Neuroscience News
@NeuroscienceNew
Followers
505K
Following
31K
Media
11K
Statuses
38K
Official Neuroscience News Twitter. Brain research news articles on neuroscience, psychology, AI, neurology, brain cancer, robotics, mental health & science.
Houston, TX
Joined April 2009
Music After Learning Boosts Memory, But Only at the Right Emotion Level. Researchers have found that listening to music after an experience can sharpen memory, but only when the emotional response to the music is at a moderate level. Volunteers who felt balanced levels of
3
84
297
A strong sense of purpose in life lowers dementia risk by 28%, new research shows—highlighting meaning, goals, and connection as powerful tools for brain resilience.
neurosciencenews.com
A new study of over 13,000 adults found that having a strong sense of purpose in life is linked to a reduced risk of dementia.
0
2
9
“Traumatic Brain Injury and Risk of Malignant Brain Tumors” by Saef Izzy et al. JAMA Network Open.
jamanetwork.com
This cohort study examines whether history of traumatic brain injury (TBI) is associated with risk of subsequent development of malignant brain tumors among US civilian populations.
0
0
3
Head Injuries Linked to Higher Risk of Brain Cancers. Moderate-to-severe TBIs are linked to a higher risk of malignant brain tumors, new research shows—highlighting the importance of long-term monitoring after serious head injuries.
neurosciencenews.com
A large study of more than 75,000 people has found that moderate-to-severe traumatic brain injury (TBI) is linked to an increased risk of malignant brain tumors.
0
0
2
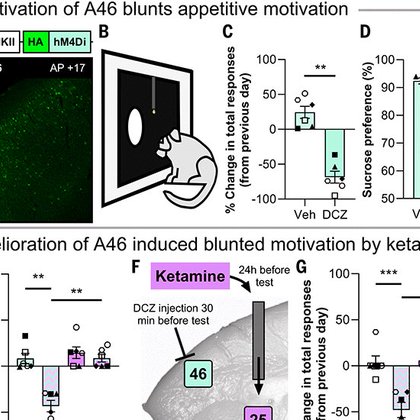
“Dysfunction in primate dorsolateral prefrontal area 46 affects motivation and anxiety” by Christian M. Wood et al. Science.
science.org
The dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (dlPFC) is a higher-order brain structure targeted for noninvasive stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Nonetheless, its causal role in emotion regulat...
0
2
19