Pillai Lab
@Pillai_Lab
Followers
39
Following
2
Media
0
Statuses
13
The Pillai Lab at Yale School of Medicine. We study RNA mechanisms in Hematopoiesis
New Haven, CT, USA
Joined February 2024
Transcription elongation defects link oncogenic SF3B1 mutations to targetable alterations in chromatin landscape: Molecular Cell
2
14
73
Dr. Prajwal Boddu and @rahul_royale share how a unified post-transcriptional mechanism regulates intron retention in splicing factor-mutant Myelodysplastic Syndromes #MDS at #ASH24. @Pillai_Lab @YaleHematology @SmilowCancer @YaleMed
https://t.co/5S0XcKUmvH
0
3
8
.@rahul_royale and Dr. Pajwal Boddu present new advances in Myelodysplastic Syndromes #MDS at #ASH24 from @YaleHematology and the lab of @ManojPill. @YaleMed @SmilowCancer @ASH_hematology @YNHH
0
3
13
Online Now: Time-resolved profiling of RNA binding proteins throughout the mRNA life cycle https://t.co/qWqQPVNslR
3
83
269
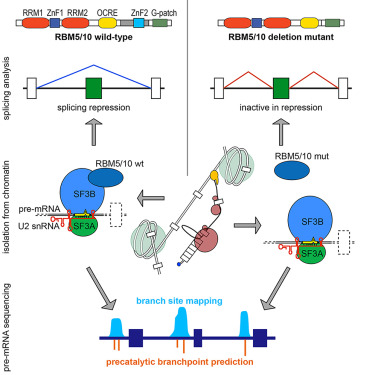
Online Now: The splicing regulators RBM5 and RBM10 are subunits of the U2 snRNP engaged with intron branch sites on chromatin https://t.co/zSCd9mNHqt
2
20
76
Online Now: Transcription elongation defects link oncogenic SF3B1 mutations to targetable alterations in chromatin landscape https://t.co/X2HStHhsNw
1
20
89
We thank all who helped including collaborators @NeugebauerKarla , @Amitvermamds , @dray_lab and many others not on twitter. Funding agencies @nih_nhlbi , @NIDDKgov , @theNCI ,#EdwardPEvansFoundation, @YaleGICancers ,@CCEH_U24
1
0
2
Since all commonly mutated splicing factors are involved in early spliceosome assembly, we propose the disrupted transcription and resultant replication stress to underlie their striking mutual exclusivity.
1
0
2
This leads to replication conflicts and altered chromatin architecture primarily at gene promoters. Thus splicing factor mutant states are functionally epigenetic disorders. These changes are reversed by inhibition of Sin3/HDAC pathway.
1
0
1
Led by Prajwal Boddu, we report how common cancer associated mutations in splicing factors SF3B1 and U2AF1 alter RNA Polymerase II transcription kinetics due to impaired early spliceosome assembly.
1
0
2