Ped Infect Diseases
@PIDJournal
Followers
3K
Following
2K
Media
470
Statuses
4K
The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal® (PIDJ) is a complete, up-to-the-minute resource on #infectious #diseases in #children.COVID19: https://t.co/uQZOjH63pg
Philadelphia, PA
Joined July 2011
Pidj Now also on Bsky Find and Follow us there https://t.co/K4p9hLs22E
0
0
0
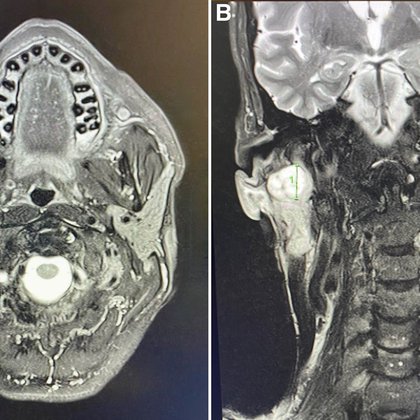
As if you needed further proof that @nigeltwitt is awesome, he even publishes his own clinical case in the @PIDJournal 🤣🥰 A Pain in the Neck Sixty Years On : The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal
journals.lww.com
This report describes the recurrence of an infected first branchial cleft cyst in an adult and highlights the importance of considering branchial cleft cysts in the differential diagnosis of cervical...
0
1
1
New @PIDJournal survey Candida in peds heme malignancy - C. tropicalis⬆️dissemination - high yield dilated 👁️exam -⬇️β-D-glucan for non-tropicalis Added by @soniamehraTXID to - "HEME ONC"▶️"PEDIATRIC" 📂 - "ORGANISMS"▶️"Fungi"▶️"Candida"📁 https://t.co/nmL05P19Ce
0
6
8
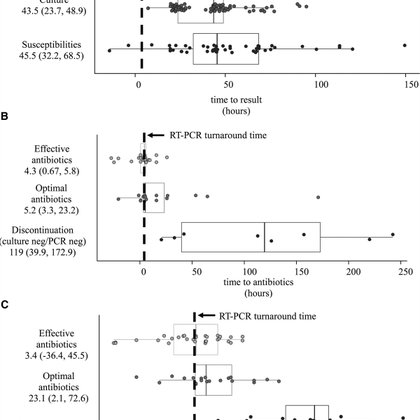
Multiplex RT-PCR demonstrates high sensitivity & negative predictive value for the detection of on-panel pathogens (Biofire FilmArray) in respi samples from critically ill children. RT-PCR use may alter antibiotic prescriptions. Osborne C et al. #PIDJ
https://t.co/wszH5BLmWR
journals.lww.com
polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) with bacterial targets is now available for clinical use. We compared the diagnostic performance of tracheal aspirate (TA) multiplex RT-PCR to culture in children...
0
0
4
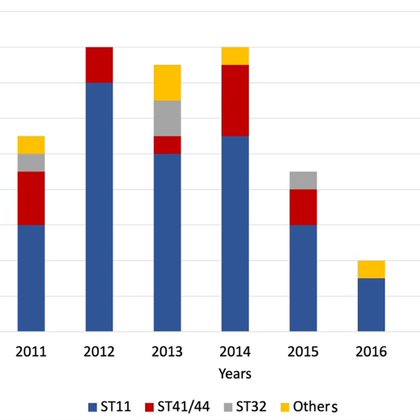
Klebsiella michiganensis, a member of K oxytoca complex, is an emerging nosocomial pathogen known to frequently carry plasmids with AMR genes, including carbapenemases. Using genomics, this study defined outbreak alert in a Spanish hospital. #klebsiella
journals.lww.com
g a blaVIM carbapenemase in a pediatric ward in a Spanish hospital. Methods: A total of 31 isolates of Verona integron-encoded metallo-β-lactamase (VIM)-carbapenemase K. oxytoca from suspected...
0
0
0
Neonatal and Maternal Immunization Supplement https://t.co/82N7p2AJ9Q "This [..] will be of relevance and importance to specialists in immunizations, pediatric infectious diseases, obstetrics, midwifery and all those who care for pregnant women, newborns and infants worldwide "
1
1
5
Article by Ines Taborda et al. reports epidemiology of late #Mycoplasma pneumoniae resurgence in Portugal; concludes that compared with pre-COVID era, disease severity and EP manifestations did not change, while median age at presentation increased #PIDJ
https://t.co/DDLefyy7BX
0
3
2
Discover the Joint Symposium: ESPID- @ESCMID happening on 28 May at #ESPID2025! 🌟 Dive into cutting-edge strategies for diagnosing & managing invasive #paediatricinfections. 🔗The full programme: https://t.co/FMWeEXmBOe
#PaediatricInfectiousDiseases #Metagenomics #PIDs
0
2
3
Highly recommended revisit to our AMR supplement "Antimicrobial Stewardship and IPC in LMICs" with read worthy open access articles. https://t.co/P7buf46rs3
0
0
0
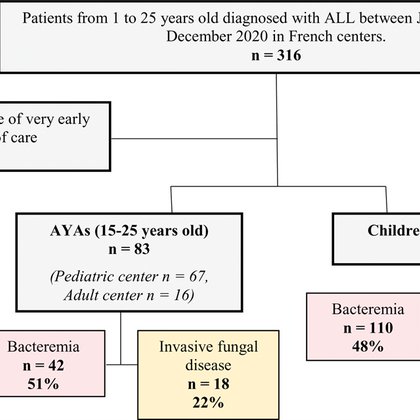
Are adolescents and young adults on ALL treatment more vulnerable to invasive bacterial/ fungal infections than pediatric ALL patients? Read new insights from Trimbour et al. in #PIDJ
journals.lww.com
the occurrence of bacterial bloodstream infection (BSI) and proven and probable invasive fungal infection (IFI) in AYAs (15–25 years old) and children (1–14 years old) treated for acute lymphoblastic...
0
0
1
Cepas hipervirulentas de Neisseria meningitidis y manifestaciones clínicas en niños con enfermedad meningocócica invasiva The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal. Agosto 2023 @PIDJournal
https://t.co/4uoesq9zgf
journals.lww.com
ective study in patients hospitalized by IMD microbiologically confirmed at three children’s tertiary health care centers in Santiago, Chile, between 2010 and 2018. Demographic, clinical information...
0
1
2
0
1
1
🔬 A Swiss study in @PIDJournal reveals the impact of Enterovirus D68 (EV-D68) in kids—linked to severe respiratory illness, higher ICU admissions, and greater need for oxygen & steroids. 📖 Read more: https://t.co/SwVG10isX9
#PaediatricInfectiousDiseases #PIDs #ChildHealth
1
1
2
🔬 New @PIDJournal study finds children with Long COVID show increased platelet activation, hinting at ongoing inflammation & immune dysregulation. 📖 Learn more: https://t.co/Ht53SQpGSC
#LongCOVID #PIDs #ChildHealth #PaediatricInfectiousDiseases
0
1
2
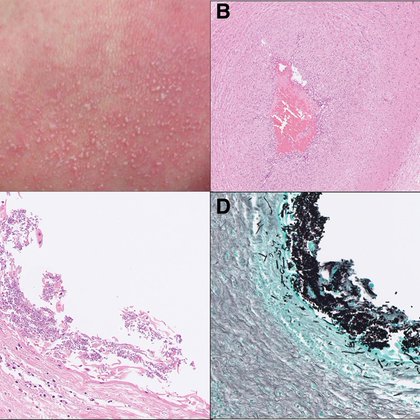
Elevated plasma (1, 3) β-D-glucan (BDG) level might be a useful predictor for systemic progression of congenital cutaneous candidiasis in neonates. Watanabe et al. #PIDJ #EditorsChoice
https://t.co/H6n97y0QDi
journals.lww.com
An abstract is unavailable.
0
0
0
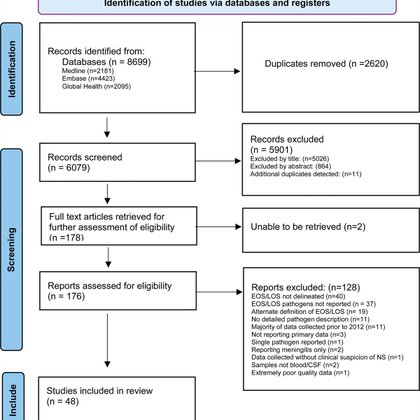
Are pathogens causative of neonatal sepsis changing? This latest analysis reports increasing proportion of GN bacteria responsible for serious bacterial infections in infants, suggests revision of current empirical antibiotic recommendations. #PIDJ
https://t.co/VE529IguSi
journals.lww.com
ive. We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the contemporary bacterial pathogens responsible for early-onset sepsis (EOS) and late-onset neonatal sepsis (LOS) to ascertain if...
0
6
27
Comparison of real-world #acyclovir dosing strategies in a multicenter cohort of NICUs, against the population pharmacokinetic (PopPK) recommendations, suggests future work to clarify optimal dosing strategies in infants. Foote et al #PIDJ
journals.lww.com
rmacokinetic (PopPK) analysis. Methods: We performed a multicenter cohort study of infants in neonatal intensive care units managed by the Pediatrix Medical Group from 1997 to 2020. We included all...
0
0
3
Do researchers need to listen to the voice of the patients/ parents in RSV research? Experts say, patient-led advocacy can bring about major change in any ID research, giving an example of the power and success of HIV/AIDS community-led movement. #PIDJ
0
0
2