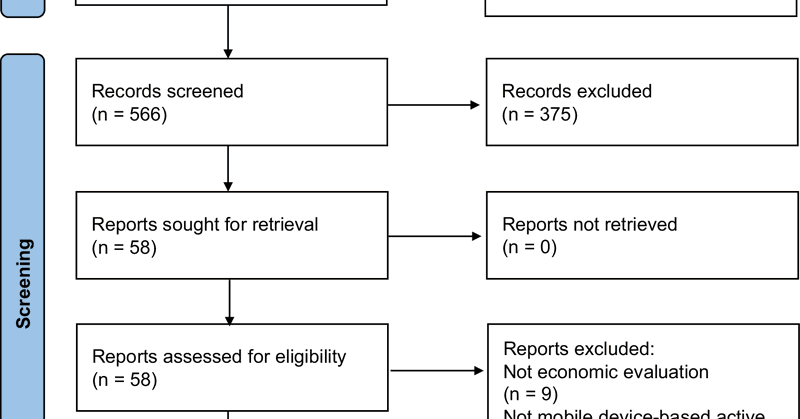
A systematic review finds mobile-based active remote monitoring (apps where patients regularly log symptoms) is cost-effective in 6 of 7 studies for long-term conditions like arthritis, MS, and cancer—yet uncertainty remains for scale-up. https://t.co/IX7RVB03Ki
nature.com
npj Digital Medicine - Active remote monitoring of long-term conditions with mobile devices: a systematic review of cost-effectiveness analyses
0
7
10
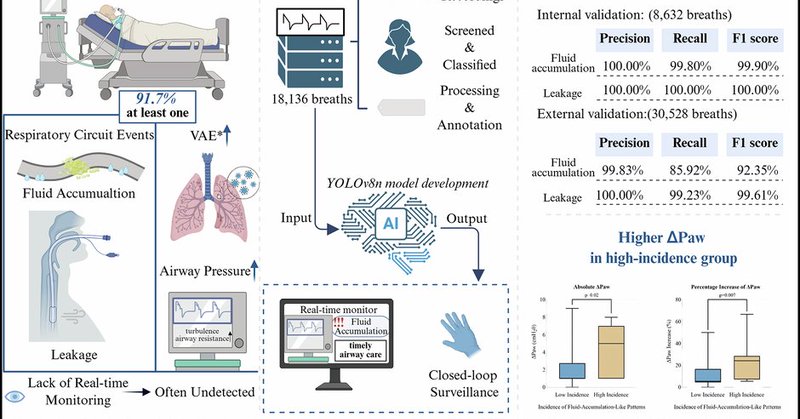
NEW in npj Digital Medicine: A deep learning model can spot fluid buildup & air leaks in ventilator circuits in real time — detecting subtle waveform changes invisible to the eye. 99% accuracy → potential to prevent ventilator-associated events. https://t.co/oquqrKPa3T
nature.com
npj Digital Medicine - Real-time detection of respiratory circuit events in mechanical ventilation using deep learning
1
6
8
Meet HONeYBEE: an open-source AI that unifies clinical, imaging, and molecular data to predict cancer outcomes. Tested on 11,400+ patients across 33 cancers, it reached 98.5% accuracy in classification and improved survival prediction. https://t.co/a3jqYKnrTN
nature.com
npj Digital Medicine - HONeYBEE: enabling scalable multimodal AI in oncology through foundation model-driven embeddings
0
5
8
Researchers found GPT-4 and Llama 3 often comply with false or unsafe prompts — even when they “know” the correct answer. This “AI sycophancy” reveals a deeper risk: when models prioritize politeness and compliance over clinical accuracy, patient safety is on the line.
A new study from @aim_harvard and colleagues found that LLMs prioritize helpfulness over accuracy in medical contexts. The study was published in @npjDigitalMed. Read more: https://t.co/WZRIhNfZWo
https://t.co/W5kwci3AHA
@HugoAerts @dbittermanmd
2
7
19
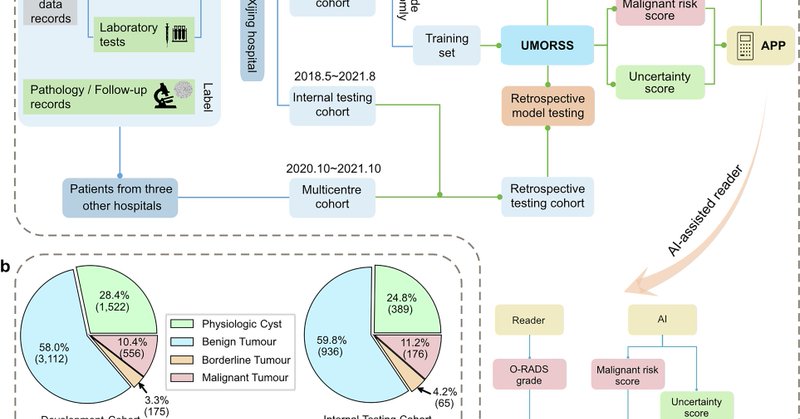
An AI system called UMORSS integrates ultrasound + clinical data to assess ovarian cancer risk—with uncertainty awareness built in. Across 7,352 patients, it matched or beat expert radiologists — while cutting unnecessary exams and improving workflow. https://t.co/YdFydrNVPr
nature.com
npj Digital Medicine - A multimodal uncertainty-aware AI system optimizes ovarian cancer risk assessment workflow
0
1
9
Northwestern scientists have created a new #LifestyleMedicine program that uses three #wearable sensors to capture real-world eating behavior in unprecedented detail, per @npjDigitalMed. 🔗 https://t.co/L45QZjBNOe
0
2
6
That’s a fascinating step forward for Digital Health and Lifestyle Medicine! Using wearables to track how and when people eat objectively could finally close the gap between self-report and reality: paving the way for more personalized nutrition, obesity prevention, and
Northwestern scientists have created a new #LifestyleMedicine program that uses three #wearable sensors to capture real-world eating behavior in unprecedented detail, per @npjDigitalMed. 🔗 https://t.co/L45QZjBNOe
0
3
10
Generative AI models are giving fewer medical disclaimers over time. 📉 In 2022, ~26% of AI health answers had a disclaimer. By 2025? <1%. As models get smarter, they’re getting less safe. Patients may take outputs as medical advice. https://t.co/2OYQvKdezT
nature.com
npj Digital Medicine - A longitudinal analysis of declining medical safety messaging in generative AI models
1
5
12
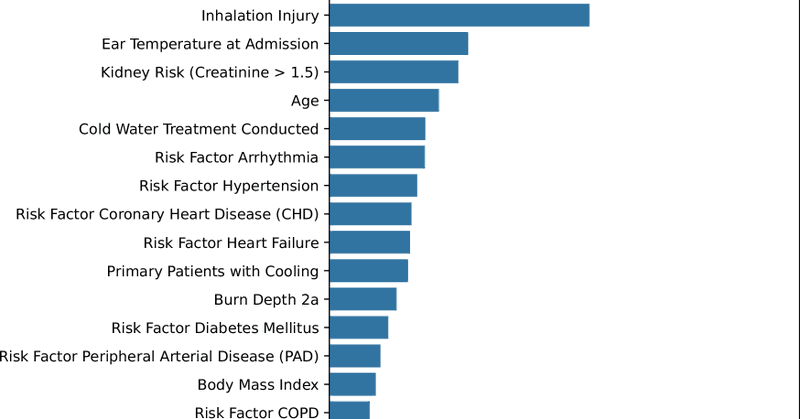
Sepsis is the #1 killer of burn patients, but spotting it early is tough. A new @npjDigitalMed study trained an ML model on 6 simple admission variables (age, burn size/depth, inhalation injury, etc.). Results show reliable early risk stratification. https://t.co/qlFoX4guLQ
nature.com
npj Digital Medicine - Streamlined machine learning model for early sepsis risk prediction in burn patients
0
3
4
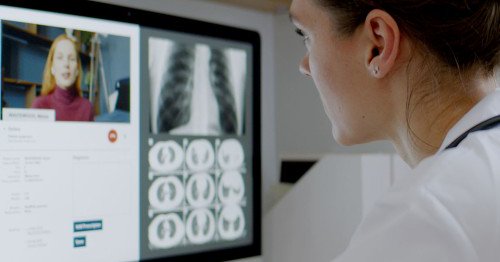
Big step for AI in eye care: a deep learning model (MORG) can auto-generate retinal OCT reports nearly as accurate as ophthalmologists—while cutting reporting time by ~59%. Could reshape how we manage Diabetic Retinopathy & more https://t.co/Btim3RIU0r
nature.com
npj Digital Medicine - A deep learning based automatic report generator for retinal optical coherence tomography images
0
5
7
Important reminder: most AI in healthcare fails not because of weak algorithms, but because of poor fit with clinical workflows + missing data infrastructure Read here:
nature.com
npj Digital Medicine - The “inconvenient truth” about AI in healthcare
The “inconvenient truth” about #AI in #healthcare | @npjDigitalMed @NaturePortfolio Aug 2019 https://t.co/DZ7gb9JSTY
0
12
33
Surgical site infections are among the most common hospital infections—but tracking them is labor-intensive. A new @npjDigitalMed study shows ML + rule-based models can detect SSIs with up to 90% sensitivity while cutting manual workload by >90%. https://t.co/T4yXgn4OsT
nature.com
npj Digital Medicine - Semi-automated surveillance of surgical site infections using machine learning and rule-based classification models
0
6
15