Paper-worm
@Yoolab_JC
Followers
74
Following
2
Media
0
Statuses
70
Introducing papers discussed at the Yoo lab of RIKEN. General tweet @Yoo_Lab_RIKEN Tweet in Japanese @SaKanYoo1
Kobe
Joined February 2021
JC by US. A temperature-tolerant CRISPR base editor mediates highly efficient and precise gene inactivation in vivo.
biorxiv.org
CRISPR nucleases generate a broad spectrum of mutations that includes undesired editing outcomes which attenuate phenotypes and complicate experimental analysis and interpretation. Here, we develop...
0
0
0
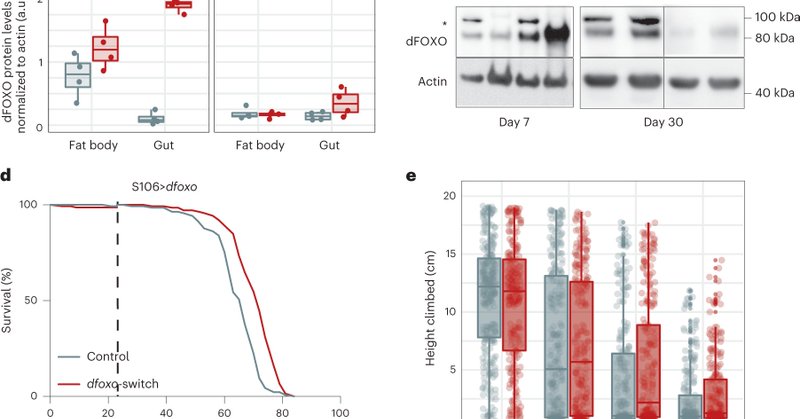
JC by SN. Transcriptional memory of dFOXO activation in youth curtails later-life mortality through chromatin remodeling and Xbp1.
nature.com
Nature Aging - Martínez Corrales et al. show that the activation of the conserved pro-longevity transcription factor FOXO solely in youth promotes subsequent health and survival in female...
0
0
0
JC by MO. Hedgehog-mediated gut-taste neuron axis controls sweet perception in Drosophila.
nature.com
Nature Communications - Food regulates taste perception, but the underlying molecular mechanisms are not clear. Here, the authors reveal that sugar intake in Drosophila induces the gut to secrete...
0
0
0
JC by SS. Hippo signaling instructs ectopic but not normal organ growth.
science.org
The function of Hippo signaling during organ growth was re-evaluated in Drosophila imaginal discs and mouse livers.
0
0
0
JC by MM. De novo apical domain formation inside the Drosophila adult midgut epithelium.
elifesciences.org
Drosophila enteroblasts form septate junctions, an apical domain and an internal lumen inside the midgut epithelium before they reach the gut surface, thereby maintaining the intestinal barrier as...
0
0
0
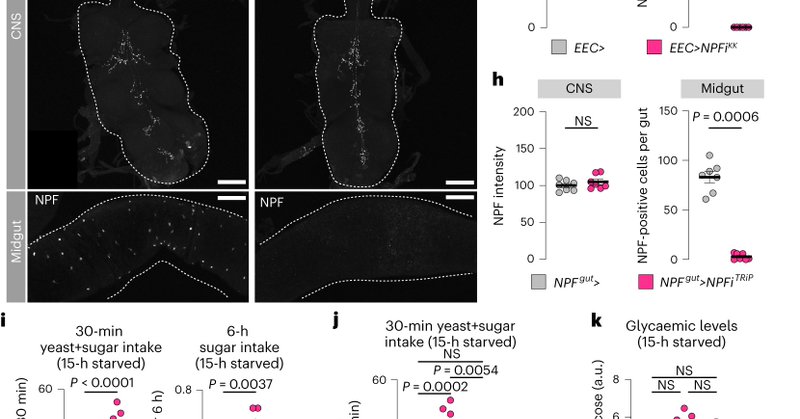
JC by US. A gut-derived hormone suppresses sugar appetite and regulates food choice in Drosophila @LabRewitz.
nature.com
Nature Metabolism - Malita, Kubrak et al. show that the gut-derived hormone neuropeptide F suppresses sugar intake and increases the consumption of protein-rich food in Drosophila. This gives...
0
0
0
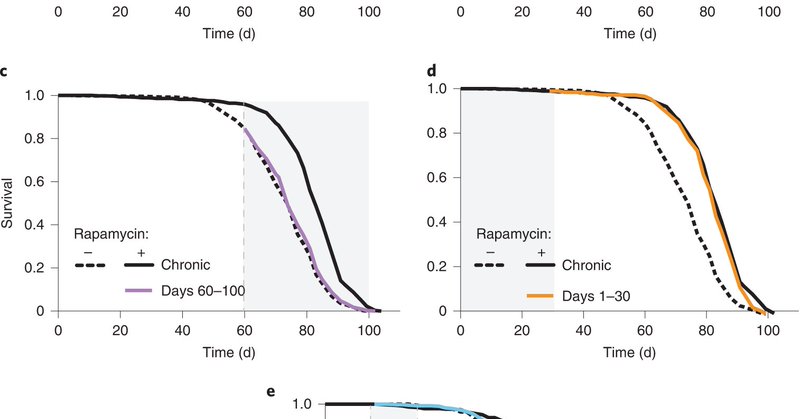
JC by YI. Long-lasting geroprotection from brief rapamycin treatment in early adulthood by persistently increased intestinal autophagy.
nature.com
Nature Aging - A key challenge for repurposing the licensed drug rapamycin for geroprotection is to avoid side effects from chronic dosing regimens. The authors show in model organisms that a brief...
0
0
0
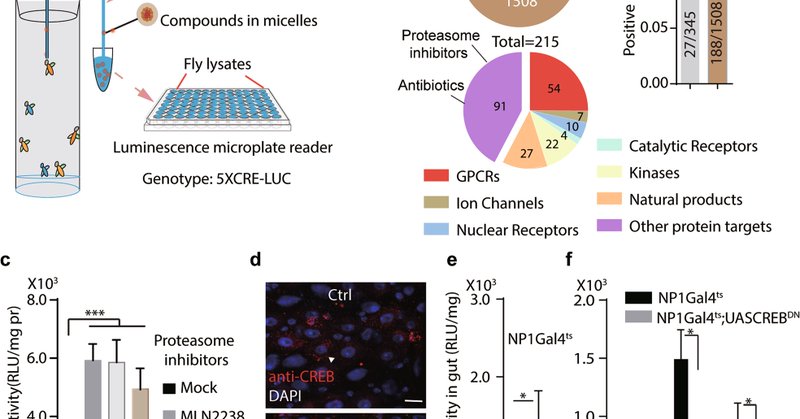
JC by SS. The CRTC-CREB axis functions as a transcriptional sensor to protect against proteotoxic stress in Drosophila.
nature.com
Cell Death & Disease - The CRTC-CREB axis functions as a transcriptional sensor to protect against proteotoxic stress in Drosophila
0
0
0
JC by US. Damage-induced regeneration of the intestinal stem cell pool through enteroblast mitosis in the Drosophila midgut.
embopress.org
image image The regenerative cell populations replenishing the intestinal epithelium upon tissue damage remain debated. This genetic tracing study reports a role for enteroblasts (EBs), an intermed...
0
0
0
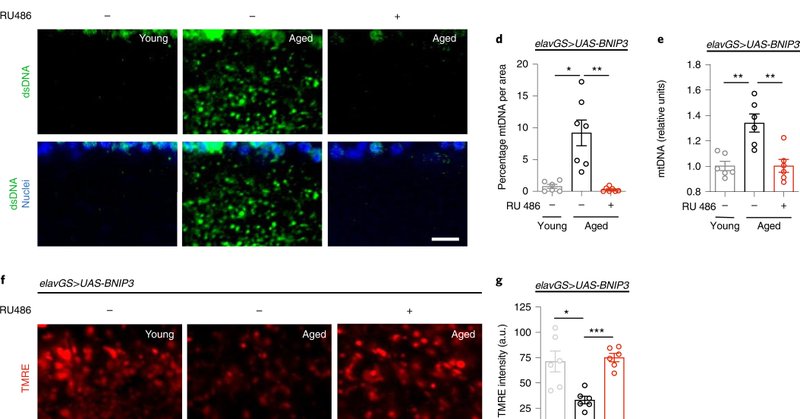
JC by SN. Neuronal induction of BNIP3-mediated mitophagy slows systemic aging in Drosophila.
nature.com
Nature Aging - This study shows that the cellular pathway that removes dysfunctional mitochondria, mitophagy, becomes impaired in the aged fly brain. Inducing mitophagy in the aging brain prolongs...
0
0
0
JC by MO. Systemic coagulopathy drives host lethality in a new Drosophila tumor model.
biorxiv.org
Malignant tumors trigger a complex network of inflammatory and wound repair responses, prompting Dvorak’s characterization of tumors as ‘wounds that never heal’ [1][1]. Some of these responses lead...
0
0
0
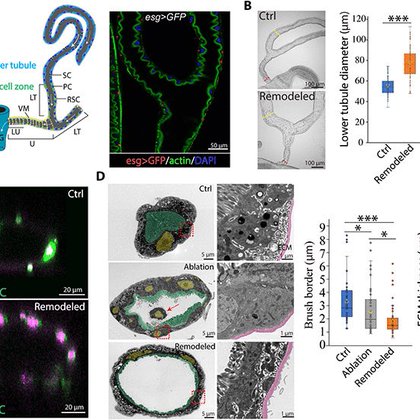
JC by SS. Drosophila renal stem cells enhance fitness by delayed remodeling of adult Malpighian tubules.
science.org
Activated Drosophila renal stem cells rebuild the adult Malphigian tubules using a less-efficient but more stone-resistant design.
0
0
1
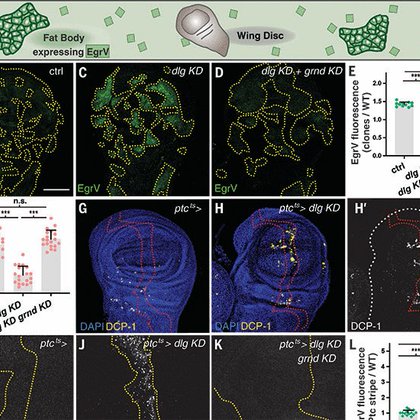
JC by MO. Epithelial monitoring through ligand-receptor segregation ensures malignant cell elimination.
science.org
Transformed cells and wounds activate a polarity-enforced latent signaling system to trigger either cell death or wound repair in fruit flies.
0
0
0
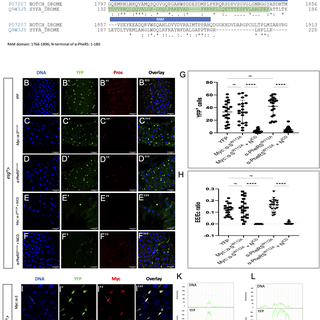
JC by US. α-Phenylalanyl tRNA synthetase competes with Notch signaling through its N-terminal domain.
journals.plos.org
Author summary Aminoacyl tRNA synthetases charge tRNAs with their cognate amino acid to ensure proper decoding of the genetic code during translation. Independent of its aminoacylation function, the...
0
0
0