MethaneNet
@MethaneNet
Followers
2K
Following
234
Media
14
Statuses
7K
Biogeochemistry, sources, fluxes, microbiology and atmospheric aspects of CH4 in the modern and ancient Earth system. Tweets by @MikePeacock86 & @GauciGauci.
University of Birmingham
Joined January 2010
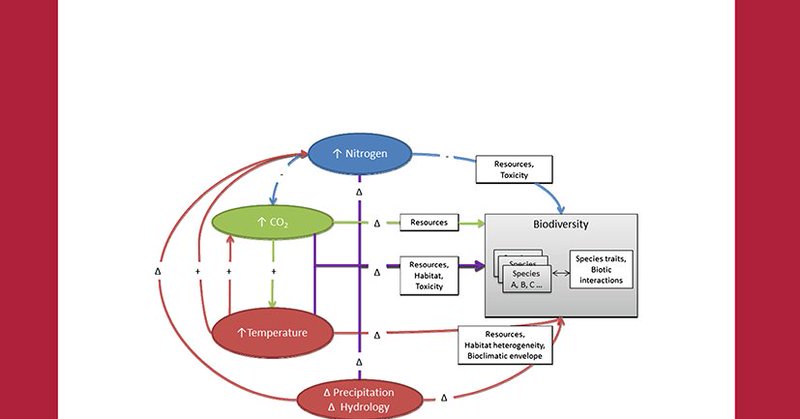
Wetland drainage produces substantial greenhouse gas emissions in the Canadian Prairie Pothole Region
facetsjournal.com
The Prairie Pothole Region of central North America is dominated by agriculture and contains numerous small mineral-soil wetlands that are often drained to expand cropland. Here, we synthesize the...
0
0
0
Microbial community adaptation to brackish water rewetting in a coastal peatland
link.springer.com
Biogeochemistry - Coastal wetlands can serve as natural laboratories for assessing the future impacts of sea-level rise and the intricacies of the effect of sulfate (SO42−) on emissions of...
0
0
1
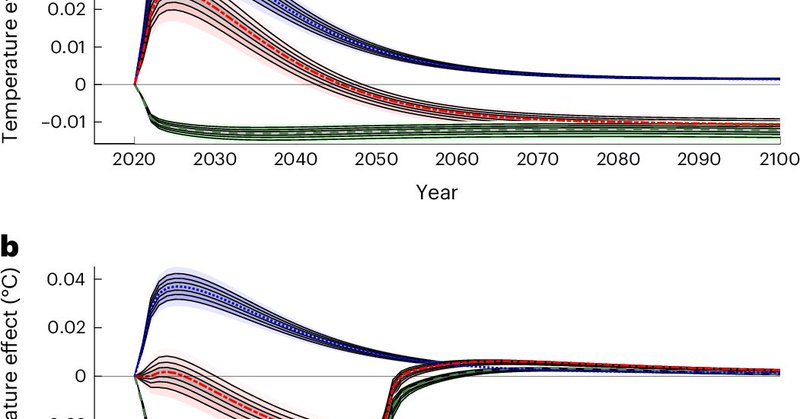
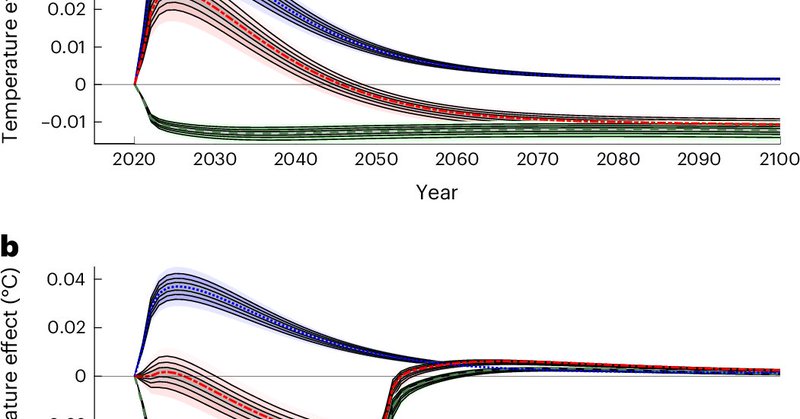
Temporary carbon dioxide removals to offset methane emissions
nature.com
Nature Climate Change - Methane emissions have a large short-term impact on temperature, which can be potentially offset by nature-based solutions that provide temporary carbon storage. This...
0
0
0
Reducing the large short-lived impact of methane emissions with temporary carbon removals
nature.com
Nature Climate Change - We consider potential non-permanence of carbon removal not as an obstacle but as a feature to focus on the compensation for the short-term warming of methane emissions. This...
0
0
1
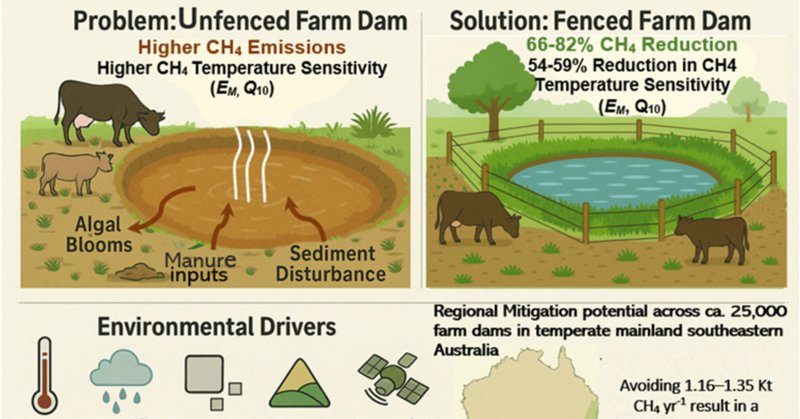
Fencing the Flux: Seasonal Trends, Environmental Drivers, and Mitigation Opportunities of Methane Emissions From Farm Dams
onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Our large-scale study reveals that fencing livestock out of farm dams is a highly effective climate solution, reducing methane emissions by 66%–82% across all seasons. Crucially, fencing also...
0
0
0
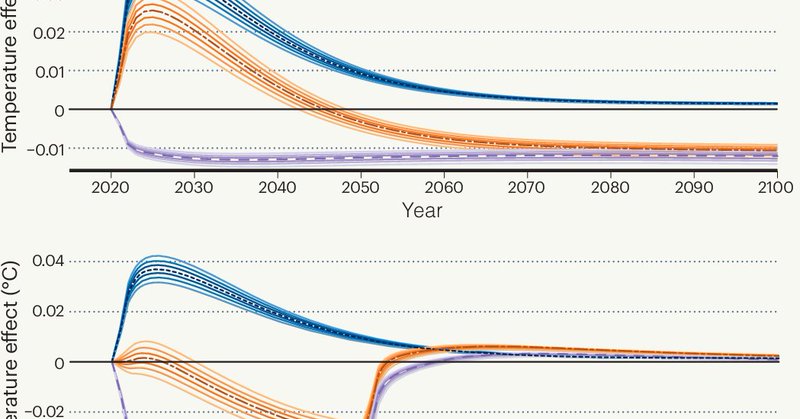
Methane emissions have a large short-term impact on temperature, which can be potentially offset by nature-based solutions that provide temporary carbon storage…
nature.com
Nature Climate Change - Methane emissions have a large short-term impact on temperature, which can be potentially offset by nature-based solutions that provide temporary carbon storage. This...
1
1
1
Probing dissolved CO2 and CH4 in glacial streams of the European Alps
tandfonline.com
Glacier meltwater streams are a source of methane (CH4) but can act as a sink for atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) through the weathering of minerals. Though both processes have been observed at gl...
0
0
0
Hydrological processes govern methane flux fluctuations in a subtropical floodplain
0
0
1
Effects of winter heatwaves on carbon dioxide and methane emissions from shallow lakes: A temperature-controlled mesocosm study
0
0
1
Hydrological seasonality shapes diel methane emission variations in China’s largest floodplain lake
0
0
2
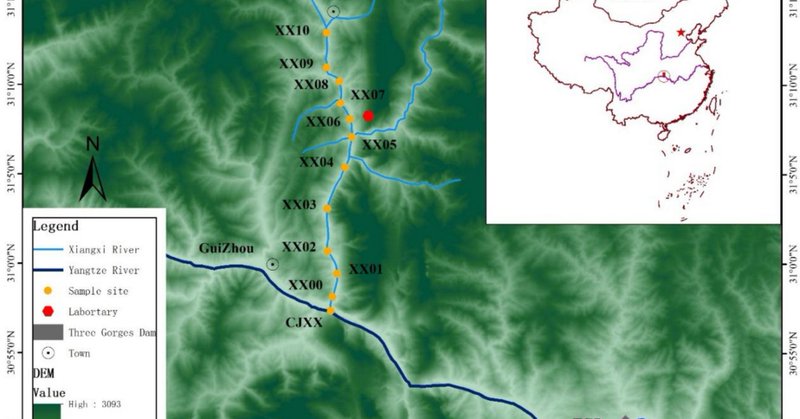
In situ acoustic quantification of methane ebullition in Xiangxi Bay, Three Gorges Reservoir
link.springer.com
Environmental Monitoring and Assessment - Ebullition constitutes a major pathway for methane emissions from reservoirs, particularly in tributary bays with steep depth gradients. However, methane...
0
0
0
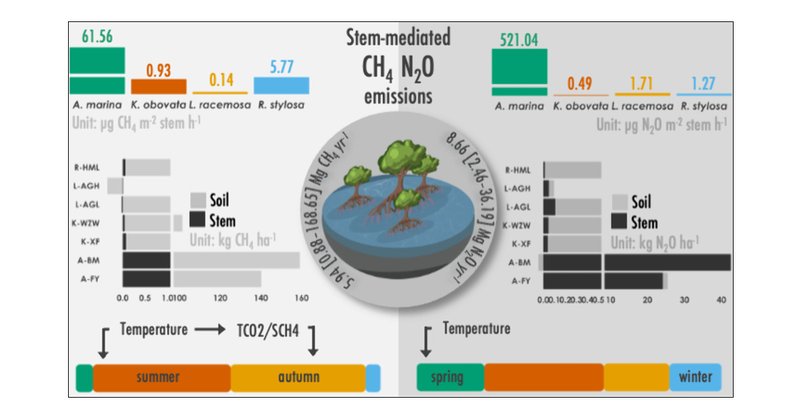
Exploring Spatial and Temporal Variations in Stem-Mediated Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Different Species of Mangroves
pubs.acs.org
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, particularly methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O), from mangroves can challenge their carbon sequestration capacity. This study measured GHG emissions from the tree...
1
0
0
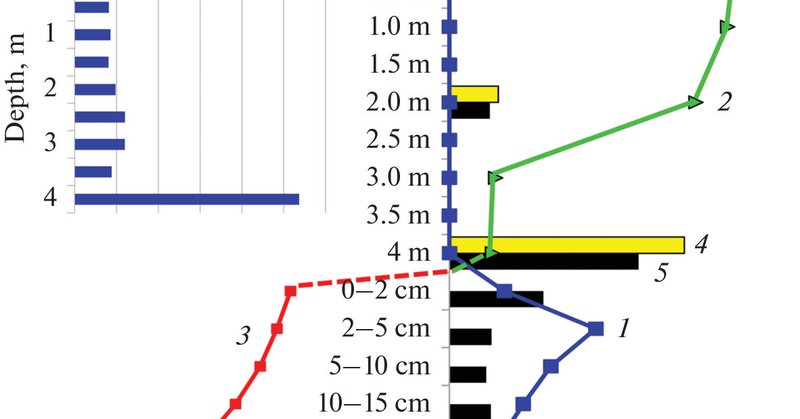
Profile Distribution of Methane Oxidation Rates and Genome Analysis Suggest Utilization of NO Dismutation Pathway by Aerobic Methanotrophs in Reduced Lake Sediments
link.springer.com
Microbiology - Aerobic methane-oxidizing bacteria (MOB) were suggested to play an important role in the process of anaerobic methane oxidation (AOM) in freshwater basins. The central hypothesis in...
0
0
1
Greenhouse Gas Fluxes from Typical Ecosystems of the Polygonal Tundra of Samoylov Island (Northeastern Siberia)
link.springer.com
Water Resources - Field measurements of methane and carbon dioxide fluxes from polygonal tundra landscapes of Samoylov Island in the Lena River Delta were carried out using the chamber method in...
0
0
0
Carbon balance in an abandoned peat extraction area influenced by spatial heterogeneity and vegetation development
0
1
1
Quantifying Carbon Pools and Fluxes in Southern Ontario Temperate Swamps
mires-and-peat.net
By Megan A. Schmidt, Veronica Santia & 3 more. Article 32.31: The North American definition of swamp disregards soil type, meaning some swamps also meet the definition of peatlands. This study...
0
1
0
Legacy effects of inundation on greenhouse gas emissions and soil dynamics in forage systems
acsess.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Pasture and hayfields under short-duration, recurring, natural inundation were evaluated. Inundation triggers immediate, progressive, and cumulative ecosystem changes influencing greenhouse gas...
0
0
0
Inter-Monthly Variations in CO2 and CH4 Fluxes in a Temperate Forest: Coupling Dynamics and Environmental Drivers
mdpi.com
Climate change, driven largely by anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions, is a major global issue. Long-term high-frequency measurements of gas fluxes remain limited, especially outside the growing...
0
1
1
Greenhouse gases emissions and energy efficiency in ewe lambs fed hay from native Pantanal grasses
link.springer.com
Tropical Animal Health and Production - The study aimed to evaluate greenhouse gases (GHGs) emissions and efficiency of dietary energy use in Santa Inês ewe lambs fed four exotic and native...
0
0
0
Carbon fluxes in two temperate ponds are mediated by stratification and primary producers
aslopubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Ponds influence global carbon (C) cycling due to high rates of organic C (OC) burial and carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4) emissions. Here, we quantified OC burial rates and CO2 and CH4 concen...
0
0
0