Nanophotonics IQF CSIC
@TNG_IQF_CSIC
Followers
237
Following
244
Media
7
Statuses
182
Theoretical Nanophotonics Group @ IQF-CSIC led by Dr. Alejandro Manjavacas.
Joined December 2020
RT @GEFES_RSEF: 📢📢 Artículos destacados octubre 2024 - marzo 2025 🎖️🎖️ 1/2.Juan Ramón Deop Ruano et al., «Thermal Radiation Force and Tor….
journals.aps.org
Nanoscale objects moving relative to a thermal radiation bath experience a drag force due to the imbalance in their interaction with the blue- and redshifted components of the electromagnetic field....
0
2
0
RT @Plasmonica: Let’s start with the first invited speaker of the workshop: Alejandro Manjavacas from @TNG_IQF_CSIC discussing on collectiv….
0
4
0
In our last work with @aifernand, Blas Durá has developed a theoretical framework to study spatially-resolved second-order correlations in quantum emitter dimers.
1
0
0
Our latest work, "Thermal radiation force and torque on moving nanostructures with anisotropic optical response," is out in Physical Review Letters! @iqf_csic @CSICdivulga @PhysRevLett .A thread 👇.
journals.aps.org
Nanoscale objects moving relative to a thermal radiation bath experience a drag force due to the imbalance in their interaction with the blue- and redshifted components of the electromagnetic field....
1
0
2
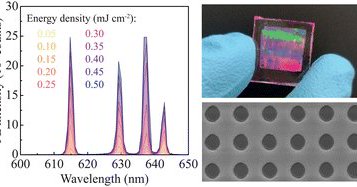
In our last publication in Nanoscale Horizons, together with the group of @agusmihi, we study a 2D photonic architecture for lasing, consisting of an array of holes in a polymer matrix coated with a high-index dielectric @CSICdivulga @iqf_csic
pubs.rsc.org
High-refractive-index (HRI) dielectrics are gaining increasing attention as building blocks for compact lasers. Their ability to simultaneously support both electric and magnetic modes provides...
1
4
8
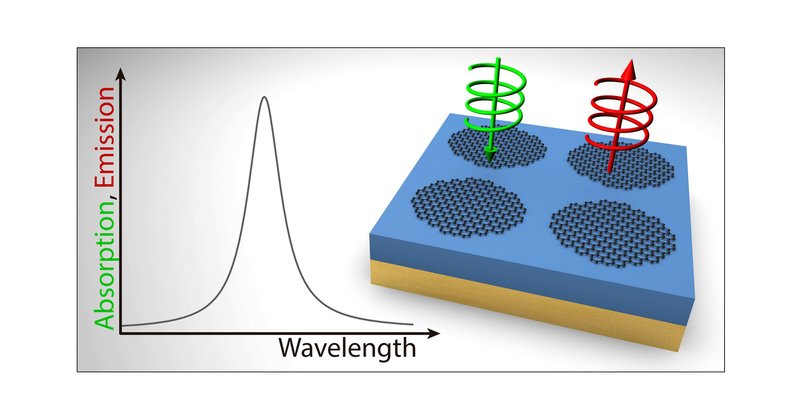
Check out our latest work, 'Chiral Light–Matter Interactions with Thermal Magnetoplasmons in Graphene Nanodisks,' which has just been published in @NanoLetters. @iqf_csic @CSICdivulga @SyddanskUni
pubs.acs.org
We investigate the emergence of self-hybridized thermal magnetoplasmons in doped graphene nanodisks at finite temperatures upon being subjected to an external magnetic field. Using a semianalytical...
1
0
5
Please contact us ( if you are interested in applying for a Juan de la Cierva fellowship and working in our group.
‼️ La @AgEInves destina 189,4 millones de euros para varias convocatorias de ayudas del año 2024 del Programa Estatal de Recursos Humanos:.🔹 Torres Quevedo: 20.100.000 €.🔹 Juan de la Cierva: 38.300.000 €.🔹 Ramón y Cajal: 131.056.800 €. Info ➡️
0
1
3