CalvoLab
@calvo_lab
Followers
960
Following
3K
Media
81
Statuses
1K
Tumour Microenvironment lab at IBBTEC, Santander (Spain) led by Dr Fernando Calvo.
Santander, Spain
Joined November 2018
This past Friday we had the annual meeting of our @ContraCancerEs Project in Santander (@IBBTEC, @unican). Great discussions and so glad to see the project developing @CejalvoM, #AngelNebreda @IRBBarcelona, @IBBTEC_Varela.
0
4
11
Se realizará en el @IBBTEC en Santander (España), con dentro del programa de doctorado de @unican y con la infraestructura del @CSIC. Estamos financiados por @ERC_Research, @ContraCancerEs, AgEInves. Se agradece difusión.
0
0
0
ALERTA EMPLEO!! Ofrecemos un contrato predoctoral para realizar la tesis doctoral en el estudio de la heterogeneidad funcional de los fibroblastos asociados a cáncer (CAFs) y su papel en resistencia terapéutica en cáncer de vejiga, asociado al proyecto (PID2024-157801OB-I00). 👇
1
35
31
Amazing master lecture by Ángel Carracedo @GMXenomica today at @IBBTEC on cllinical genomics. Learned a lot
0
3
13
Postdoctoral Fellow in Tumour Microenvironment and cancer-associated fibroblast studies | EURAXESS
0
2
7
We are recruiting! We're searching for a postdoctoral research fellow to study patient-specific regulators of plasticity in primary and metastatic CRC. Please reach out if you have any questions! https://t.co/qj5v4u5Muq
0
10
20
We are based @IBBTEC in Santander, Spain. We are part of @unican and @CSIC. We are funded through @ERC_Research @ContraCancerEs @AgEInves. We will support the scientific and professional development of the researcher that fills the position.
1
0
1
We have developed a model to investigate this process in detail and generated intriguing and exciting data that we aim to exploit in coming months. We have additional resources (clinical data, bioinformatics, molecular characterization) snd collaborations in place.
1
0
0
This is an exciting project at the interphase of cancer biology and bioengineering, employing organ-on-chip approaches to describe how CAFs influence abnormal vascularization and drug perfusion in cancer.
1
0
0
JOB ALERT!!We are offering a postdoc position within our “antiCAFing” ERC-CoG project to investigate the interplay CAFs:endothelial cells and its impact in aberrant vascularization in tumors. More details below. Please spread the word.
1
20
27
Thanks to all the authors, funding agencies (@ContraCancerEs, @ERC_Research, @AgEInves) and institutions (@unican, @CSICdivulga, @IBBTEC, @HUnivValdecilla) that support our work. Hope you enjoy it! 11/11 END!
0
0
2
Additionally, our findings establish a mechanistic link between proteostasis and mechanotransduction via the HSP90α-YAP axis and its impact in cancer development, with potential relevance in other contexts where YAP activity is implicated. 10/11
1
0
0
Notably, this regulation is particularly relevant in mechanically stressed environments like CAFs, where mechanotransduction dominates over Hippo-dependent control. 8/11
1
0
0
While previous studies linked HSP90 to heat-shock-induced YAP activation via the Hippo pathway (Luo, Nat Cell Biol 2020), our findings describe a distinct mechanism that operates under normal temperature conditions, emphasizing a direct interaction between HSP90α and YAP. 7/11
1
0
0
This mechanism was validated in non-tumoral contexts employing emergent vasculogenesis models in microfluidic devices, underscoring the broader relevance of the HSP90α-YAP axis beyond CAFs. 6/11
1
0
0
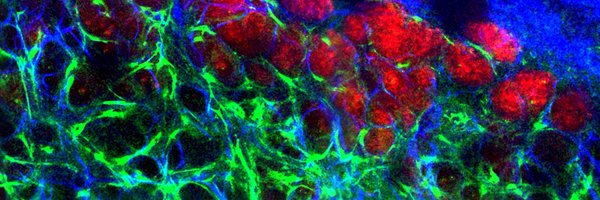
We identify the mechanotransducer YAP as a key effector of HSP90α. YAP is activated in CAFs through mechanotransduction, playing a critical role in CAF function. e show that HSP90α depletion compromises YAP stability, and that YAP is the main mediator of HSP90α functions in CAFs.
1
0
0
Our findings reveal a crucial role for the master chaperone HSP90α in shaping CAF functionality, influencing extracellular matrix (ECM) remodelling, tumour growth, and dissemination in experimental breast cancer models. 4/11
1
0
0
This is exciting because the pro-tumorigenic function of HSP90 and proteostasis mechanisms has not been considered outside the cell autonomous context of cancer cells. 3/11
1
0
0