Wei Cao
@weicao_phd
Followers
354
Following
1K
Media
4
Statuses
1K
Professor working on #neuroinflammation, #Alzheimer’s disease, and #aging in #UTHealthHouston
Houston, Texas, USA
Joined May 2015
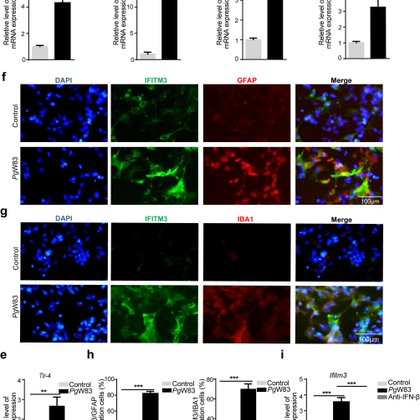
Periodontitis-induced neuroinflammation triggers IFITM3-Aβ axis to cause alzheimer’s disease-like pathology and cognitive decline | Alzheimer's Research & Therapy | Full Text
alzres.biomedcentral.com
Background Periodontitis is a risk factor linked to Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and characterized by amyloid-beta (Aβ) pathology. Mounting evidence suggests a contributory role of periodontitis in the...
1
5
31
The knockout of Moesin leads to excess microglia-mediated synaptic pruning and impairs social novelty in a mouse model: Cell Reports
cell.com
Lai et al. report that the knockout of the autism-risk gene, MOESIN, from male mice leads to social deficits and repetitive behaviors. Mechanistic studies suggest the possible involvement of microg...
1
3
31
The Global Neurodegeneration Proteomics Consortium: biomarker and drug target discovery for common neurodegenerative diseases and aging | Nature Medicine
nature.com
Nature Medicine - The largest harmonized proteomic dataset of plasma, serum and cerebrospinal fluid samples across major neurodegenerative diseases reveals both disease-specific and transdiagnostic...
0
2
10
TET2-mutant myeloid cells mitigate Alzheimer’s disease progression via CNS infiltration and enhanced phagocytosis in mice: Cell Stem Cell
cell.com
Matatall et al. uncover a mutation-specific association between clonal hematopoiesis (CH) and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) in mice and humans. TET2-mutant CH conferred lower odds of AD in humans and...
0
0
4
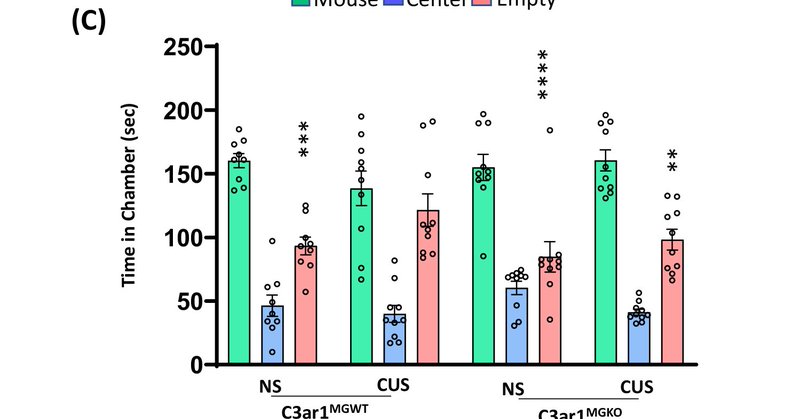
Opposing roles of microglial and macrophagic C3ar1 signaling in stress-induced synaptic and behavioral changes | Molecular Psychiatry
nature.com
Molecular Psychiatry - Opposing roles of microglial and macrophagic C3ar1 signaling in stress-induced synaptic and behavioral changes
1
5
28
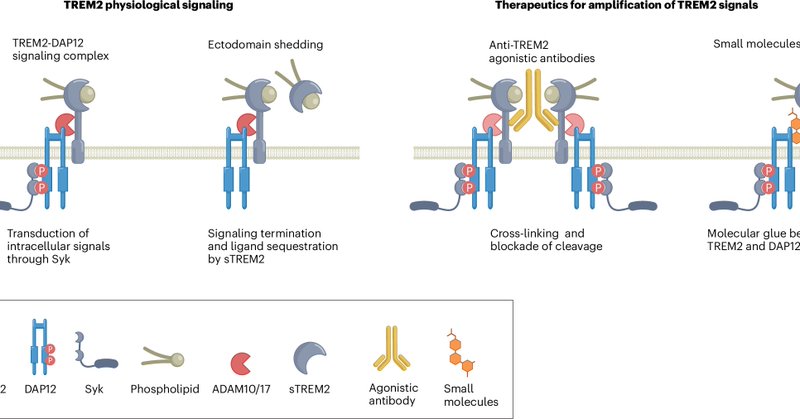
Rethinking TREM2 as a target for Alzheimer’s disease after the INVOKE-2 trial failure | Nature Medicine
nature.com
Nature Medicine - Rethinking TREM2 as a target for Alzheimer’s disease after the INVOKE-2 trial failure
1
12
44
#preprint on @researchsquare from Cynthia Lemere's group: Global C3 lowering in adulthood protects against hippocampal dysfunction and cognitive impairment in aged mice
researchsquare.com
Background: Complement component 3 (C3) is increasingly recognized for its role in neurodegenerative processes; however, its specific impact on age-related hippocampal dysfunction remains poorly...
1
3
10
Epigenetic attenuation of interferon signaling is associated with aging-related improvements in systemic lupus erythematosus | Science Translational Medicine
science.org
Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus exhibit aging-related decreases in interferon signaling that correlate with improved disease activity.
0
6
38
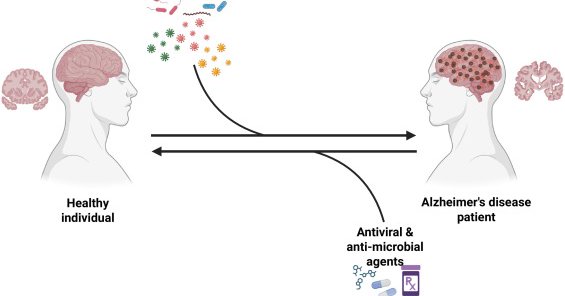
Happy to share our perspectives on chronic infections in AD etiology - What would it take to prove that a chronic infection is a causal agent in Alzheimer’s disease?: Trends in Neurosciences
cell.com
Accumulating evidence over several years suggests that microbial infections (e.g., bacteria, viruses, fungi) may play a role in the etiology of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). In this review, we discuss...
1
13
44
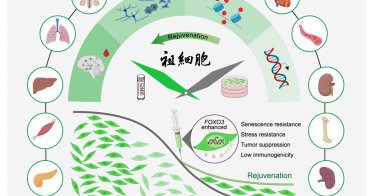
Senescence-resistant human mesenchymal progenitor cells counter aging in primates: Cell
cell.com
Genetically engineered senescence-resistant human mesenchymal progenitor cells can reduce aging markers and improve tissue and cognitive functions in aged macaques, highlighting their potential as a...
0
0
1
Cell-surface proteomic profiling identifies CD72 as a regulator of microglial tiling
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Microglial tiling-the phenomenon of consistent cell-to-cell distances and non-overlapping processes-is regarded as a qualitative indicator of homeostasis, but mechanisms of microglial tiling are...
0
1
14
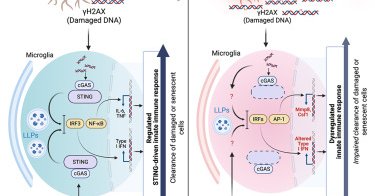
Microglial STING is a central safeguard against neurological decline with age: Cell Reports
cell.com
Immune pathways and cell types that protect against neurodegenerative processes with aging remain poorly understood. Sulka et al. demonstrate that the innate immune adaptor, STING, provides essential...
1
21
98
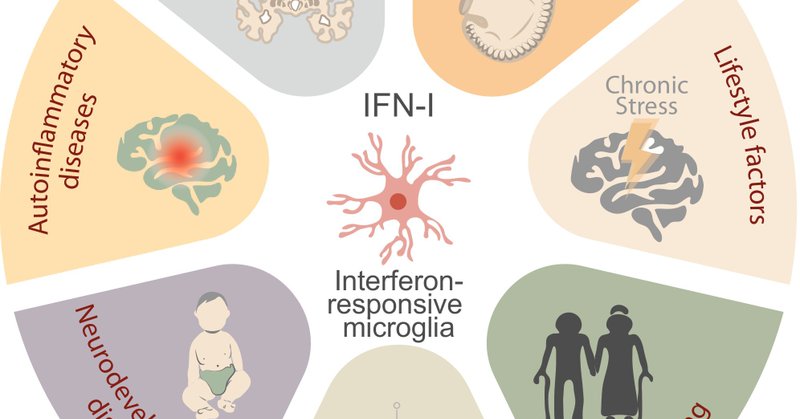
Regulators of Interferon-Responsive Microglia Uncovered by Genome-wide CRISPRi Screening
biorxiv.org
Microglia dynamically support brain homeostasis through the induction of specialized activation programs or states. One such program is the Interferon-Responsive Microglia state (IRM), which has been...
2
12
47
Inactivation of the PHD3-FOXO3 axis blunts the type I interferon response in microglia and ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease progression | Science Advances
science.org
PHD3 inhibition slows down the pathology and behavioral decline of an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model.
0
2
18
Predicting and preventing Alzheimer’s disease | Science
science.org
With all the advances in both the science of aging and artificial intelligence (AI), we are in a propitious position to accurately and precisely determine who is at high risk of developing Alzheime...
0
2
17
Association of nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor use with reduced risk of Alzheimer's disease risk - Magagnoli - 2025 - Alzheimer's & Dementia
alz-journals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
INTRODUCTION Inflammasome activation is implicated in Alzheimer's disease (AD). We previously demonstrated that nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), drugs approved to treat human...
0
4
10
Type I interferon signalling and interferon‐responsive microglia in health and disease - Lopez‐Atalaya - The FEBS Journal - Wiley Online Library
febs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Recent insights reveal that type I interferon (IFN-I) signalling plays critical roles in the nervous system beyond antiviral defence. Dysregulated IFN-I activity is increasingly linked to neurologi...
0
14
61
RT @NeuroCellPress: Online now: CLU alleviates Alzheimer’s disease-relevant processes by modulating astrocyte reactivity and microglia-dep….
0
8
0
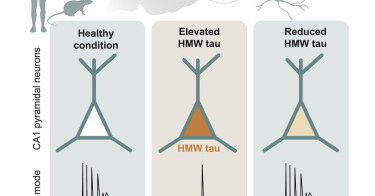
Alzheimer’s disease patient-derived high-molecular-weight tau impairs bursting in hippocampal neurons: Cell
cell.com
In mouse models, tau impairs neuronal complex spike bursting and associated network processes in hippocampus CA1 alongside CaV2.3 downregulation. Soluble high-molecular-weight tau species drive these...
0
3
27