Michal P. Heller
@HellerInTheory
Followers
2K
Following
1K
Media
248
Statuses
638
Professor of theoretical physics @UGent. Chasing good questions and out of the box ideas. Opinions my own.
Ghent, Belgium
Joined July 2018
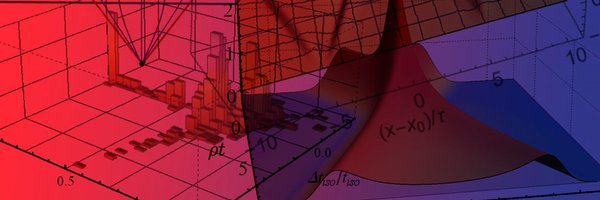
Today on the arXiv: https://t.co/ZhFprXuToy by @ugent and @cuhksz researchers. In this theoretical physics work we re-examined how high energy physics systems approach equilibrium and revealed a unifying mathematical structure despite variety of systems we considered. Why bother?
arxiv.org
Contemporary understanding of thermalization in quantum field theory stems largely from understanding properties of transient excitations of equilibria. These nonhydrodynamic excitations are known...
2
0
8
This plot from the paper shows both weak (vertical zigzag line) and strong (black x's) coupling equilibration mechanisms together as incorporated by our hybrid model.
1
0
0
In particular, this allows us to formulate hybrid models that incorporate elements of both weak and strong coupling and otherwise interpolate to regimes in between, which is not accessible using other means. This is were the biggest innovation of this new work of ours lies.
1
0
0
In our paper https://t.co/ZhFprXuToy we discover a new organizing symmetry principle that allow us to describe both weak and strong coupling scenarios in a unified way.
arxiv.org
Contemporary understanding of thermalization in quantum field theory stems largely from understanding properties of transient excitations of equilibria. These nonhydrodynamic excitations are known...
1
0
1
At weak coupling, the insights originate from kinetic theory describing interactions between microscopic consistuents: gluons and quarks. There, equilibrium is approached much slower than at very large couplings. This is intuitive: without interactions equilibrium is not reached.
1
0
0
At very large coupling, the insights so far were obtained from holography (AdS/CFT) in which case equilibrium is approached exponentially fast with a timescale set by the amount of energy in your system.
1
0
0
This varying interaction strength together with intrinsically nonequilibrium nature of processes at RHIC and LHC pose a significant challenge for theorists. In practice this means that theoretical descriptions target idealized scenarios of either very weak or very large coupling.
1
0
0
The main motivation comes from high energy nuclear collisions at RHIC @BrookhavenLab and LHC @CERN. The system in question there are strong interactions that, despite their name, have a varying interaction strength: strong at large distances and weak at short.
1
0
0
We believe this is not the last word stemming from our idea. From a broader physics perspective, fluid mechanism is an example of an effective field theory and our approach looks very relevant also for the initial value problem in e.g. modification of general relativity.
1
0
3
Such degrees of freedom affect how velocity and temperature evolve in a hard to control way and, therefore, are a liability. In our new paper we show how to decouple them in a systematic way without running into any conceptual and practical trouble.
1
1
3
It turns out that a straightforward approach to include friction in such fluids leads to both conceptual and practical problems. Long story short, to date the most accepted way forward involved adding new degrees of freedom on top of fluid’s velocity and temperature.
1
1
3
New theoretical physics paper from @ugent @unisouthampton, @ncbj_swierk and @uwbtwt: https://t.co/sceEzWt7UZ. We show a novel way of predicting future behaviors of fluids whose microscopic constituents or macroscopic volumes move close to the speed of light. Why relevant?
arxiv.org
We provide a systematic framework for solving the initial value problem for relativistic hydrodynamics formulated as a gradient expansion. Secular growth is handled by a suitable covariant...
1
4
24
https://t.co/BL4N3EuX7S in press
arxiv.org
Recently, several notions of entanglement in time have emerged as a novel frontier in quantum many-body physics, quantum field theory and gravity. We propose a systematic prescription to...
A new framework computes temporal entanglement in relativistic #quantum field theory directly from standard spatial notion via analytic continuation, laying the groundwork for systematic exploration of temporal entanglement in holography. 🔗 https://t.co/XLMtYVMiO9
0
0
5
New paper from @ugent: in https://t.co/iPOa6Du1dg we show for the first time how to define a top-down notion of holographic complexity in an expanding universe using double-scaled SYK. Quite surprising, the notion arises from temporal rather than spatial volumes of the universe.
arxiv.org
We utilize the recent connection between the high energy limit of the double-scaled SYK model and two-dimensional de Sitter solutions of sine dilaton gravity to identify the length of a family of...
1
0
0
Simultaneously with ours https://t.co/BL4N3EvuXq,
https://t.co/EXLEGoVi3h by C. Nunez and D. Roychowdhury appeared that also studied analytic continuation of holographic entanglement entropy from spacelike to timelike subregions. If you got interested, please also have a look.
0
0
4
As it turns out, some of these surfaces in the temporal regime might originate from complex surfaces in the spacelike regime. One lesson, rooted in self-consistency, is that complex extremal surfaces should not be subleading contributions to holographic entanglement entropy.
1
0
0
In particular, the key conceptual difficulty we overcome is what to do if there are several candidate complex extremal surfaces to temporal entanglement. The answer to seek for their origin in terms of valid entanglement entropy candidates in the spacelike regime.
1
0
0