Nature Materials
@NatureMaterials
Followers
55K
Following
340
Media
1K
Statuses
5K
Cutting-edge research in materials science, and at the interface with physics, chemistry, biology and medicine. Editorially independent. Tweets sent by editors.
London, NYC, Shanghai & Berlin
Joined February 2009
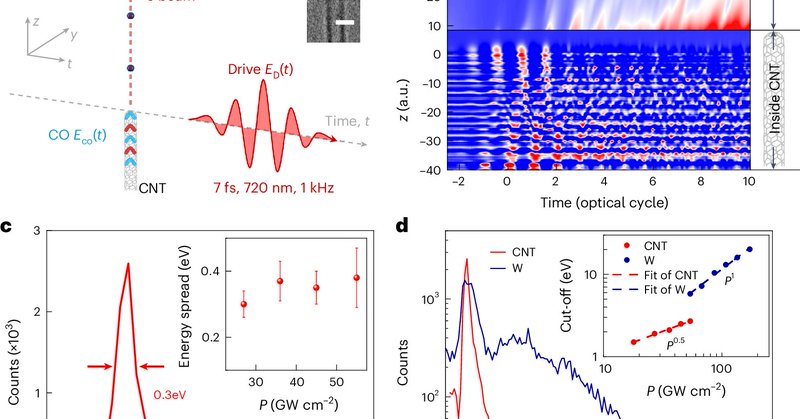
Metal-tip-based electron sources are constrained by a trade-off between energy spread and pulse width. Here the authors report a carbon-nanotube-based electron source with a 0.3-eV energy spread and an electron pulse width of about 13 fs.
nature.com
Nature Materials - Metal-tip-based electron sources are constrained by a trade-off between energy spread and pulse width. Here the authors report a carbon-nanotube-based electron source with a...
0
9
27
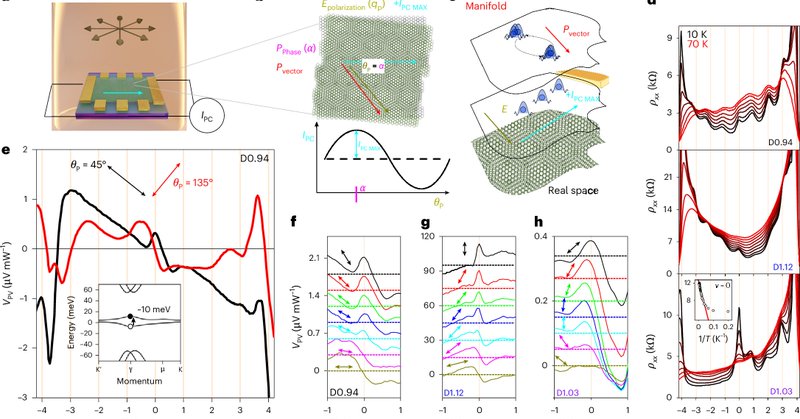
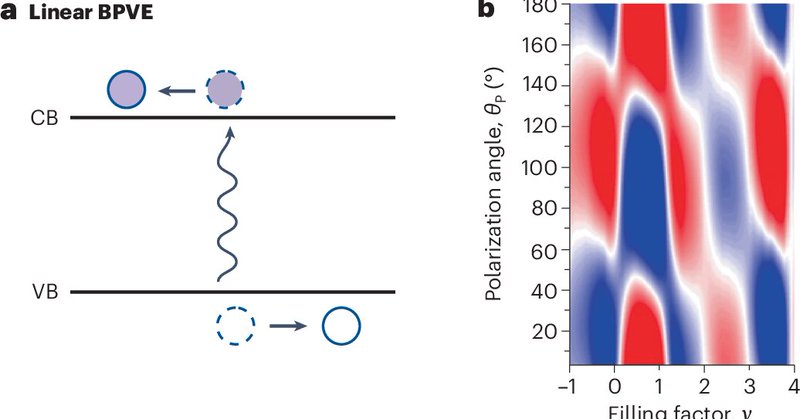
Related paper: Terahertz photocurrent probe of quantum geometry and interactions in magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene.
nature.com
Nature Materials - Exploiting the intrinsic response of magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene to resonant terahertz radiation, the interplay between electron interactions and quantum geometry is...
0
1
2
News & Views: Shedding light on quantum geometry.
nature.com
Nature Materials - Measuring the bulk photovoltaic effect in twisted bilayer graphene provides a fascinating way to probe the quantum geometry shaped by interactions.
1
3
23
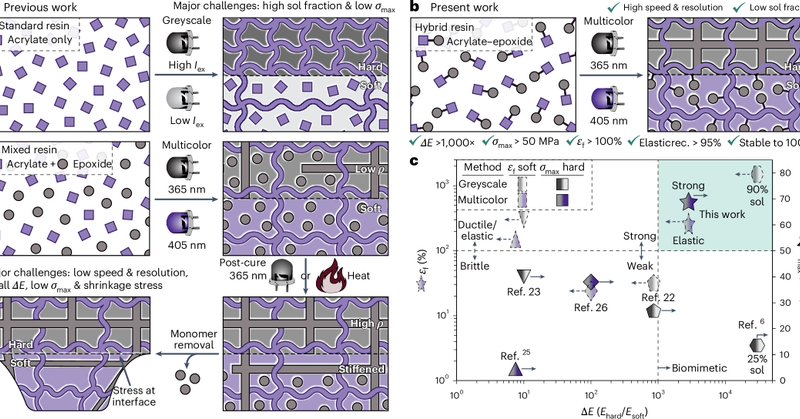
A hybrid epoxy–acrylate resin is reported for the digital light processing 3D printing of bioinspired metamaterial structures with precisely patterned hard and soft domains. @ZPageGroup .
nature.com
Nature Materials - A hybrid epoxy–acrylate resin is reported for the digital light processing 3D printing of bioinspired metamaterial structures with precisely patterned hard and soft domains.
0
11
28
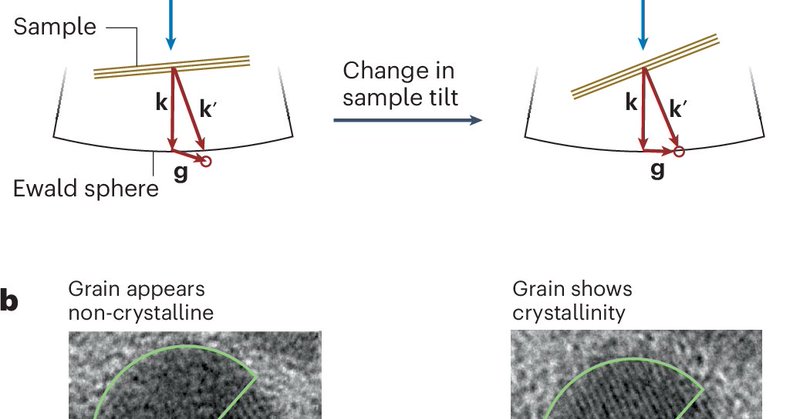
Comment: Identification of the glassy state in nanoparticles by transmission electron microscopy.
nature.com
Nature Materials - Identification of amorphous phases in nanoparticles by atomic-resolution transmission electron microscopy (TEM) requires analyses such as tilt-angle-dependent TEM imaging and...
0
7
29
Editorial: A Hall lot of effects.
nature.com
Nature Materials - The Hall effect has been a powerful probe of the physics of materials for more than a century.
0
3
16
Cell migration in confined environments is initiated by a cytoplasmic pool of anillin and Ect2 that promotes RhoA/myosin II-mediated activation at the poles of migrating cells, in a process dependent on the extracellular environment stiffness.
nature.com
Nature Materials - Cell migration in confined environments is initiated by a cytoplasmic pool of anillin and Ect2 that promotes RhoA/myosin II-mediated activation at the poles of migrating cells,...
1
4
13
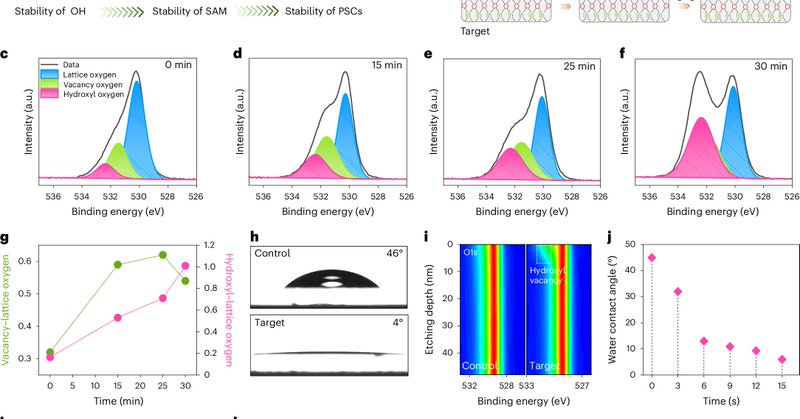
Formation of a stable self-assembled monolayer for high-efficiency perovskite solar cells remains a challenge. Here uniform and stable SAM anchoring is achieved on a hydroxylated ITO surface, leading to highly efficient stable perovskite solar cells.
nature.com
Nature Materials - Formation of a stable self-assembled monolayer for high-efficiency perovskite solar cells remains a challenge. Here uniform and stable SAM anchoring is achieved on a hydroxylated...
1
2
30
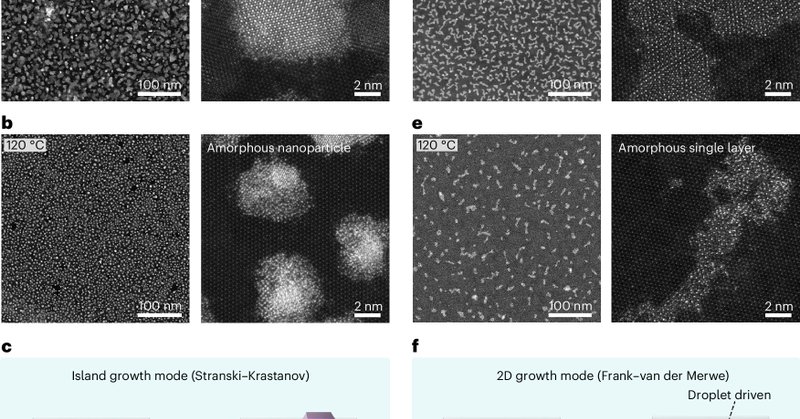
Here a droplet-driven nanoribbon-to-film growth strategy is reported to achieve amorphous metal chalcogenides at the single-layer limit.
nature.com
Nature Materials - The synthesis of atom-thin amorphous films remains challenging as their thermodynamically favourable grains are neither two dimensional nor layered. Here a droplet-driven...
0
6
24
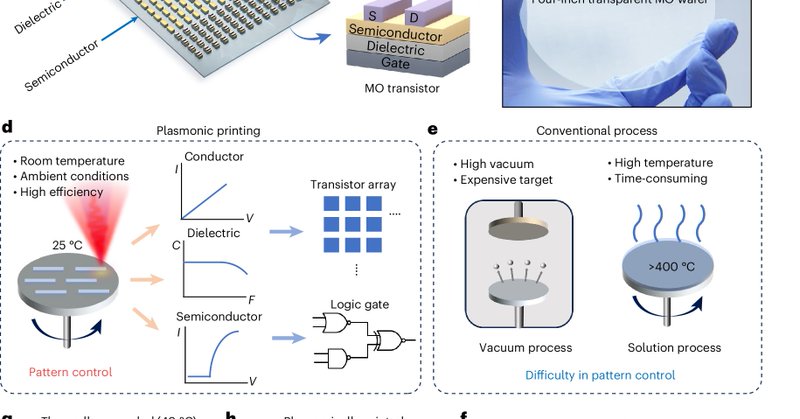
A universal, high-resolution printing technology for metal oxide thin-film transistors is lacking. A plasmonic printing technology fabricates solution-processed all-metal oxide thin-film electronics under room temperature and ambient conditions.
nature.com
Nature Materials - A universal, high-resolution printing technology for metal oxide thin-film transistors is still lacking. A plasmonic printing technology is reported to fabricate...
0
6
35
The authors use nitrogen-vacancy centre magnetometry to explore layer number and magnetic field evolution of ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic domains in the A-type antiferromagnet CrPS4.
nature.com
Nature Materials - The authors use nitrogen-vacancy centre magnetometry to explore layer number and magnetic field evolution of ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic domains in the A-type...
0
3
28
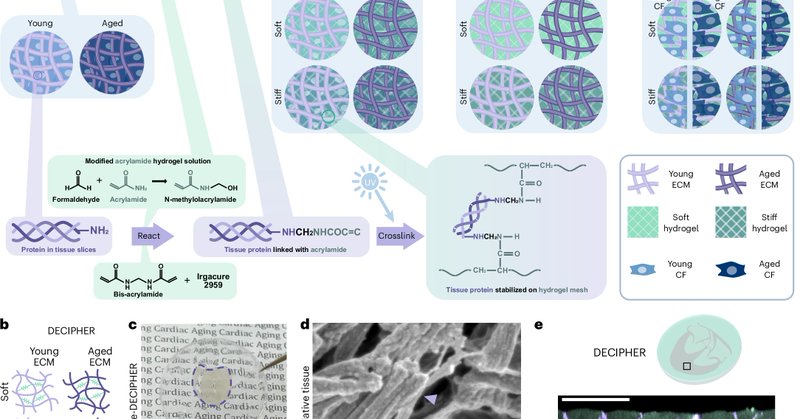
A hybrid ECM-hydrogel with tunable mechanical stiffness and biochemical composition of young or aged cardiac tissue is used to identify the specific contributions of ECM ligands and mechanics for fibroblast aging. @nano_jenn.
nature.com
Nature Materials - A hybrid extracellular matrix–hydrogel with tunable mechanical stiffness and biochemical composition of young or aged cardiac tissue is used to identify the specific...
0
13
57
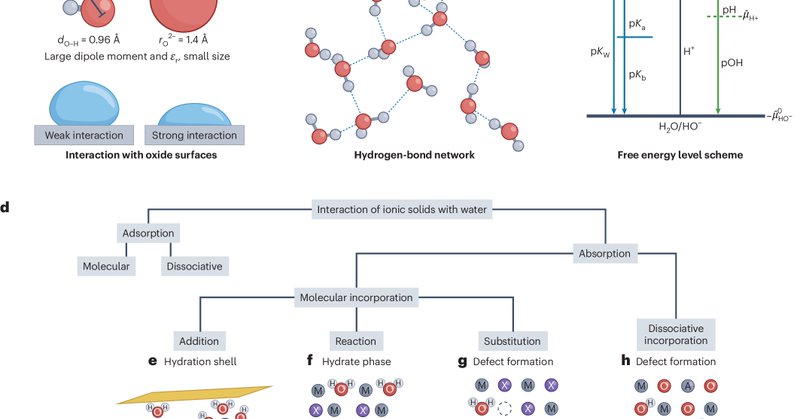
Review: Water uptake of solids and its impact on ion transport.
nature.com
Nature Materials - The uptake of water by polar solids can modify electrical and mass transport properties. This Review discusses hydration mechanisms and surveys case studies of the effects water...
0
7
39
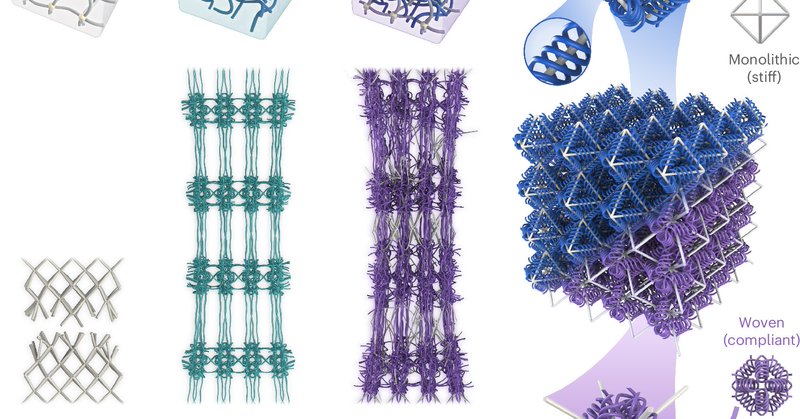
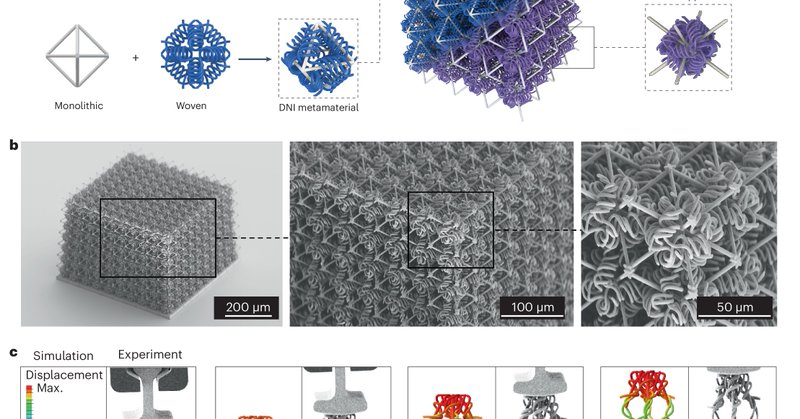
Related paper: Double-network-inspired mechanical metamaterials.
nature.com
Nature Materials - Inspired by the entangled structure of double-network hydrogels, the authors integrate stiff truss and compliant woven components into metamaterial architectures to realize...
0
3
9
News & Views: Stiff yet stretchy dissipative metamaterials @CarlosMPortela.
nature.com
Nature Materials - Hydrogels inspire a class of double-network mechanical metamaterials with an unprecedented combination of stiffness, stretchability and energy dissipation.
2
9
40
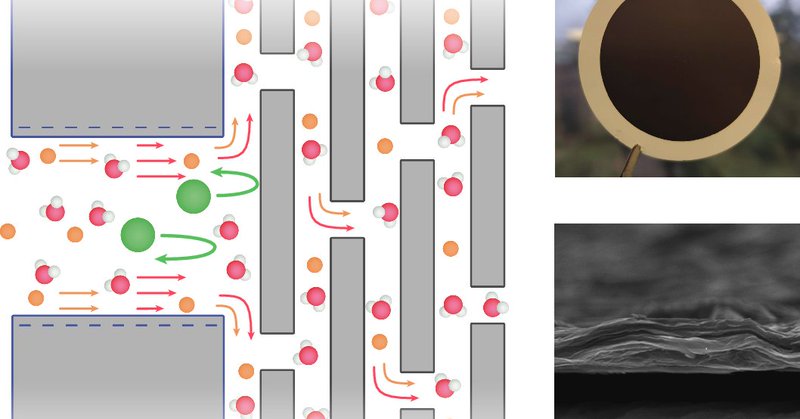
While nanofluidics demonstrate unconventional properties at the nanoscale, large-scale implementation remains challenging. Macroscale resonant electro-osmotic transport is demonstrated in asymmetric membranes for advanced water filtration applications.
nature.com
Nature Materials - While nanofluidics demonstrate unconventional properties at the nanoscale, large-scale implementation remains challenging. The authors demonstrate macroscale resonant...
0
9
21
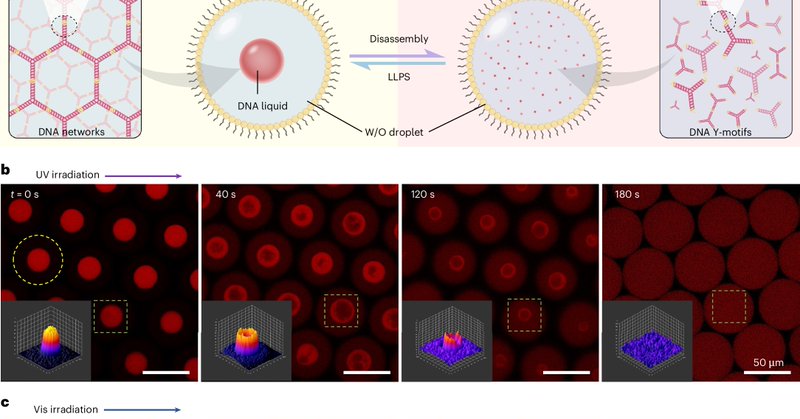
Related paper: DNA photofluids show life-like motion @dengnannan.
nature.com
Nature Materials - Artificial DNA photofluids exhibit dissipative life-like motion when fuelled by light in space and time, converting photoenergy into out-of-equilibrium structures on the macroscale.
0
2
7
News & Views: DNA droplets shuffle in the spotlight @WaltherLab.
nature.com
Nature Materials - When exposed to polarized light, DNA condensate droplets with molecular photoswitches undergo life-inspired shape changes and motion.
1
3
10