Cell
@CellCellPress
Followers
265K
Following
362
Media
4K
Statuses
13K
Cell aims to publish the most exciting and provocative research in biology. Posts by Scientific Editors on the Cell Editorial team.
Cambridge, MA
Joined August 2009
The new issue is out 👉 https://t.co/ye9kiMN3jk On the cover: Ludin et al. identify antigen-rich tumor niches, CRATERs, on the solid tumor surface, which facilitate CD8+ T cell-tumor interactions and tumor killing.
1
14
67
Now online! Psilocybin triggers an activity-dependent rewiring of large-scale cortical networks
cell.com
Psilocybin reshapes brain networks through activity-dependent plasticity, including a weakening of recurrent cortical loops that could underlie its therapeutic effects.
0
6
36
Now online! A fin-loop-like structure in GPX4 underlies neuroprotection from ferroptosis
cell.com
A fin-like structural loop in GPX4 is critical for anchoring the enzyme to cellular membranes, thereby preventing ferroptosis. A patient-associated R152H mutation destabilizes this loop, leading to...
0
9
27
Now online! Renal PIEZO2 is an essential regulator of renin
cell.com
The force-sensing ion channel PIEZO2 is an essential regulator of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), a pathway that controls blood volume. Loss of PIEZO2 in the kidney cells that...
0
14
53
Now online! Autoantibody-triggered podocyte membrane budding drives autoimmune kidney disease
cell.com
Kidney podocytes of the blood-urine filter form autoimmunoglobulin-triggered extracellular vesicles (AIT-EVs) for intra- and extracellular waste removal into the urine, a cellular reaction that links...
0
13
32
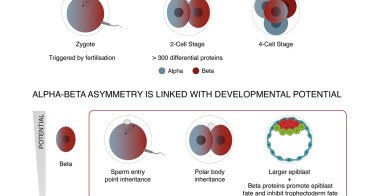
Now online! Fertilization triggers early proteomic symmetry breaking in mammalian embryos
cell.com
Single-cell proteomics finds asymmetries between sister blastomeres from the 2-cell stage in human and mouse embryos, defining two states: alpha and beta. Alpha-beta asymmetry can be traced back to...
0
4
23
Now online! Retraction notice to: Transcriptome-scale RNA-targeting CRISPR screens reveal essential lncRNAs in human cells
cell.com
(Cell 187, 7637–7654.e1–e29; December 26, 2024)
2
30
207
Now online! The effect of shingles vaccination at different stages of the dementia disease course
cell.com
A natural experiment found that herpes zoster vaccination reduced the occurrence of mild cognitive impairment and deaths due to dementia, indicating that the vaccine may slow the progression of...
0
5
13
Now online! pTα enhances mRNA translation and potentiates CAR T cells for solid tumor eradication
cell.com
Addition of a pre-TCR domain to chimeric antigen receptors boosts mRNA translation and enables durable tumor control by T cells in both blood and solid cancers.
0
7
22
Now online! Membrane potential mediates the cellular response to mechanical pressure
cell.com
Cells in tissues need to know when to start growing and when to stop growing to quickly heal wounds but prevent tumorous overgrowth. Membrane potential allows cells to sense physical forces, includ...
0
29
93
Excited to hear from #CSImmuneHomeostasis26 keynote Diane Mathis @harvardmed! She’ll be sharing her groundbreaking talk on how meningeal Tregs regulate brain health and influence neurodegeneration. Don’t miss it! @CellSymposia
https://t.co/lRXRCgu2vJ
0
5
8
Now online! A stepwise decoding mechanism for heat sensing in plants connects lipid remodeling to a nuclear signaling cascade
cell.com
A complete hierarchical thermo-decoding mechanism in plants connects cell membrane lipid remodeling during heat stress to the downstream signaling cascade in the nucleus. Field trials demonstrate the...
0
9
28
Now online! The unique architecture of umbrella toxins permits a two-tiered molecular bet-hedging strategy for interbacterial antagonism
cell.com
Umbrella toxin particles produced by Actinobacteria contain five spokes tipped with variable lectin domains. Here, Zhao et al. show that these lectins mediate species-specific binding to a previously...
0
11
28
How does inflammation shape aging? Find out from Vishwa Deep Dixit (@YaleMed) this October at @CellSymposia #CSAging2026. Submit your abstract by June 5 for a chance to join the program. https://t.co/t0OvY6iWnY
0
3
9
Now online! An archaeal transcription factor bridges prokaryotic and eukaryotic regulatory paradigms
cell.com
Methanogenic archaea use the one-component system AmzR to sense methylamines and regulate the expression of methylamine-metabolizing genes. Unlike other prokaryotic one-component systems, the...
0
16
53
Now online! Innate immune and metabolic signals induce mitochondria-dependent membrane lysis via mitoxyperiosis
0
14
65
In the latest issue! Activation-induced cytidine deaminase: The missing piece of many puzzles
cell.com
Twenty-five years ago, two Cell papers reported the key missing functional piece in three molecular puzzles. The genetic swapping of immunoglobulin constant regions, the mutational fine-tuning of...
0
2
17
In the latest issue! Turning up the volume: BNST couples internal state to consumption
cell.com
In this issue of Cell, Canovas and colleagues identify a consummatory dial in the brain that controls ingestion levels in a state-dependent manner. By continuing to trace the flow of sweet taste...
0
2
11
We're excited to host a distinguished lineup of speakers at @CellSymposia #CSHallmarks2026, including keynotes Johanna Joyce @Joycelab & Faisal Mahmood @AI4Pathology View the full speaker lineup: https://t.co/ZdHnywFLE3
0
3
15
In the latest issue! A systematic approach to tuberculosis vaccine development
cell.com
M. tuberculosis is once again the leading infectious cause of death worldwide despite the existence of a licensed vaccine (BCG). In this issue of Cell, Vidal et al. systematically evaluate 42...
0
2
12
In the latest issue! Feeding from the sun—Successes and prospects in bioengineering photosynthesis for food security
cell.com
This review explores how recent advances in bioengineering photosynthesis can enhance crop productivity and address global food security challenges.
0
4
12