Nicholas Chew
@Nicholaswschew
Followers
880
Following
3K
Media
71
Statuses
841
Cardiologist at #NUHCS, Singapore. Research interest in cardiometabolic + coronary + valve disease. Collaborations on Heart-Liver-Endocrine axis. Views my own.
Singapore
Joined June 2020
Cardiovascular-Liver-Metabolic Health: Recommendations in Screening, Diagnosis and Management of #MASLD in #CVD ❗️MASLD should be considered as a cardiovascular risk-enhancing factor 🆕@CircAHA
https://t.co/AR49lJCCVh
ahajournals.org
There is a new awareness of the widespread nature of metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and its connection to cardiovascular disease (CVD). This has catalyzed collabor...
1
3
13
The natural history of patients with medically managed CCS is not as benign as we think. Our analysis of reconstructed individual patient's data from 29 trials and 53,000 pts shows AMI rates of 12.5% at 5 years and 8.6% mortality rate. Outcomes will be much worse in non RCT
2
26
101
What if your🫀, liver & metabolic health are interlinked? Published in @NatRevCardiol, Dr Nicholas Chew, Assoc. Consultant, & A/Prof Mark Chan, Deputy Executive Director, #NUHCS, uncover how🫀disease, fatty liver etc., are linked & propose a new method. https://t.co/Z3LOM3QAmx
nature.com
Nature Reviews Cardiology - In this Review, Nicholas Chew and colleagues use epidemiological data on the cardiovascular–liver–metabolic disease syndemic to illustrate current and future...
0
2
3
New online! The global cardiovascular–liver–metabolic syndemic: epidemiology, trends and challenges https://t.co/nj3hdwjLF4
0
2
4
Coexistent #MASLD and #CKD portend high cardiometabolic risk and cardiovascular mortality. #AHAJournals @Nicholaswschew
https://t.co/JmrC6qsHa6
0
1
2
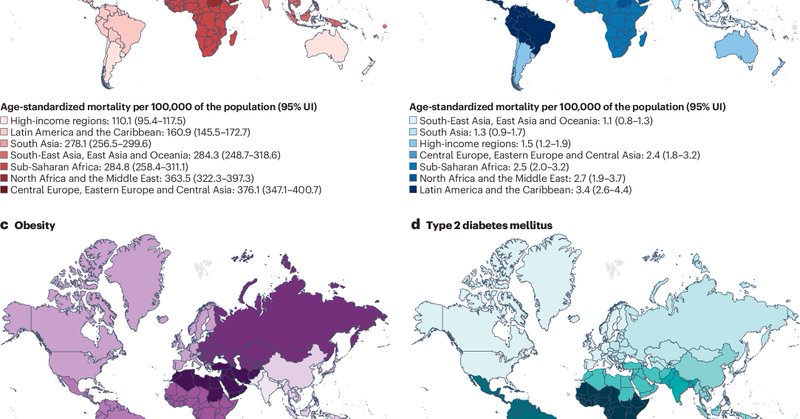
The global cardiovascular disease (CVD) burden is expected to rise in the next few decades, driven primarily by an ageing populace worldwide. High blood pressures, dietary risks, and high cholesterol are the predominant risk factors expected to drive CVD. https://t.co/GeyO4Vvvki
3
74
203
Pleased to be able to contribute- congratulations to Mark chan, @Nicholaswschew and team
The global cardiovascular disease (CVD) burden is expected to rise in the next few decades, driven primarily by an ageing populace worldwide. High blood pressures, dietary risks, and high cholesterol are the predominant risk factors expected to drive CVD. https://t.co/GeyO4Vvvki
1
4
23
Cardiovascular disease is the world’s leading cause of death, but many of its risks are avoidable. A global study in @JACCJournals with #NUHCS cardiologists, looks to 2050 & reveals a paradox: even as some risk factors improve, the overall burden may grow: https://t.co/z08GPqBCMT
0
1
2
The impact of cardiovascular disease in the Asia-Pacific Region is profound. "The time for collaborative, tailored, and equitable solutions is now." Introducing the Lancet Commission on Tackling Cardiovascular Disease in the Asia–Pacific Region: https://t.co/Gmh6gAI4K6
1
7
33
🆕 Tackling cardiovascular disease in the Asia–Pacific region: a new Lancet Commission 🙏 Privileged to join brilliant colleagues, led by Carolyn Lam & Stephen Nicolls, on the new @TheLancet Commission tackling heart disease in Asia–Pacific. ❤️ Why? CVD is the world’s #1
2
7
29
Our paper led by @Nick1133 temporal trends of ST-elevation myocardial infarction mortality according to infarct size and location: insights from the UK National MINAP registry from 2005 to 2019 The prognostic impact of infarct size has declined over time , more evident for
6
18
71
The Global Syndemic of Modifiable Cardiovascular Risk Factors Projected From 2025 to 2050 https://t.co/vIM36BR3Ec
#JACC
@JACCJournals @DrMarthaGulati @mirvatalasnag @mmamas1973 @JamalRanaMD @HeartOTXHeartMD
1
13
30
Risk factors are rising, even as care improves. This global forecast reveals a syndemic of #CVD risk fueled by aging and growth 📊⚠️ 🔗 https://t.co/uoRUee9ylZ
#JACC #GBDstudy
0
36
90
@TheLancetPH • Burden of mental disorders: https://t.co/wVUmQzHUx8 • Burden of CVD: https://t.co/PYEAylDtzP • Burden of smoking: https://t.co/2D4AVWsgsn • Burden of injuries: https://t.co/BuH4lv2std
0
2
5
Great turnout at Steady Heart, Steady Pressure event by Jurong Medical Centre! From heart health tips by Dr Nicholas Chew, Assoc. Consultant, #NUHCS, to cardio dances, it was inspiring to see the community take charge of their 🫀 health. Proud to be part of this meaningful day!
0
4
5
#InDepth Recommendations for Screening, Diagnosis and Management of Metabolic Dysfunction Associated Steatotic Liver Disease in CVD https://t.co/eB87sHFx4b
1
7
20
Dr Nicholas Chew, Associate Consultant, #NUHCS, led a global effort to develop guidelines on the link between metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease & cardiovascular disease. Published in @CircAHA, it aims to improve patient outcomes. https://t.co/ZT6vIYldOx
linkedin.com
Published in 𝘊𝘪𝘳𝘤𝘶𝘭𝘢𝘵𝘪𝘰𝘯, the flagship journal of the JAHA — Journal of the American Heart Association, NUHCS has spearheaded an international effort to address the intersection of...
0
4
7
3⃣FIB-4 score can be used as a first-line point-of-care test for the screening of advanced fibrosis. 4⃣Management of individuals with MASLD, assessed to be at low risk of fibrosis based on FIB-4 score, can be managed by clinicians within the cardiovascular specialty
0
0
1
Several key points: 1⃣Screen for CVD in individuals with MASLD, regardless of presence of traditional risk factors, with risk-factor evaluation at a minimum. 2⃣MASLD should be considered a risk-enhancing factor for ASCVD.
1
0
1